Aspidosiphon (Paraspidosiphon) coyi
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.187023 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5672005 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3B3687EB-BF1F-D152-FF35-FAEF188E586B |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Aspidosiphon (Paraspidosiphon) coyi |
| status |
|
Aspidosiphon (Paraspidosiphon) coyi View in CoL de Quatrefages
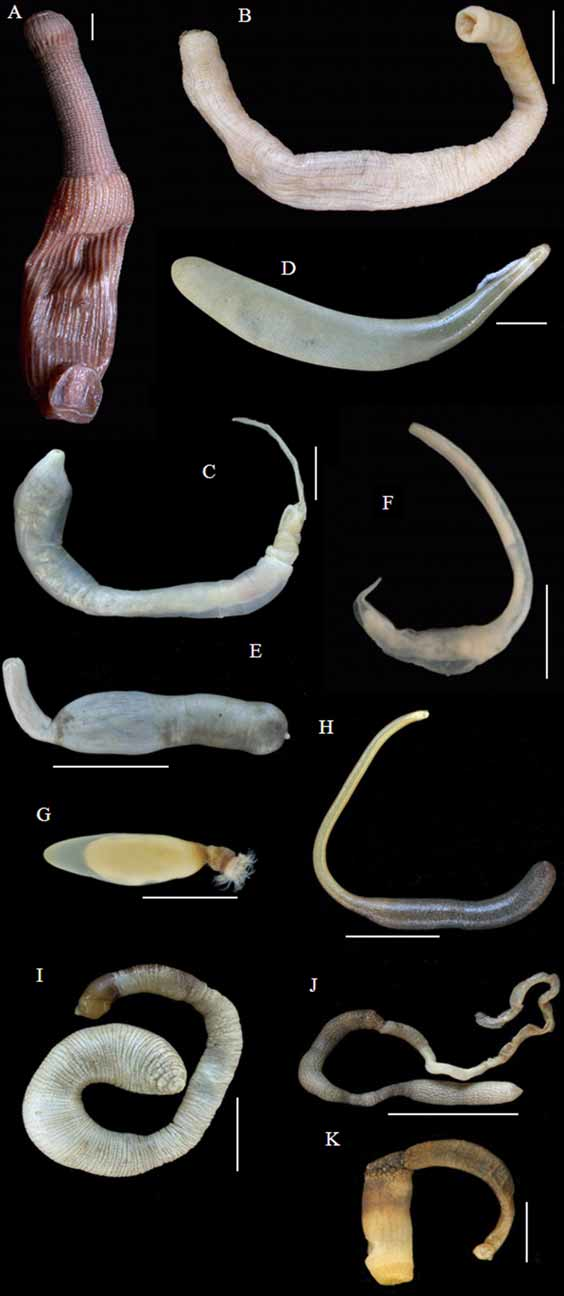
Figs 2 View FIGURE 2. A K, 3G–H
Aspidosiphon coyi Cutler, 1994: 221 View in CoL (for complete synonymy).
Material examined. One specimen (NMNS-5928-022), Sunsheintai (23°06.899' N, 121°24.012' E), Taitung County, eastern Taiwan, intertidal coral reefs, coll. P.-W. Hsueh, 14 October 2007.
Remarks. Aspidosiphon coyi and A. laevis de Quatrefages are the only two species in Aspidosiphon (Paraspidosiphon) , defined by the anal shield possessing extensive grooves or furrows ( Hsueh et al. 2006: 371, fig. 3B; present study, Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3. A G). Aspidosiphon coyi differs from A. laevis by the presence of a very small secondary tooth on introvert hooks and its retractor originating at the posterior end (95–100%). The present specimen agrees with most of the above key characters, with the introvert hooks each having a secondary tooth ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2. A H) and the retractor originating at the posterior end but about 93% of the length of the trunk. This species inhabits intertidal coral rock and has been recorded from several locations in the western Pacific Ocean, from central Japan through Okinawa, Philippines, Indonesia to the Kermadec Islands ( Cutler 1994).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Aspidosiphon (Paraspidosiphon) coyi
| Hsueh, Pan-Wen & Kuo, Chia-Ming 2009 |
Aspidosiphon coyi
| Cutler 1994: 221 |