megops Sars, 1862
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4527.1.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C9D04EAA-61CD-4706-9B54-026C5A7FD98F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5960197 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/38745B7F-FFAB-FF9C-FF4E-CAFBFEDEC52C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
megops Sars, 1862 |
| status |
|
Ceriodaphnia megops Sars, 1862
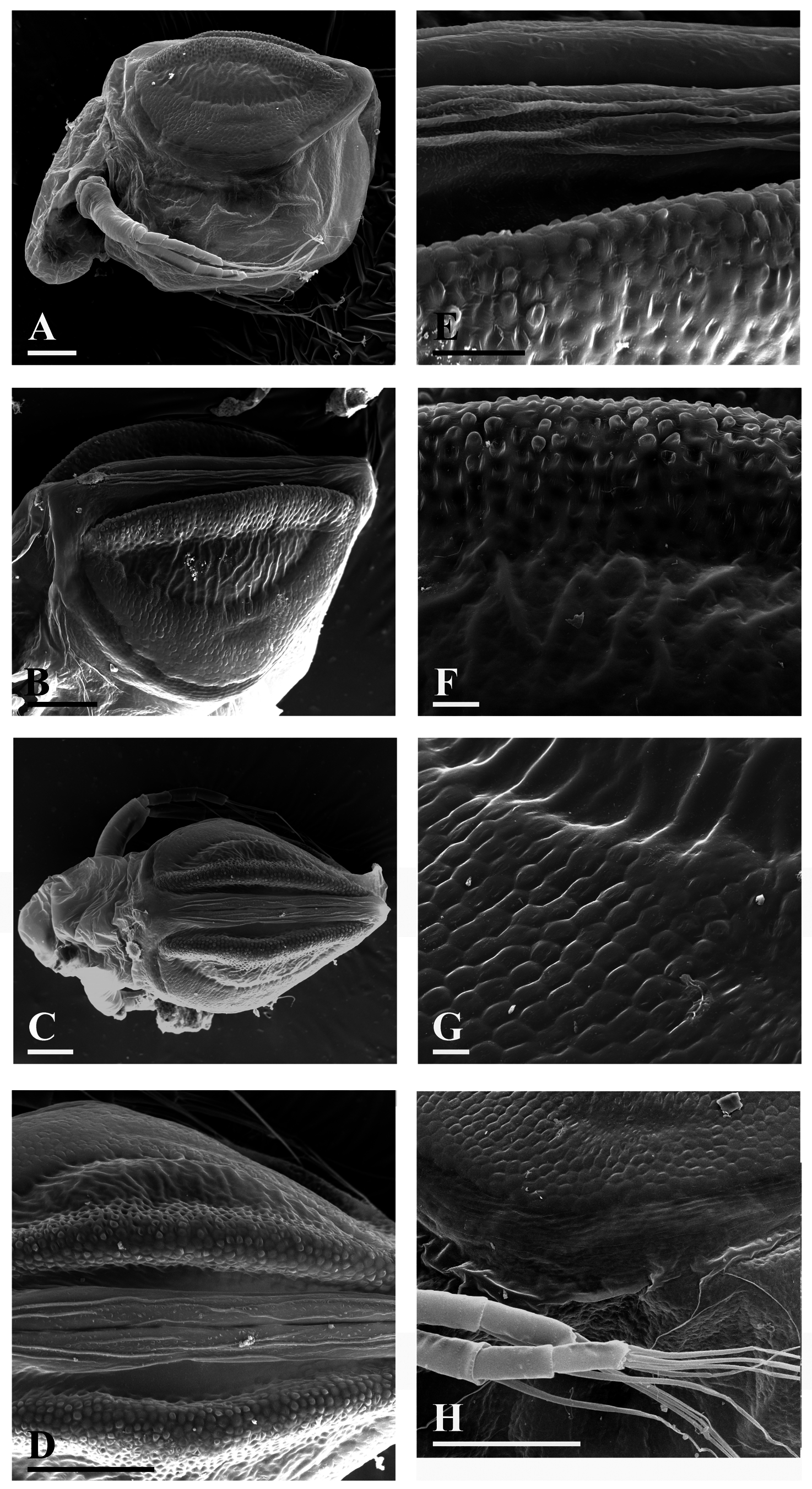
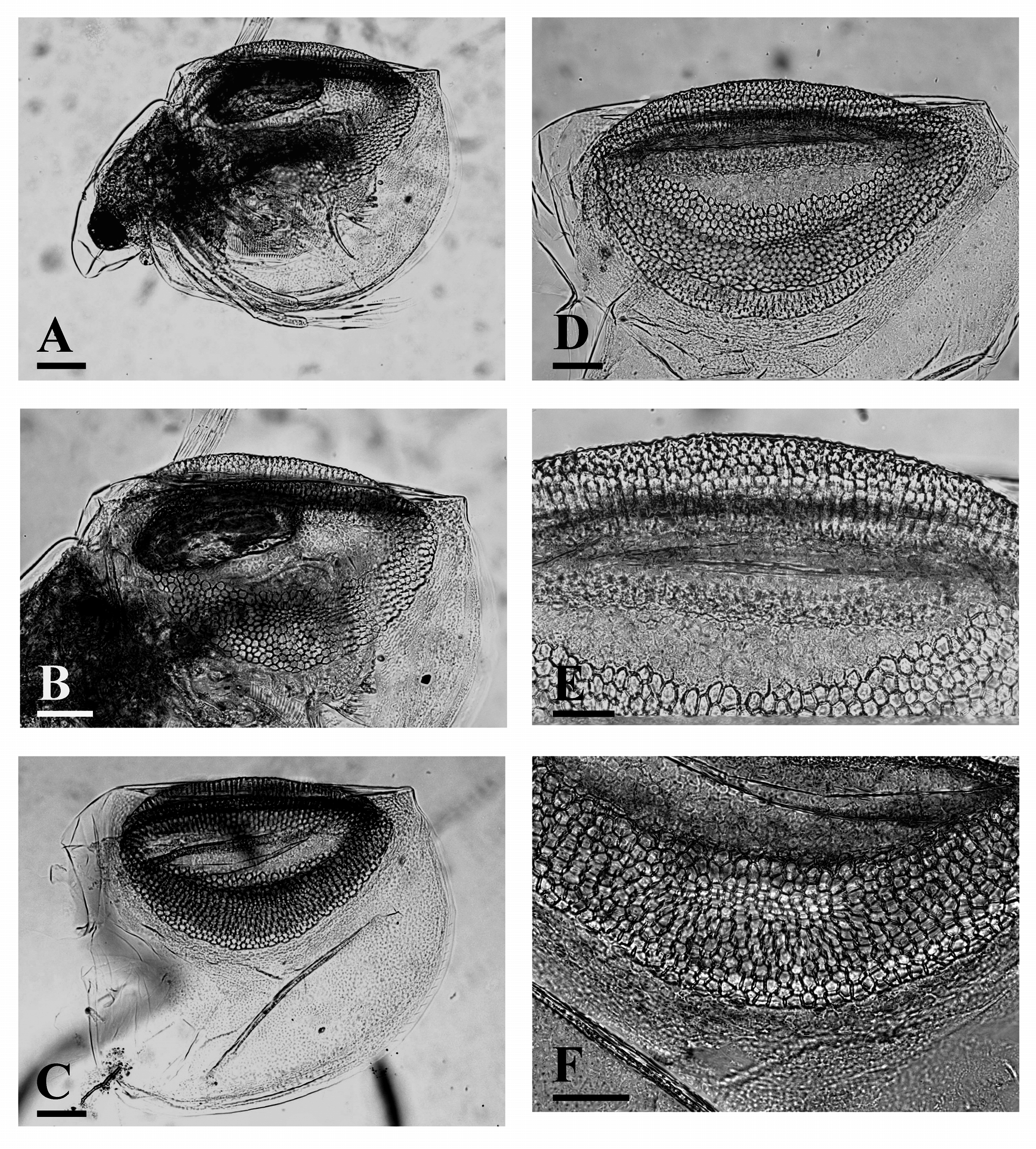
( Figs. 1–2 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 )
Length about 0.5–0.55 mm, width about 0.7 of length. In lateral view, ephippium almost semicircular, somewhat asymmetrical, stronger narrowing posteriorly; dorsal margin almost straight; ventral margin regularly curved from postero-ventral to antero-ventral angle ( Figs. 1A View FIGURE 1 , 2 View FIGURE 2 A–D). Paired latero-dorsal ridges strongly expressed ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 B– D), extend above dorsal margin as seen laterally ( Figs. 1A View FIGURE 1 , 2 View FIGURE 2 A–D), their dorsal margin slightly and regularly convex. A distinct depression along dorsum separating two halves of ephippium and, respectively, two halves of dorsal plate; sculpture of dorsal plate consisting of a series of longitudinal wrinkles ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 D–E). Sculpture on latero-dorsal ridges low, consisting of small semicircular projections ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 D–F); the external signs of roundedhexagonal air-spaces well-visible under light microscope ( Fig. 2E View FIGURE 2 ). Egg locule smooth, only somewhat extending laterally, with poorly expressed vertical wrinkles ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 , F–G); under optical microscope, surface of locule relatively smooth, with small irregularities ( Fig. 2E View FIGURE 2 ). Rest of ephippium surface covered by low, dense, flattened domes ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 G–H); the external signs of air-spaces well-visible under light microscope ( Figs. 2D, F View FIGURE 2 ). Such air spaces absent in the locule region. Ventral rim of ephippium lacking air spaces, with obscure polygonal reticulation ( Figs. 1H View FIGURE 1 , 2F View FIGURE 2 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.