Trachypeplus parafulgoris, Dang, Kai, Guilbert, Eric & Bu, Wenjun, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3669.4.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:B3A73AAC-48B3-450C-9768-7FA71176158C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6165438 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/33097206-404A-0007-1FC6-F9CCFDE9A5E3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Trachypeplus parafulgoris |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Trachypeplus parafulgoris sp. nov.
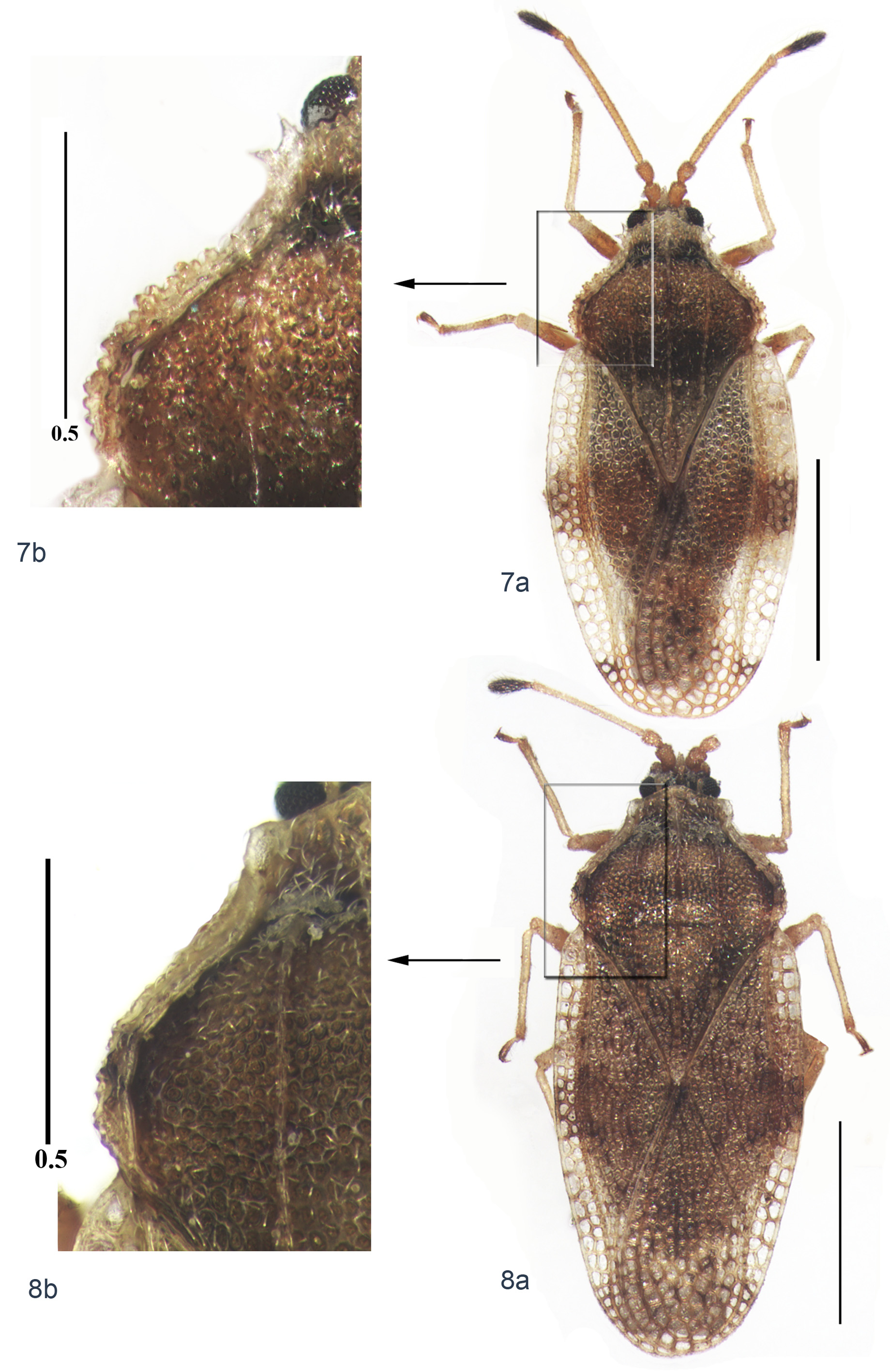
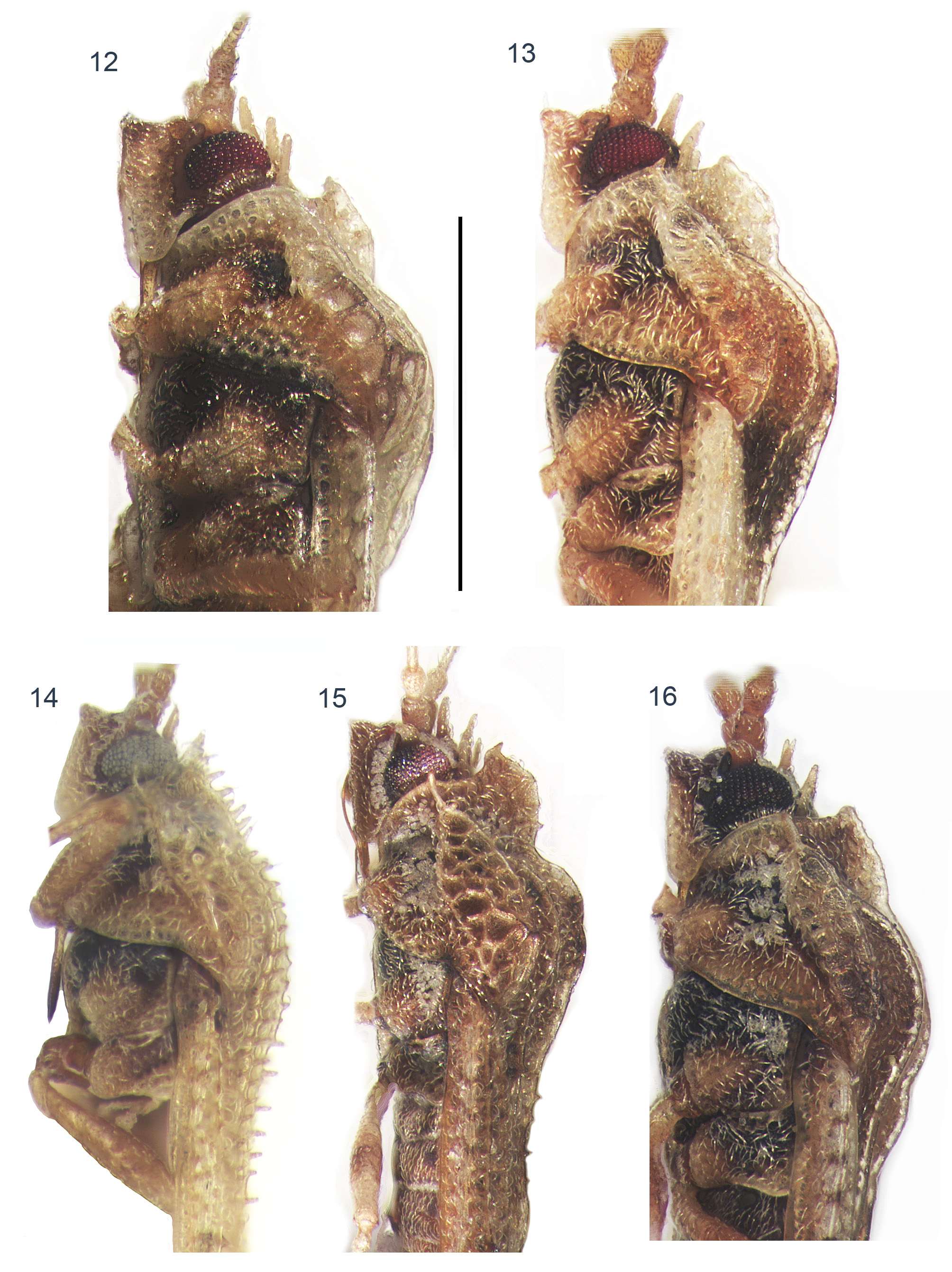
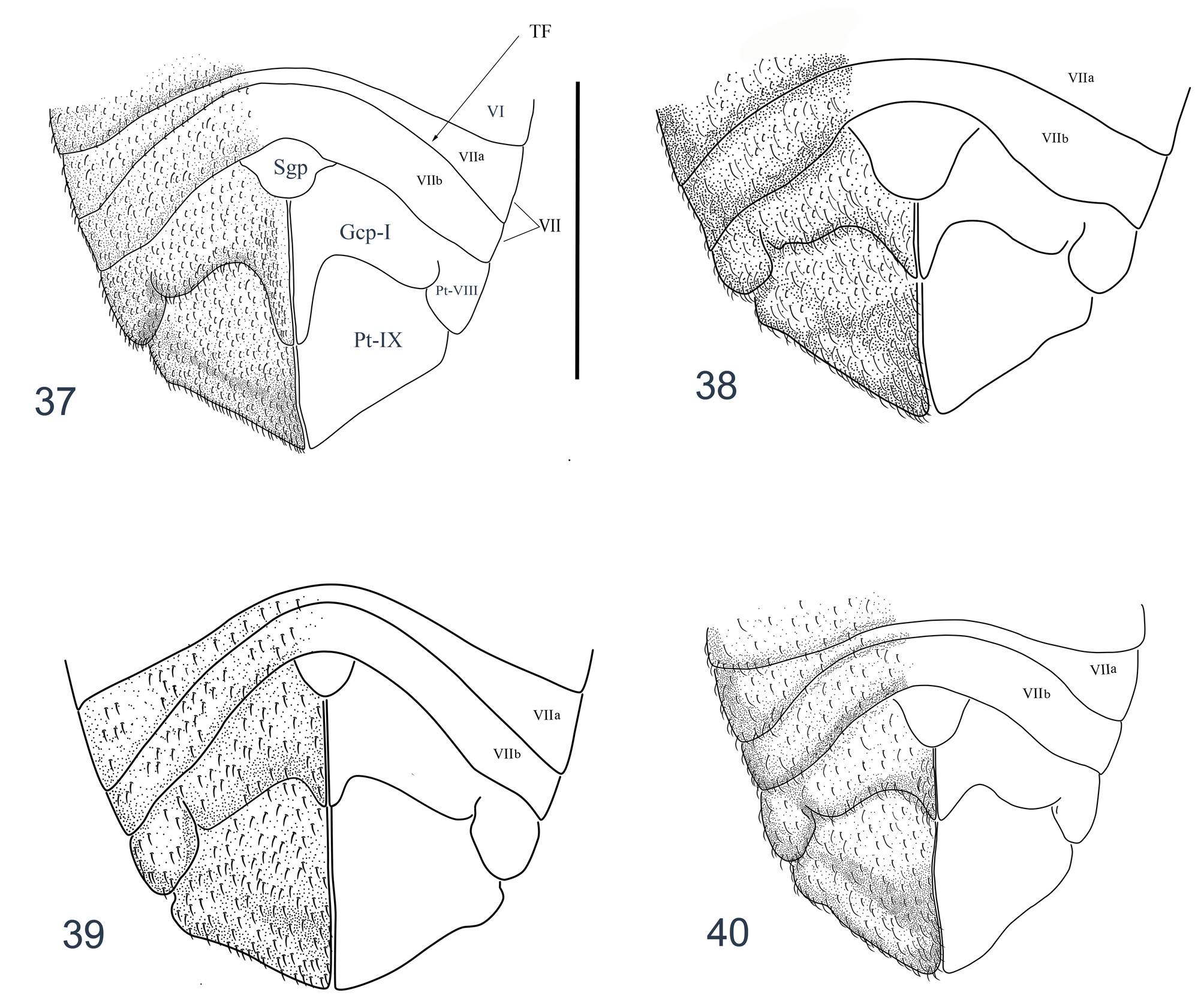
Figs. 7 View FIGURES 7 – 8 , 13 View FIGURES 12 – 16 , 23 View FIGURES 20 – 23 , 31 View FIGURES 29 – 33 , 40 View FIGURES 37 – 40 .
Description. Body shiny, light yellowish, with a transversal, broad, brown fascia across hemelytra at middle part and a narrow at end ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7 – 8 a); head black, antennae and leg yellowish brown, but fourth antennal segment and apex of tarsus dark brown, pronotal disc brown; calli black; thorax ventrally dark brown or black; abdomen ventrally yellowish brown.
Head pilose, especially densely around eyes, armed with five long, slender, spines, suberect, pointed forwards ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 12 – 16 ). Antennae pilose but hairs on fourth segment longer and suberect, first two segments stouter, third one slender, more than two times as long as fourth one, last inflated. Bucculae mostly biseriate, apex a little surpassing in front of clypeus, closed in front. Rostral sulcus narrow on prosternum, widening gradually on mesosternum, and broader on metasterum, here its sulcus laminae arched, cordate, closed behind ( Fig. 31 View FIGURES 29 – 33 ); rostrum extending to posterior margin of mesosternum.
Pronotum long, strongly gibbose ( Figs. 13 View FIGURES 12 – 16 , 23 View FIGURES 20 – 23 ). Collar biseriate wide, median portion raised as a tectiform hood, dorsal margin arched in lateral view, produced forwards ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 12 – 16 ). Three carinae parallel, uniseriate, lateral carinae as high as median carina. Paranota bi- to triseriate, reflexed, mostly resting on pronotum, but outer margins and parts at opposite humeri elevated, anteriorly armed with very few tubercle-spines; areolae depressed deeply, ridges of areolae covered with many tubercle-hairs (tubercle apically armed with a curved hair), tubercle small ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7 – 8 b). Distance between outer margin of paranotum and lateral carina narrow anteriorly; posteriorly, this distance widening and distinctly wider than that between lateral and median carinae. Distance between lateral and median carinae on posterior pronotal process quadriseriate.
Hemelytra long, wider than pronotum, boundary veins raised. Costal area bi- to triseriate, mostly triseriate ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7 – 8 a). Subcostal area narrow, erected, nearly as wide as 1/2 of costal area, biseriate. Discoidal area extending backwards, nearly as long as 2/3 of hemelytra, nine areolae broad at widest part. Sutural area eight to nine areolae wide at widest part. Hypocostal area narrow, uniseriate, areolae small, and round.
Measurements. Males (N = 5) and females (N = 5) respectively. Body length: M, 2.64–2.72 (2.67), F, 2.68– 2.92 (2.82); width: M, 1.18–1.24 (1.22), F, 1.26–1.38 (1.33). Length of pronotum: M, 1.35–1.46 (1.43), F, 1.44– 1.56 (1.50); width: M, 0.96–1.04 (0.99), F, 1.02–1.08 (1.06). Length of hemelytra: M, 1.84–1.92 (1.87), F, 1.88– 2.04 (1.94). Length of discoidal area: M, 1.10–1.20 (1.15), F. 1.20–1.30 (1.24). Antennal segments measurements: M, I: 0.11–0.13 (0.12), II: 0.10, III: 0.70–0.74 (0.72), IV: 0.26–0.28 (0.27); F, I: 0.11–0.12 (0.12), II: 0.09–0.10 (0.10); III: 0.62–0.66 (0.65); IV: 0.26–0.28 (0.28).
Material examined. Holotype: male, China, Hainan Province, Ledong County, Nature Reserve, alt. 800 m, 1.IV.2008, Bo Cai and Gengping Zhu leg. Paratypes: 1 male, 1 female, same locality as holotype, 2. IV.2008, Gengping Zhu leg.; 22 males, 14 females, China, Hainan Province, Ledong County, Jianfengling, alt. 855 m, 13.VIII.2010, Guo Zheng leg.; 1 male, China, Hainan Province, Ledong County, Jingfengling, alt. 975 m, 15.VIII.2010, Guo Zheng leg.; 3 males, China, Hainan Province, Ledong County, Jianfengling, alt. 959 m, 15.VIII.2010, Guo Zheng leg.; 1 male, 1 female, China, Hainan Province, Baisha County, Yinggeling Nature Reserve, Yinggezui Station, alt. 728 m, 20.VIII.2010, Guo Zheng leg.; 1 male, China, Hainan Province, Baisha County, Yinggeling Nature Reserve, Yinggezui Station, alt. 609 m, 24.VIII.2010, Guo Zheng leg. These type specimens were deposited at NKUM.
Etymology. The name of the species refers to the fact that it is very similar to its congener Trachypeplus fulgoris (Drake, 1937)
Comments. The new species is similar to T. fulgoris (Drake, 1937) in sharing the bi- to triseriate paranota. However, it differs from the latter by its ridges of areolae on its paranota covered with many small tubercle-hairs, and its costal area mostly triseriate at its length (costal area of T. fulgoris biseriate at its length, cf. Figs. 7 View FIGURES 7 – 8 a–b, 8a–b).
In addition, Trachypeplus parafulgoris sp. nov. differs from T. guinaicus Drake, 1960 (New Guinea) by its smaller size (2.67–2.82 VS. 3.20 in T. guinaicus ), its frontal and median spines slender ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 12 – 16 ) but stout and blunt in T. guinaicus , and its discoidal area wider (nine areolae vs. six to seven areolae in T. guinaicus ). The median carina of T. parafulgoris sp. nov. is uniseriate in its length, and the paranota is relatively narrower with two to three areolae broad, whereas T. guinaicus has its median carina partly biseriate and four to five areaolae broad on paranota (based on the type deposited in National Museum of Natural History (NMNH), Washington D.C., observed by the co-author E. Guilbert).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |