Ornebius lunam He, Zhang & Ma, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4942.1.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:85440EDA-EBC3-4091-95C0-B832DE5510CD |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4621227 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3137A61D-FFB7-0B02-4799-AD7FFCD1FE80 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ornebius lunam He, Zhang & Ma |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Ornebius lunam He, Zhang & Ma View in CoL sp. n.
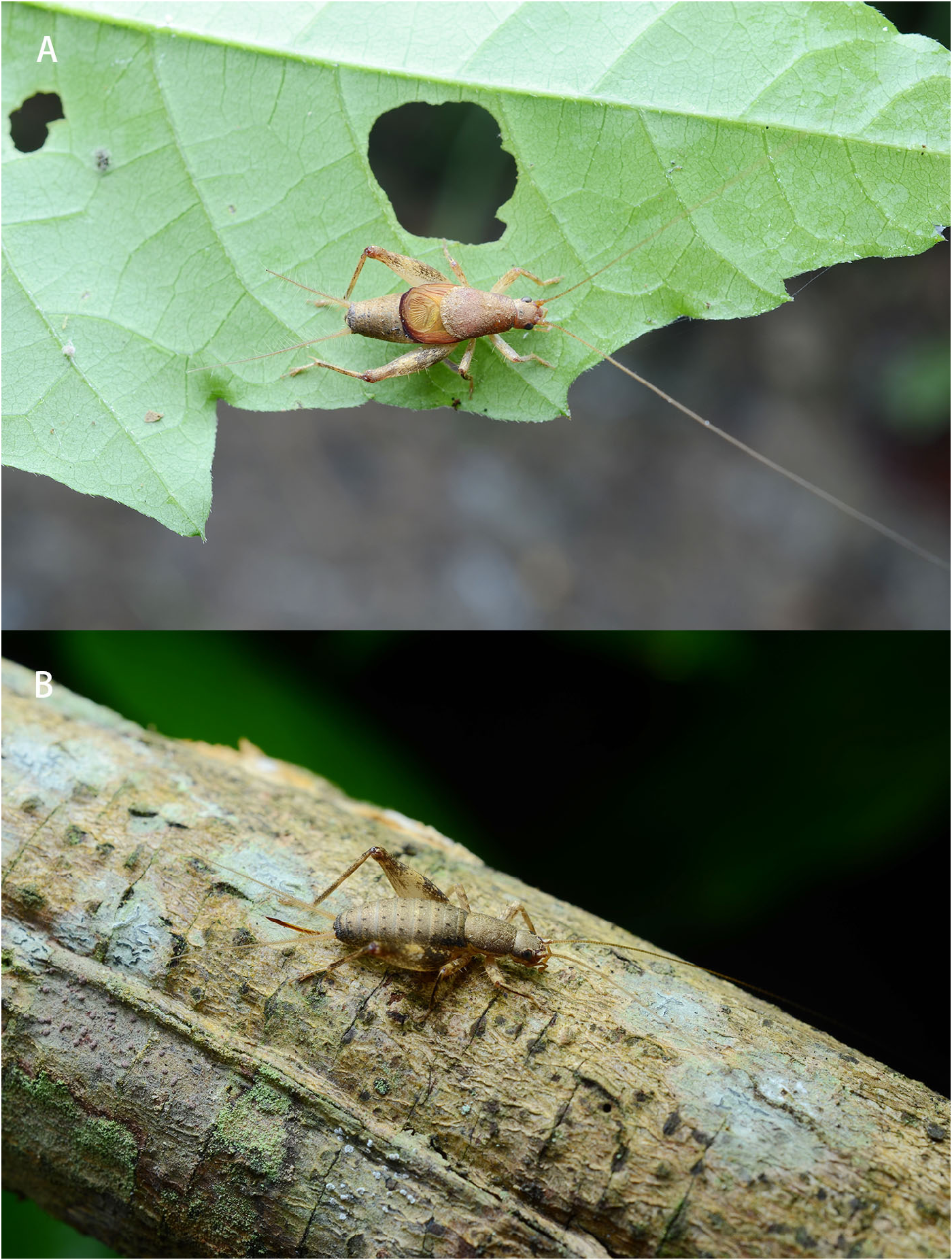
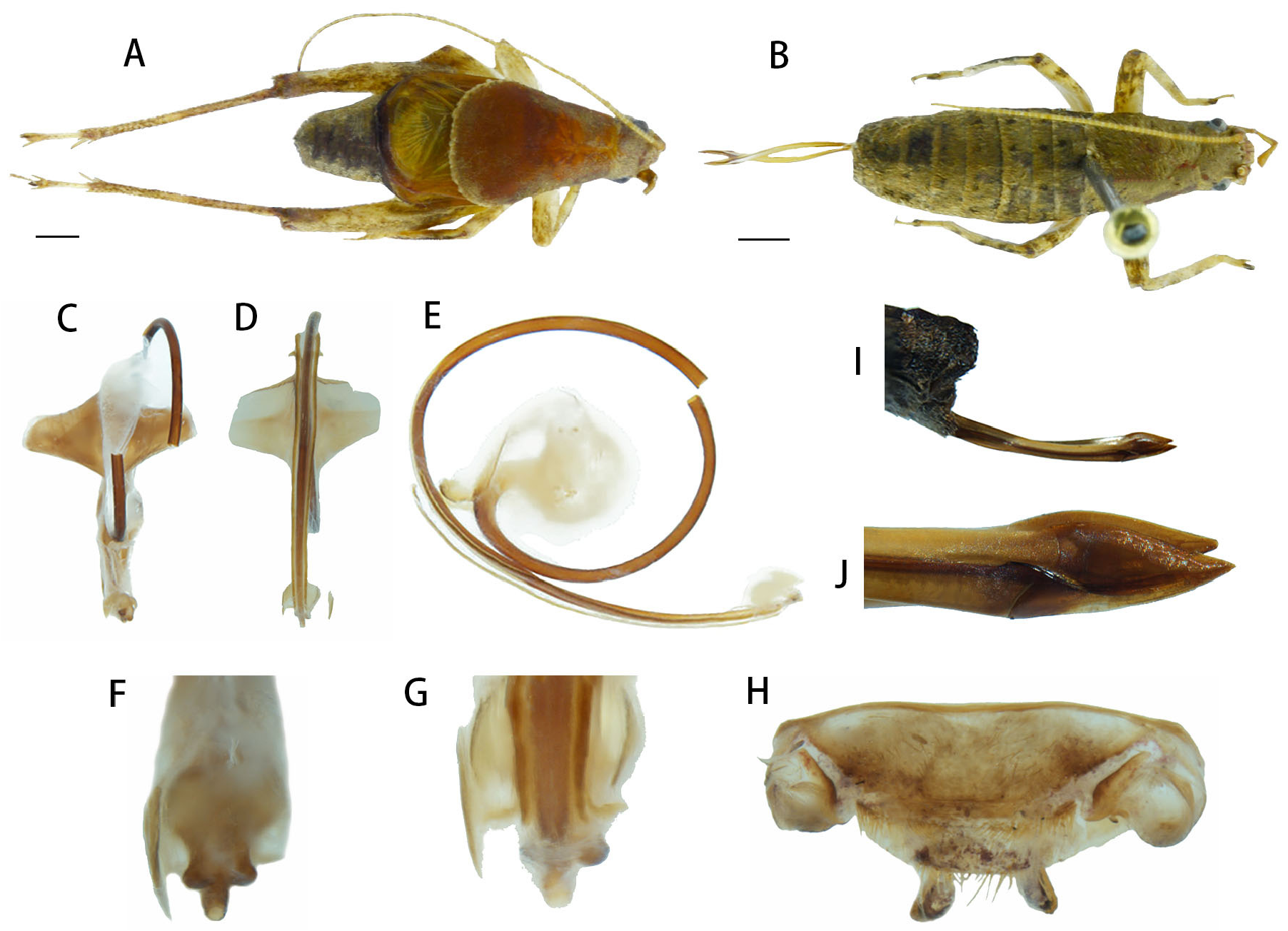
Figs 6–8 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8
Type materials. Holotype. China: Male, Guangxi, Chongzuo , 5th May 2019, Ma Libin and Zhang Tao coll. Paratypes. 8 males, Guangxi, Chongzuo , 5th May 2019, Ma Libin and Zhang Tao coll. ; 5 females, Guangxi, Chongzuo , 5th May 2019, Ma Libin and Zhang Tao coll. ( SNNU) .
Description. Male. Typical body of the genus. Head small with yellow scales on surface, posterior margin straight. Rostrum strongly swollen, furrowed, about 1.5 times wider than antennal scape; each segment of antenna possessing two short hairs at the base; antennal scape slightly longer than width, and symmetrical moon-shaped lateral ocelli between the antennae in dorsal view. The ratio of maxillary palpus from base to apex is approximately 1: 1.2: 3: 2.8: 3.2, apical segment broadened. Pronotum somewhat 2.8 times longer than head, also longer than width; anterior margin straight and posterior convex with white scales surrounded, reaching the base of mirror. Fore tibia internal tympanum large and oval; without external tympanum. Tegmen with most parts exposed; mirror roughly triangular, length longer than width; apical field convex, wider than pronotum. Nearly half portions of abdomen covered by tegmen ( Fig. 6A View FIGURE 6 ). Hind femur pubescent, longish; hind tibia 1.2 times longer than hind femur, 2.8 times longer than hind metatarsus, the dorsal margin of hind tibia serrate in two rows of denticles about 21–23 teeth each, there are many protuberances between two rows, also pubescent by the side of rows but shorter than in hind femur; dorsal margin of hind metatarsus serrate in two rows of denticles about 5–6 teeth each. Abdomen: Supra-anal plate with last abdominal tergite and epiproct distinctly separated by a transverse suture and bristles along the suture; basal margin slightly convex, apical margin of epiproct rounded and hirsute. Paraproct process medium length, compressed, curved, yellowish, ventral-apical area partly black ( Fig. 7G View FIGURE 7 ). Genitalia: Male phallic complex with the medial valve curved to a spiral in the basal part with its base forming an axis in the centre of spiral ( Fig. 7E View FIGURE 7 ). In dorsal view, two sides of the axis centre strongly projecting perpendicular of spiral and pale yellow (ejaculatory duct was destroyed in the middle) ( Fig. 7C View FIGURE 7 ). In ventral view, internal sclerite of medial valve with two elongated and straight narrow guild rods ( Fig. 7D View FIGURE 7 ), gently curved at the base in lateral view ( Fig. 7E View FIGURE 7 ); apex widen into a transverse spade-like lobe, apical margin truncated and not surpass the apex of ejaculatory duct ( Fig. 7F View FIGURE 7 ); ventral median lobe (lost a piece) little shorter than epiphallus ( Fig. 7G View FIGURE 7 ). Ejaculatory duct basal part strongly curled into a large spiral and spermatophore sac massive.
Female. Similar to male, apterous, body slender. The ratio of head, pronotum and abdomen is approximately 1: 2: 3. Abdomen black with stripes yellow scales, and uniform black spots on dorsal surface ( Fig. 6B View FIGURE 6 ). Abdomen: Supra-anal plate small, triangular and setose. Ovipositor short and curved, smooth.
Colouration. Dorsal view, head and pronotum reddish-brown; antenna dark yellow, frontal rostrum red. Tegmen most parts yellowish, posterior margin black. Hind femur pale with black scales outward. Cerci yellow.
Calling song. Echeme sequence period 7–17 s, echeme sequence duration continue 3–7 s with 4–10 s echeme sequence interval. Each echeme sequence includes 5–11 echemes. Each echeme period 0.6 s, echeme duration 0.1 s with 0.5 s echeme interval. Each echeme includes 2 syllables. Echeme sequence rate is about 3 syllables/s. The dominant harmonic peak observed in the spectrogram is 5.4–5.6 kHz ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 ).
Measurements. Male: BL 10.06, PL 4.35, PW 3.26, TL 3.30, TW 3.51, HFL 5.02, HTL 5.25, HML 1.67; Female: BL 8.23, PL 2.85, PW 2.57, OL 4.50.
Etymology. The name refers to its lateral ocelli conspicuously moon-shaped.
Remarks. The colouration of body and male genitalia of this species is similar to O. formosanus , O. yunnanensis , O. panda and O. aurumalas sp. n.. It differs from O. formosanus , O. yunnanensis and O. aurumalas in shape and size of supra-anal plate, its epiproct rather wide; it differs from O. panda in tegmen and size of genitalia, its dark brown area rather small and genitalia rather large; it also differs from O. aurumalas in body characteristic of female and calling song, its calling song less rapid than O. aurumalas .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Mogoplistinae |
|
Genus |