Centromeria triangulata, Song & Webb & Liang, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1111/zoj.12401 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2A0F87C6-FFD6-FFC7-8BC5-9292064AF962 |
|
treatment provided by |
Marcus |
|
scientific name |
Centromeria triangulata |
| status |
sp. nov. |
CENTROMERIA TRIANGULATA View in CoL SP. NOV.
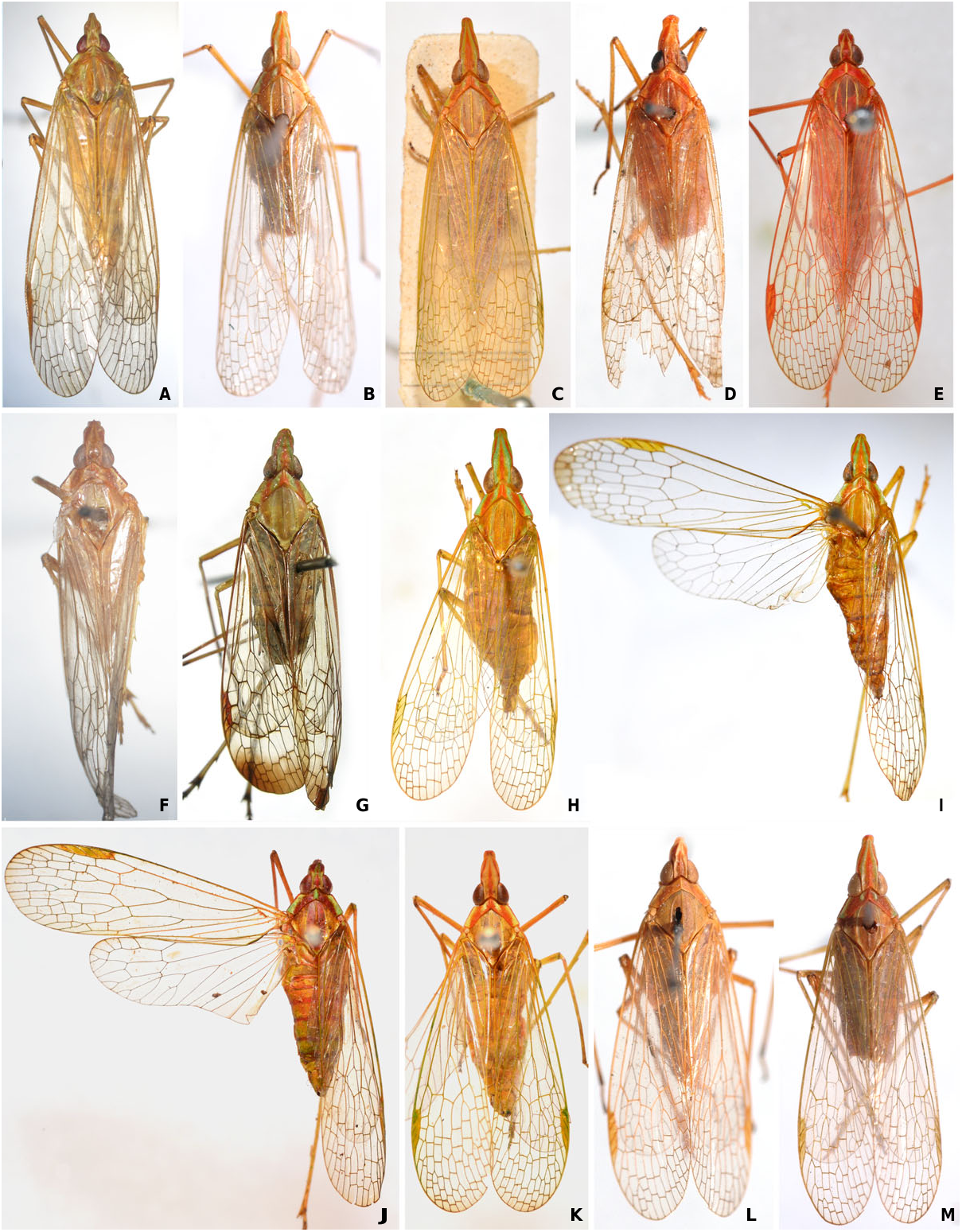
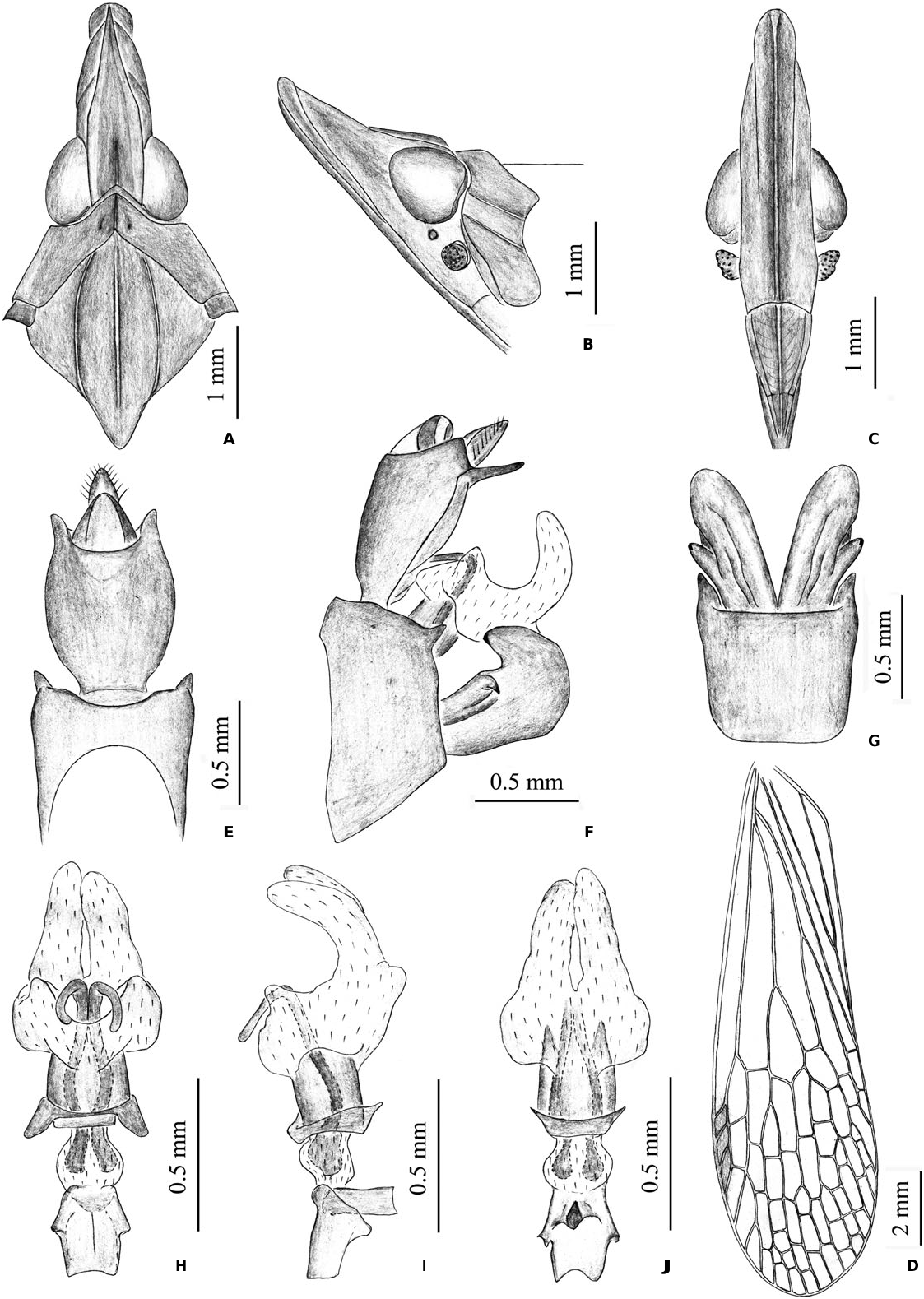
FIGS 2M View Figure 2 , 26A – J View Figure 26
Type specimens. Holotype: ♂, Philippines, G[Z] amloanga, Mindanao, Cp. 8, 10.xii.1921, F.X. Williams ( BPBM).
Paratypes: Malaysia, 1♂, British N. Borneo, Keningan [u], 12 – 17.i.1959, T . C. Maa ; 1♂ , North Borneo, Tenompok, Mount Kinabalu , 6.ii.1959, T . C. Maa (both in BPBM); 1♀ ( MIZ 313229 ), Nord-Borneo, Waterstradt; Centromeria longipennis Walk. [Schmidt’s handwriting], ♀, Edm. Schmidt, determ. 1915; Mus. Zool. Polonicum, Warszawa, 12/45 ( MIZPAS) .
Etymology. This new species name is derived from the Latin ‘ triangulus ’, referring to segment X with a long triangular process at apical ventral margin.
Diagnosis. The new species is very similar to C. cuspidata sp. nov., but can be separated from the latter by the apical margin of ventral lobes of the pronotum virescent, and the phallobase without pair of lateral lobes.
Description. BL, ♂ 15.8 – 16.9 mm, ♀ 17.8 mm; HL, ♂ 2.2 – 2.6 mm, ♀ 2.7 mm; HW, ♂ 1.5 – 1.7 mm, ♀ 1.7 mm; TL, ♂ 11.8 – 12.6 mm, ♀ 13.9 mm.
Cephalic process in lateral view relatively elongate, distinctly longer than length from anterior margins of eyes to posterior margin of vertex; moderately upturned and ascending at about 20° in front of eyes ( Fig. 26B View Figure 26 ). Vertex relatively broad, posterior margin nearly as wide as transverse diameter of eyes; in dorsal view ratio of length to width between eyes about 3.4: 1 ( Fig. 26A View Figure 26 ). Pronotum ( Fig. 26A View Figure 26 ) with intermediate carinae slightly present in base. Fore femora with a minute spine at apex; hind tibiae with seven lateral spines; hind tarsomeres I with eight or nine apical teeth and tarsomeres II with between eight and ten apical teeth.
Male genitalia with pygofer in lateral view broad and high, distinctly wider ventrally than dorsally (about 3: 1); posterior margin with a short small process near middle, acute apically ( Fig. 26E View Figure 26 ). Gonostyles ( Fig. 26E View Figure 26 ) relatively small, upper process large and stout, subacute apically. Aedeagus ( Fig. 26G – I View Figure 26 ) moderately large, endosomal processes extended posteriorly and curved dorsoanteriorly; phallobase sclerotized and pigmented at base, membranous and inflated apically, with one pair of lateral lobes distinctly short and small, slightly projecting posteriorly, and pair of ventral lobes elongate and thumb-like, directed posteriorly, without spines ( Fig. 26H, I View Figure 26 ). Segment X large and elongate, apical ventral margin projecting a long triangular black process, in dorsal view with ratio of length to width near middle about 1.4: 1 ( Fig. 26D View Figure 26 ).
Distribution. Philippines (Mindanao), Malaysia (north-eastern Borneo).
| BPBM |
Bishop Museum |
| T |
Tavera, Department of Geology and Geophysics |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.