Paracypris fijiensis, Chand, Prerna & Kamiya, Takahiro, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4158.3.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3BDDA341-7AE8-4BE7-B52F-83B4909F67BE |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6057820 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/275187EF-870D-FF8C-A9B3-FB76FB3AFEF8 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Paracypris fijiensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Paracypris fijiensis n. sp.
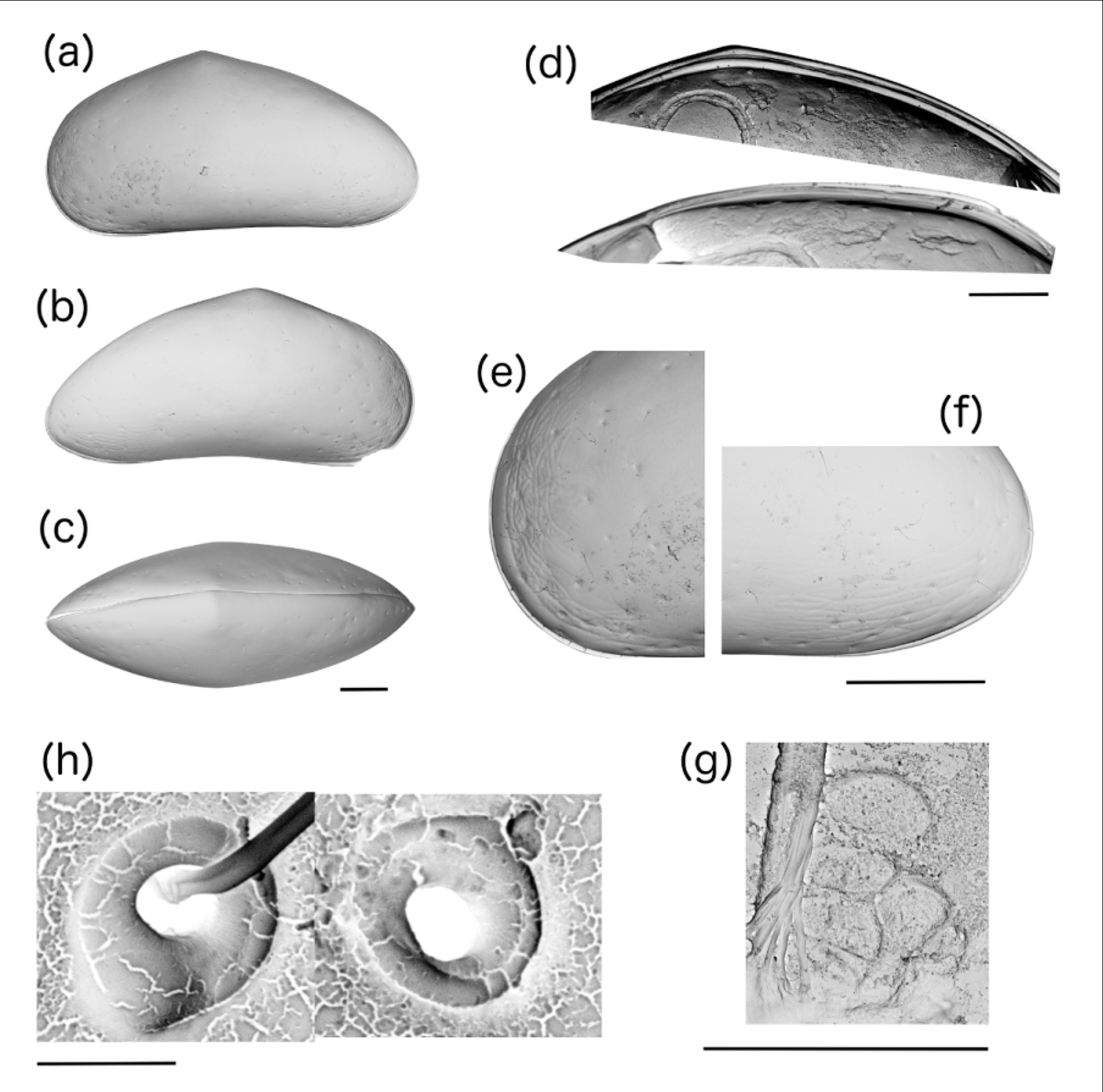
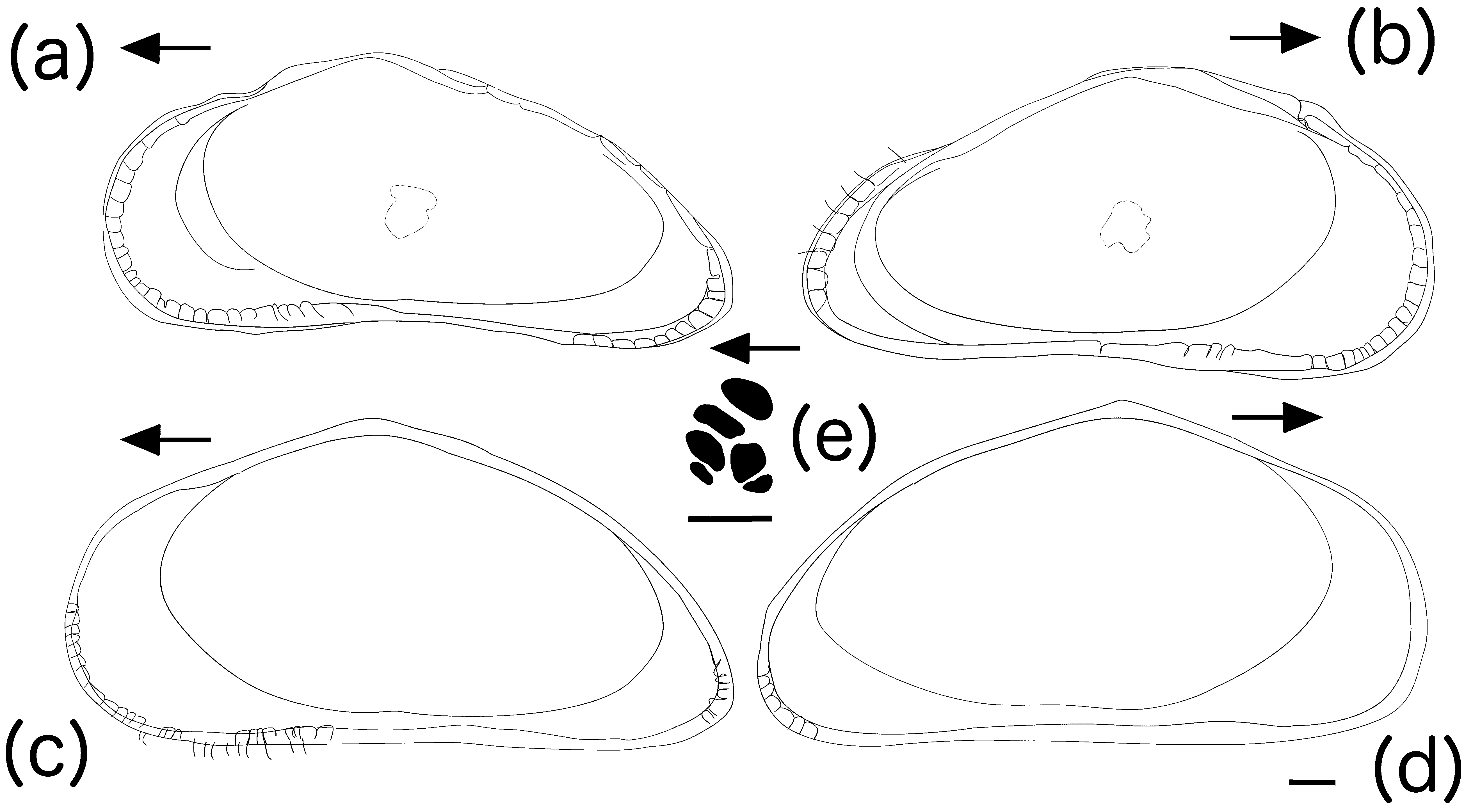
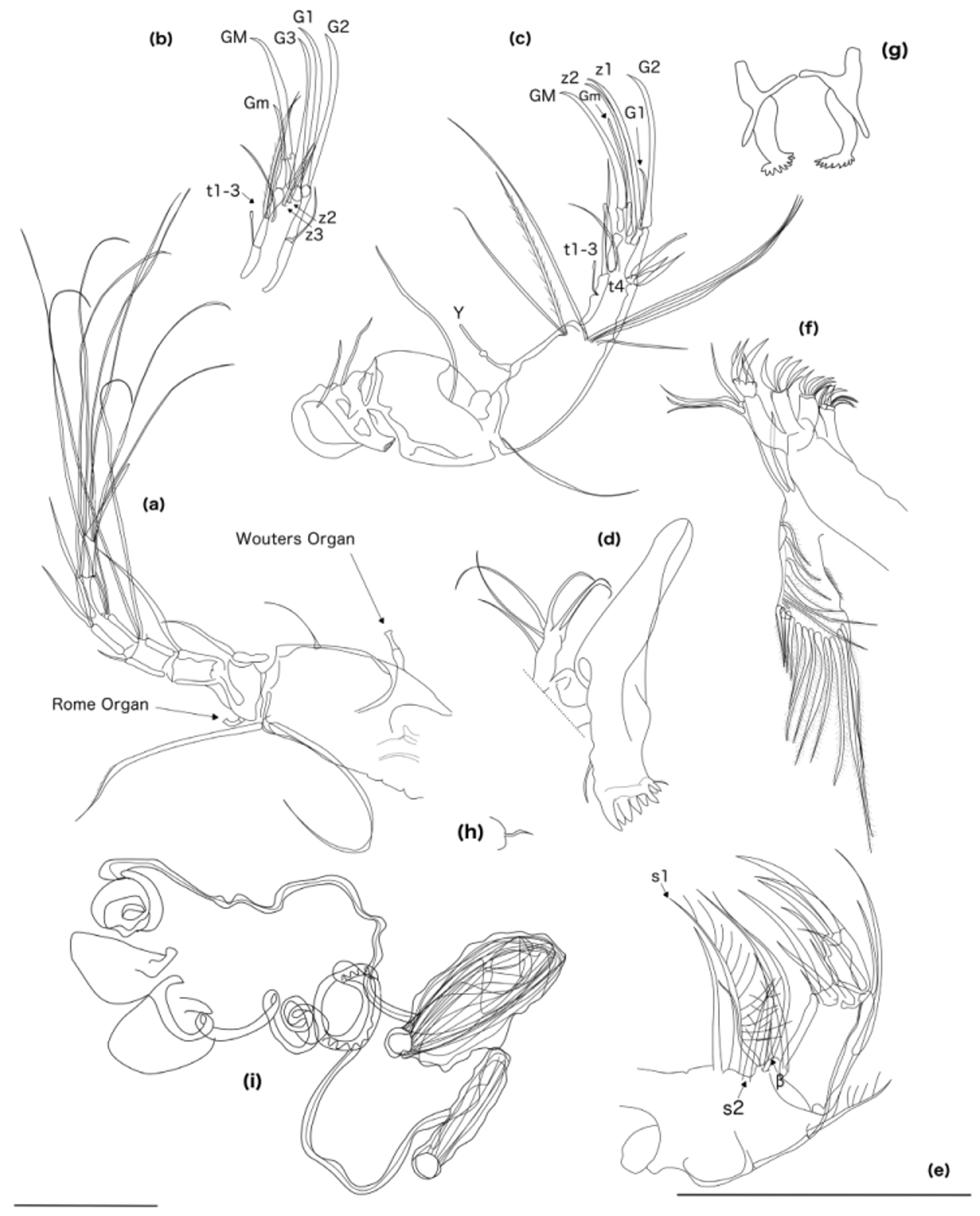
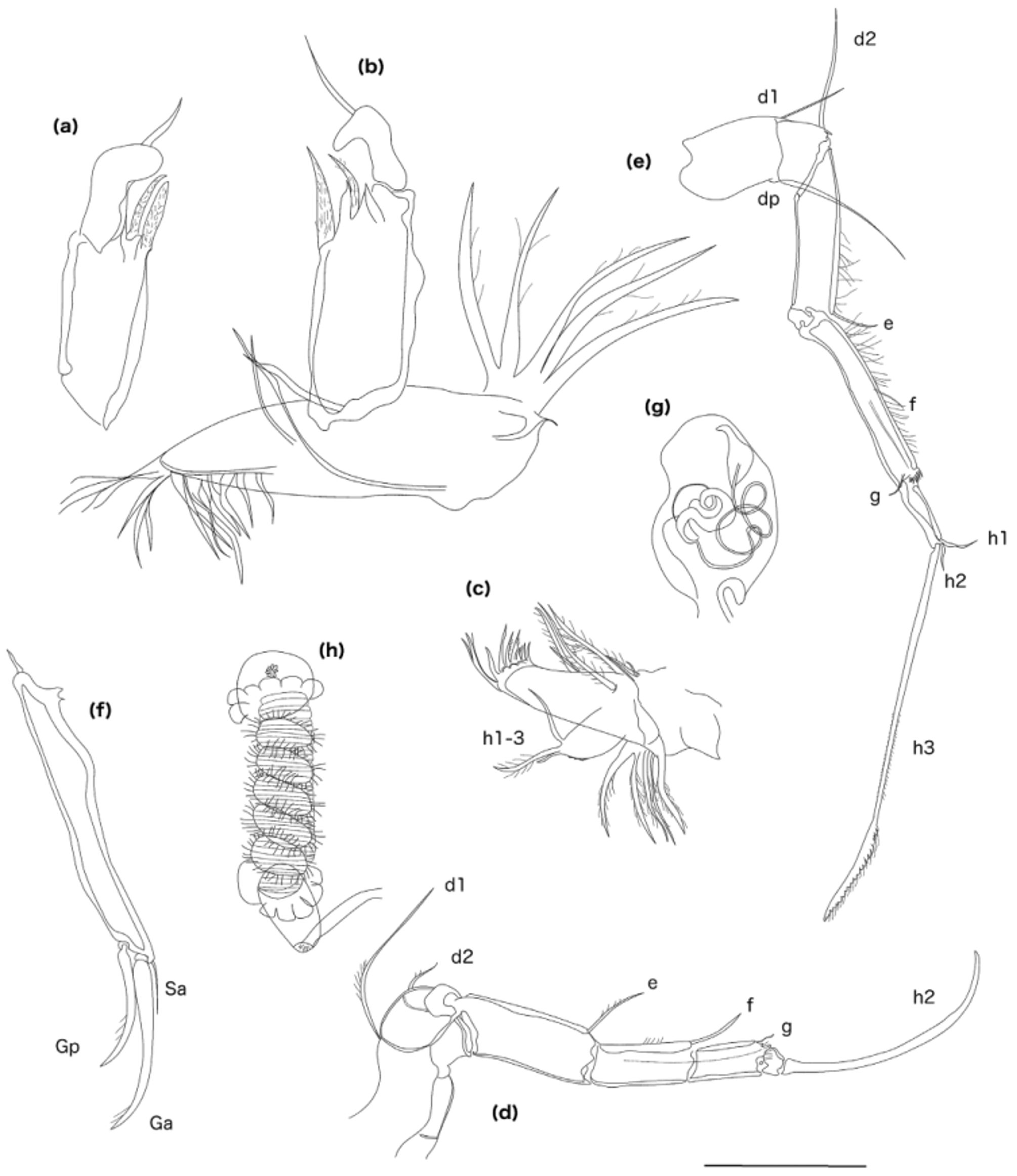
( Figures 2–5 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 )
Type material. Holotype: male UMUT RA32515–RA32516. Paratypes: one male and three females ( UMUT RA32517–RA32523). The holotype and paratypes are deposited at the University Museum, University of Tokyo, Japan; soft parts on glass slides, and valves in paleontological cavity slides.
Type locality. The holotype was collected from Naselesele , Taveuni Island ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ); habitat: green filamentous algae ( Ulva intestinalis ), water parameters temperature 32°C, dissolved oxygen 8.14 mg /L, salinity 31.4 ‰.
Additional localities.: The paratypes were collected from (i) the southeast coast of Tavewa Island, in the Yasawa Group of Islands ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ), habitat: short brown algae ( Pterocladiella sp.), water parameters: temperature 21.6°C, dissolved oxygen 5.09 mg /L, salinity 33.65 ‰, and (ii) along the coast of Korovou, on Naviti Island, in the Yasawa Group of Islands ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ), habitat: short brown algae ( Pterocladiella sp.) and bluegreen algae, water parameters: temperature 21.7°C, dissolved oxygen 4.9 mg /L, salinity 33.2 ‰.
Etymology. fijiensis since this species is from Fiji.
Diagnosis. Anterior margin wide and rounded, posterior margin narrow and acutely rounded, maximum height before the mid length. Sexually dimorphic carapace; males are slightly smaller in size than the females; living specimens of males have a very dark blue-grey coloration while females appear cloudy white with some dark bluegrey patches. An1 with Rome organ and Wouters organ, mouth equipped with a pair of rake-shaped organs, male L5 with asymmetrical hooks, female L5 a short palp with 3 setae (h1 -3). Zenker organ with five rosettes and fanlike lobate ends. CR with a short Sa seta and Ga claw longer than Gp claw.
Description. Carapace is trigonal, elongated with widely rounded anterior and sharply rounded posterior ends ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 a–c, 3a–d). Male valve length and maximum height: 740 µm and 360 µm, respectively (UMUT RA32516). Female valve length and maximum height: 810 µm and 420 µm, respectively (UMUT RA32520). Widely rounded anterior with a slight but clear dorsal angle; the posterior is sharply rounded with a sharp dorsal angle. Straight ventral margin. Wide anterior and posterior vestibula, which narrows near the ventral edge. Simple hinge ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 d) and two types of pores: simple normal pores with sensilla and exocrine pores without sensilla ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 h). Muscle scars: anterior arcuate row of four elongated scars and posterior row of two scars (angled towards the second and third scars of the anterior row) ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 e, 3e).
An1 composed of seven podomeres ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 a). The first is large with a Wouters organ ( Smith & Matzke-Karasz 2008) and a fine seta on the dorsal side and two long distal ventral setae (one with setules on the tip). The second podomere is small with a Rome organ on the ventral side and a distal dorsal seta. Podomeres 3-7 are short and rectangular; the third has one seta at the distal end; the fourth has two long (whip-like) dorsal setae at the distal end and one short ventral seta at the distal end; the fifth has two setae at the distal ends—one short and one long on the ventral side and two long on the dorsal side; the sixth podomere is similar to the fifth podomere and the seventh has a short stout seta, two long ventral setae and two long dorsal setae.
An2 sexually dimorphic; males have six podomeres ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 c) while females have five ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 b). The first three podomeres in both sexes are the same: protopodite (first two segments) with two setae on the ventral side and one long exopodite seta at the distal end; the first podomere of the endopodite is large and rectangular with a slender aesthetasc Y seta on the ventral proximal end and two long setae (one with setules) near the ventral distal end, five natatory setae (length does not exceed the chelate claw) at the junction of the third and fourth podomeres ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 c). Female: setae t1-3 long (t1 with setules), z2 and z3 short, claws G1-3 long and stout with similar lengths, claw GM long and stout, with similar lengths as G1-3 and Gm less than half the length of GM ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 b). Male: t1, t3 are long and slender with a pointed tip, t2, t4 wide with a rounded tip, claws G2, z1, z2 and GM long, stout and of similar lengths, G1 is less than half the length of G2 and Gm is slender with a rounded tip and about two third the length of GM ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 c).
Md palp with one long s1 seta, lined with setules on one side, one long s2 seta lined with setules on both sides and a short, fine β seta ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 e). Final segment of the palp terminates with three slender claws. Exopodite with six setae and the endite of coxa with wide, stout teeth (fig. 4d). Mx palp with two segments: four setae on the outerapical corner of the first segment, three stout, claw-like and two smaller setae on the second segment ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 f). Mouth equipped with a pair of rake-shaped organs, each with nine terminating teeth ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 g).
L5 sexually dimorphic ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 a–c). Male: asymmetrical hooks; left hook wide, stout and lobate, right hook more slender than the left hook, stout with a prominent hook-shape ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 a–b). Inner edge of left hook with two hirsute setae; inner edge of right hook with two hirsute and two smooth setae. Both left and right hooks have a long distal seta each. Endite with numerous setae and exopodite with five long setae with setules. Female L5 basis with three short smooth setae and three long setuled setae. Endite with at least 10 terminating setae. Endopodite reduced to a palp, terminating with two slightly long (one has setules) and one short setae (h1–3) ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 c).
L6 with five podomeres ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 d). Basis with a long d1 seta and a shorter d2 seta; setae e and f at distal ends of the second and third podomeres, respectively; fourth podomere with a very short and fine seta g. Fifth segment; small with a long, straight h2.
L7 with four podomeres ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 e). First podomere with setae d1, d2 and dp; second podomere with seta e; third podomere with setae f and g and fourth podomere with short setae h1, h2 and and very long h3 (almost as long as the lengths of podomeres two, three and four combined).
CR long and stout ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 f), with a very short and fine Sa. Claw Ga longer and wider than Gp; Gp about two thirds the length of Ga. Both Gp and Ga with a few fine setules at the distal end. A single short fine posterior seta is situated near the proximal end of the CR ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 h).
Hp with ventral lobe; the ejaculatory duct forms a wide s-shape that connects to three loops before extending into a leaf-like tapered distal end ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 g). Zenker organ with five spine rosettes and fan-like lobate ends ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 h). Female reproductive system consists of a pair of sac-like genital lobes. Each lobe is connected to a spiral canal that in turn connects to a yarn-ball-like structure (possibly ovaries) by transparent tubes ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 i).
| UMUT |
University Museum, University of Tokyo |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |