Bombus eximius Smith, 1852
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5852/ejt.2020.719.1107 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A4500016-C219-4353-B81C-5E0BB520547F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14372044 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/252087CA-1F64-9517-FDED-FA26DFFDF840 |
|
treatment provided by |
Valdenar |
|
scientific name |
Bombus eximius Smith, 1852 |
| status |
|
Bombus eximius Smith, 1852 View in CoL
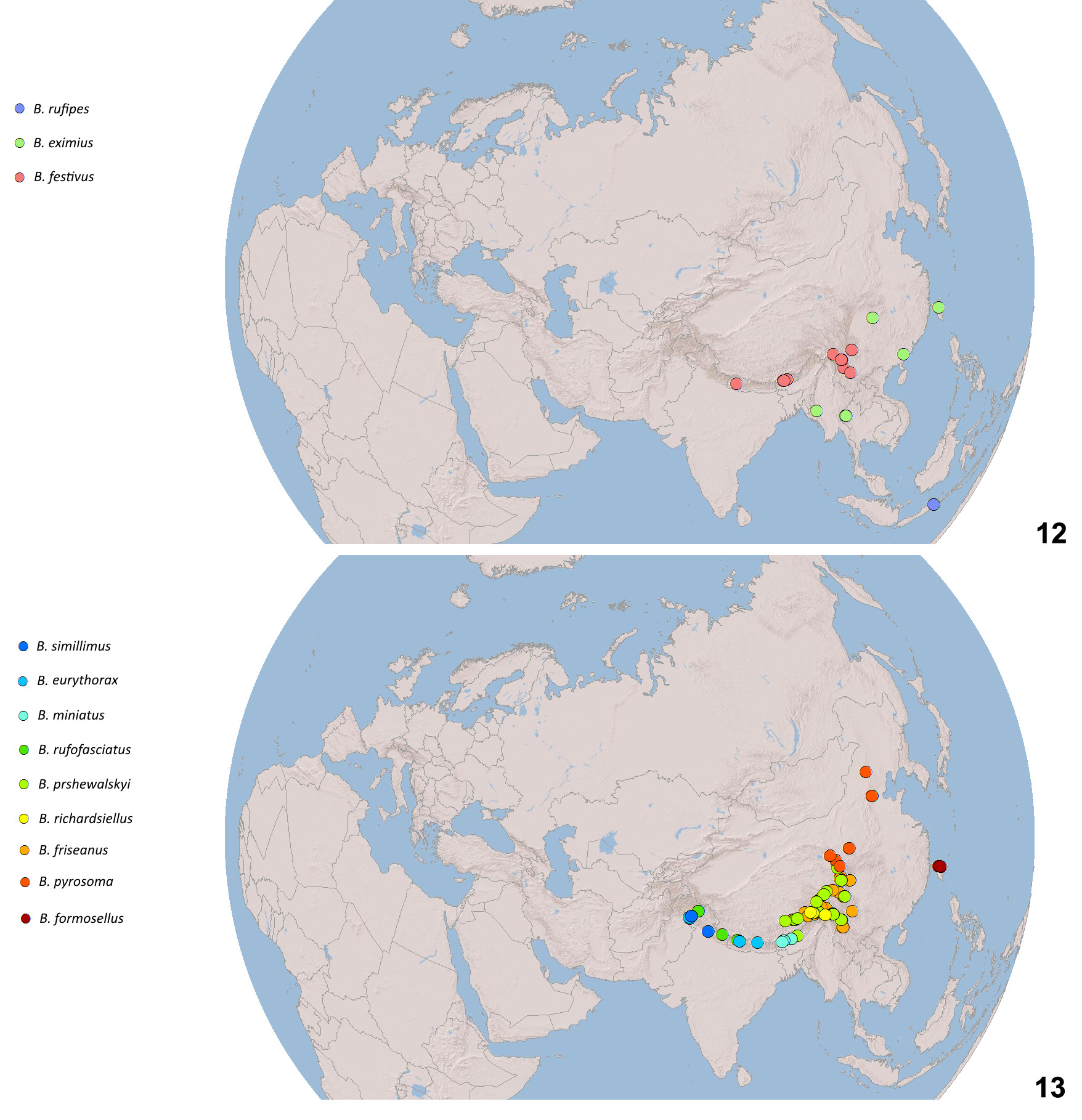
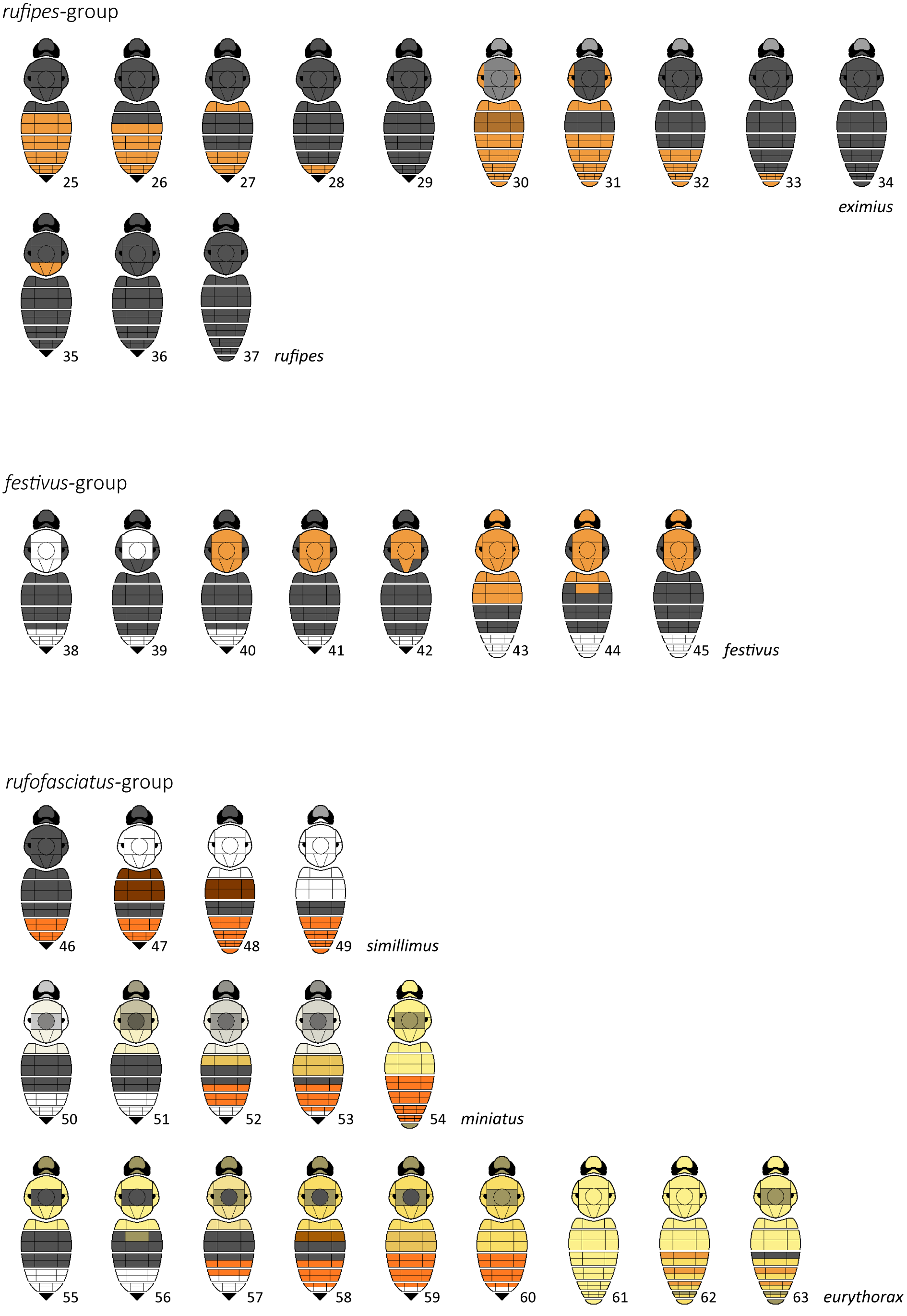
Figs 1 View Figs 1‒6 , 12 View Figs 12‒13 , 25–34 View Figs 25–63 , 181 View Figs 181‒189
Bombus eximius Smith, 1852a: 47 View in CoL .
Bombus latissimus Friese, 1910: 404 View in CoL .
Bombus rufipes View in CoL var. [subsp.] tonkinensis Friese, 1914: 11.
Bombus latissimus View in CoL var. [subsp.] detritus Friese, 1916: 109.
Bombus latissimus View in CoL var. [subsp.] segmentarius Friese, 1916: 109.
Bombus latissimus View in CoL var. [subsp.] tricoloratus Friese, 1916: 109.
Bombus rufipes View in CoL var. [subsp.] lutescens Friese, 1918: 517 (non Pérez, 1890: 154 = B. flavidus Eversmann View in CoL ).
Bombus discrepans Pendlebury, 1923: 64 View in CoL .
Bombus geei subsp. nigribasis Cockerell, 1931: 5 View in CoL .
Bombus eximius View in CoL var. [subsp.] fulvobrunneus Chiu, 1948: 65.
Bombus eximius View in CoL var. [subsp.] pallidus Chiu, 1948: 66 (non Cresson, 1863: 92 = B. pensylvanicus (DeGeer)) View in CoL .
Bombus rufipes var. tonkininsis – Friese 1918: 527, incorrect subsequent spelling.
Bombus latiszimus – Friese 1931: 304, incorrect subsequent spelling.
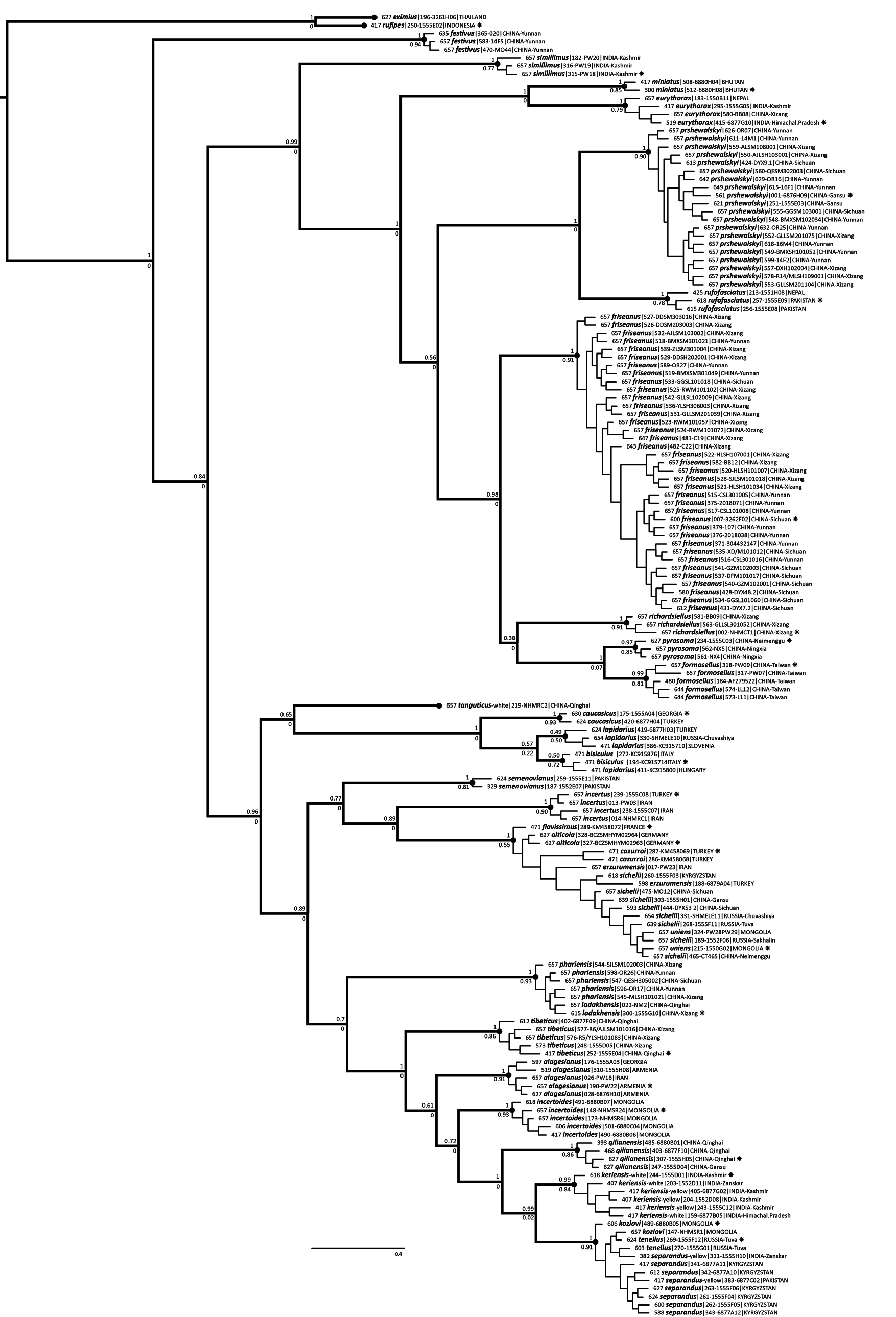
Bombus eximius and B. rufipes have a distinctive morphology and previously were placed in a separate subgenus, Rufipedibombus ( Skorikov 1923) . A close relationship with other species of the subgenus Melanobombus was supported by an analysis of five genes by Cameron et al. (2007) and these subgenera were then synonymised by Williams et al. (2008).
Our PTP analysis ( Fig. 10 View Fig ) of coalescents in the COI gene within the rufipes- group supports two species B. eximius and B. rufipes , corroborated by differences in morphology. It supports as conspecific within B. eximius s. lat. the individuals from Taiwan that may have much of the hair of T2–6 orange (taxon latissimus ), the individuals from southern China and Southeast Asia that often have T2–3 predominantly black and T4–6 orange, and the individuals from the Himalaya that have T2–4 black and T5–6 either orange or black (taxon eximius s. str.).
Diagnosis
Females ( Fig. 1 View Figs 1‒6 )
Queens very large body length 23–30 mm, workers 13–20 mm. Can be distinguished by their combination of wings yellow with the veins orange (cf. B. rufipes ), the hair and integument of mid and hind tibiae and of all barsitarsi orange (cf. some B. rufipes ). The labral lamella has the anterior edge broad and nearly straight (cf. B. ( Pyrobombus) flavescens Smith, 1852 , B. ( Alpigenobombus) genalis Friese, 1918 ).
Males
Body length 16–19 mm. Can be distinguished by their combination of wings yellow with the veins orange (cf. B. rufipes ), similarly coloured to the worker but with the hair of the face black intermixed with grey (cf. B. rufipes ) and the thoracic dorsum black or sometimes intermixed with grey (cf. B. festivus ). Genitalia ( Fig. 181 View Figs 181‒189 ) with the gonostylus reduced to a transverse ‘S’-shaped band (cf. non- rufipes -group), the proximal inner projection not broadened distally and simple (cf. B. rufipes ); volsella projecting beyond the gonostylus by ca 6 × its breadth at its midpoint (cf. B. rufipes ), and without an obvious inner distal process or hook (cf. non- rufipes -group); penis valve head with the outer flange greatly expanded as a triangular projection (cf. non- rufipes -group); eye unenlarged relative to female eye.
Material examined
Holotype
BANGLADESH • ♀ (queen), holotype of Bombus eximius Smith, 1852 by monotypy ( Williams et al. 2009); “ Silhet ” [= Sylhet]; NHMUK (examined PW).
Material sequenced ( 7 specimens)
THAILAND • 1 ♀ (worker); Chiang Mai, Doi Inthanon ; 18.553º N, 98.48º E; 2 Feb. 2007; Y. Areeluck leg.; BOLD seq: 3773E10; PCYU: ML180 View Materials GoogleMaps • 1 ♀ (worker); same collection data as for preceding; 16 Feb. 2007; Y. Areeluck leg.; BOLD seq: 3773E11; PCYU: ML195 View Materials GoogleMaps • 1 ♀ (worker); Chaiyaphum, Tat Tone NP; 15.988º N, 102.041º E; 12 Oct. 2006; Y. Areeluck leg.; BOLD seq: 3261H06; PCYU: ML196 View Materials GoogleMaps .
CHINA • 1 ♀ (queen); Guangdong; 22.2933º N, 111.2061º E; 16 Jan. 2013; BOLD seq: 1555A07; PW: ML178 GoogleMaps • 1 ♀ (worker); Chongqing; 30.13º N, 108.1018º E; Aug. 2010; BOLD seq: 1555A08; PW: ML179 GoogleMaps .
TAIWAN • 1 ♀ (queen); Taichung, Dashuishan road; 24.2561º N, 121.0108º E; 18 Jun. 2004; C. Dietrich leg.; BOLD seq: 1555A06; PW: ML177 GoogleMaps .
BURMA • 1 ♀ (worker); Chin, Natmataung ; 21.2198º N, 93.9401º E; 2 Jun. 2010; D. Zimmermann leg.; BOLD seq: 6880E04; NHMW: ML502 View Materials GoogleMaps .
Global distribution
(Himalayan, south Chinese and southeast Asian mountain species including some of the northern islands) East Asia: CHINA: Xizang, Sichuan, Yunnan, Chongqing, Jiangxi, Guizhou, Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Taiwan. – Himalaya: INDIA: Sikkim, Darjiling Bengal, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya; NEPAL, BHUTAN. – Southeast Asia: BANGLADESH, BURMA, THAILAND, VIETNAM. ( IAR, IOZ, KIZ, NHMUK, NHMW, NME, PCYU, PW, RMNH, SEHU, SMNS, USNM, ZMHB, ZMUM.) The species is widely distributed but not common in collections.
Behaviour
Expected to be food-plant generalists ( Kjellsson et al. 1985).
| NHMUK |
Natural History Museum, London |
| PW |
Paleontological Collections |
| PCYU |
The Packer Collection at York University |
| NHMW |
Naturhistorisches Museum, Wien |
| KIZ |
Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| NME |
Sammlung des Naturkundemseum Erfurt |
| RMNH |
National Museum of Natural History, Naturalis |
| SMNS |
Staatliches Museum fuer Naturkund Stuttgart |
| USNM |
Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History |
| ZMUM |
Zoological Museum, University of Amoy |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
|
SubGenus |
Melanobombus |
Bombus eximius Smith, 1852
| Williams, Paul H., Altanchimeg, Dorjsuren, Byvaltsev, Alexandr, Jonghe, Roland De, Jaffar, Saleem, Japoshvili, George, Kahono, Sih, Liang, Huan, Mei, Maurizio, Monfared, Alireza, Nidup, Tshering, Raina, Rifat, Ren, Zongxin, Thanoosing, Chawatat, Zhao, Yanhui & Orr, Michael C. 2020 |
Bombus eximius
| Chiu S. C. 1948: 65 |
Bombus eximius
| Chiu S. C. 1948: 66 |
| Cresson E. T. 1863: 92 |
Bombus geei subsp. nigribasis
| Cockerell T. D. A. 1931: 5 |
Bombus discrepans
| Pendlebury H. M. 1923: 64 |
Bombus latissimus
| Friese H. 1916: 109 |
Bombus latissimus
| Friese H. 1916: 109 |
Bombus latissimus
| Friese H. 1916: 109 |
Bombus rufipes
| Friese H. 1914: 11 |
Bombus latissimus
| Friese H. 1910: 404 |
Bombus rufipes
| Perez J. 1890: 154 |
Bombus eximius
| Smith F. 1852: 47 |