Amphidromus (Amphidromus) mundus (Pfeiffer, 1853)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4509237 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/215887E3-BA08-FFA0-FF62-FEEB3A239B45 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Amphidromus (Amphidromus) mundus (Pfeiffer, 1853) |
| status |
|
Amphidromus (Amphidromus) mundus (Pfeiffer, 1853) View in CoL
Bulimus mundus Pfeiffer, 1853a: 57 View in CoL ( Type locality: Sincapore [= Singapore]). Pfeiffer, 1853b: 651. Pfeiffer, 1856: 261, 262, pl. 70, figs. 21 & 22.
Bulimus mundus View in CoL var. β Pfeiffer, 1853a: 57 (Locality: Borneo?). Pfeiffer, 1853b: 651.
Amphidromus mundus View in CoL —Missing citation: Morgan, 1885: 387. Fulton, 1896: 71. Pilsbry, 1900: 174, pl. 61, figs 57-59. Laidlaw & Solem, 1961: 589, 590, 642, 643, fig. 38. Richardson, 1985: 31. Maassen, 2001: 119.
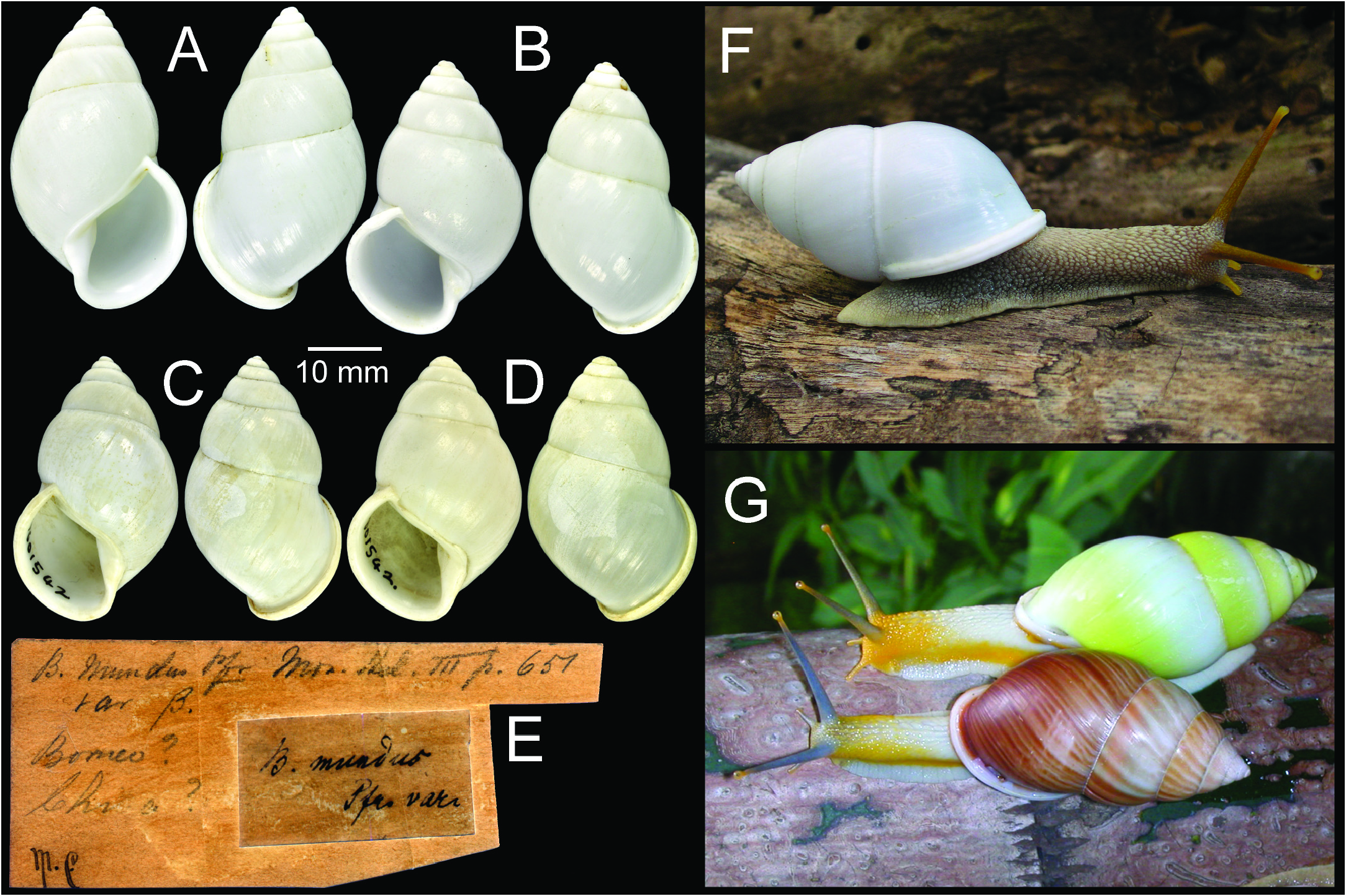
Type material. – Neotype, herein designated, CUMZ 4917 View Materials (1 shell, Fig. 1A View Fig , height 35.3 mm, width 21.3 mm, 5¾ whorls, h/d ratio 1.66). Topotypic material, CUMZ 4913 View Materials ( Fig. 1B View Fig ) (14D, 19S in ethanol, height 35.6 ± 1.69 mm, width 21.6 ± 0.93 mm, 5½ – 6 whorls, h/d ratio 1.65 ± 0.06), 4914 (7D, 6S shells, height 35.6 ± 1.25 mm, width 21.4 ± 0.90 mm, 5½ – 6 whorls, h/d ratio 1.66 ± 0.05); BMNH 20110305 (1D, 1S shells), ZRC-MOL 3068 (1D, 1S shells), SMF 336637 About SMF (1D, 1S shells).
Type locality. – Based on the neotype, the type locality is Pulau Besar , Mersing, Johor, Malaysia ( 2° 26' 7.02" N, 103° 58' 38.59" E) GoogleMaps .
Other material examined. – Pfeiffer’s examined specimens of var. β from Borneo (?) or China (?): BMNH 19601542.1 (2S shells, Fig. 1 View Fig C–E). Singapore: ZMB, Paetel coll. (1S shell); RMNH #19a (1D shell); BMNH 98.10.25.131 (2S shells). Singapore or Borneo: RBINS Dautzenberg ex. Crosse coll. (1D shell), Dautzenberg coll. 6990 (1D shell). Java: ZMB Seckendorf coll. (1D shell). Unknown locality: ZMB Bürger coll. (1S shell), Wallenberg coll. (1S shell); RBINS Dautzenberg coll. #6990α (1S shell); ZMUC #295 (2S shells).
Taxonomic remarks. – The nominal species “ Bulimus mundus ” was described from “Gruner’s collection”. After his death, the collection was sold and the most part was purchased by H. Maltzan, whose collections are currently housed in Aquazoo-Löbbecke Museum in Düsseldorf. However, some of Gruner’s specimens are also extant in other museums including SMF and ZMB ( Tëmkin et al. 2009: 44). After a long investigation, the original type series of “ Bulimus mundus ” from “Gruner’s collection” was not located, and is presumed to be lost (M. Glaubrecht, R. Janssen, B. Hausdorf, R. Seemann and S. Stoll, personal communication). The absence of type material of the nominate form has been the cause of doubt about the identity and status of this species (Laidlaw & Solem, 1961). We consider that the specimen of Bulimus mundus var. β cited by Pfeiffer (1853a) from the Cuming collection, is an example of this species but having been identified by Pfeiffer as a variety, it was excluded from the original type series of Bulimus mundus . Because of the uncertain origin of this lot according to the label information (‘Borneo?’ and ‘ China?’), the form β is deemed unsuitable for designation as a neotype. The neotype selected here from our Pulau Besar collection allows a proper re-description of this taxon with the aim to stabilise the taxonomy.
Description. – Shell ( Fig. 1A View Fig ): Medium sized to small, (height 32.7–40.3 mm, diameter 19.3–23.8 mm) white, solid, ovate conic; umbilicus perforate; chirally dimorphic. Apex acute; spire short; suture depressed. Whorls slightly convex; last whorl round to ovate. Dark varix absent; periostracum thin and transparent. Aperture broadly ovate. Lip thickened, expanded and reflexed but not attached externally to last whorl. Parietal callus thickened; columella twisted.
External anatomy ( Fig. 1B View Fig ): Living specimens with pale brown body, covered with darker recessed reticulations on skin. Foot broad and long with pale margin, extended across posterior tail. Upper tentacles drumstick-shaped, orange-brown, with dark eyespots on tentacular tips. Lower tentacles short, orange to pale orange; head and mouthparts brown. Mantle edge light orange; mantle cavity with dark pigmentation.
Genital anatomy ( Fig. 2A View Fig ): Atrium (at) relatively short (n = 5). Penis (p) cylindrical, about ¾ of vagina length, and enlarging slightly distally. Epiphallus (e) long and slightly smaller in diameter than penis. Flagellum (fl) almost the same length as epiphallus with coiled distal portion. Appendix (ap), located beyond coiled portion of flagellum, nearly same length as flagellum. Vas deferens (vd), a narrow tube, extending from free oviduct ending at epiphallus. Penial retractor muscle (pm) long, thin, originating distally from penis, attached to penis near distal end.
Internal wall of penis corrugated, exhibiting series of thickened, swollen, longitudinal penial pilasters (pp), which form a fringe around conical penial verge. Penial verge (pv) short, conic with smooth surface ( Fig. 2B View Fig ).
Vagina (v) long, slender and cylindrical. Gametolytic duct (gd) extends from vagina, proximally as enlarged cylindrical tube, abruptly tapering to small tube distally, terminally connected to gametolytic sac (gs). Free oviduct (fo) short, oviduct compact and enlarged to form lobule alveoli. Prostate gland ventrally fused with oviduct. Albumen gland (ag) slightly large and lingulate. Hermaphroditic gland (hg) contracts from numerous small lobules; narrow and convoluted hermaphroditic duct (hd) connects to middle of talon ( Fig. 2A View Fig ).
Internally the vagina possesses longitudinal vaginal pilasters (vp). Pilasters have continuous ridges with short smooth ridges near genital orifice; extends to slightly swollen portion with irregular shaped, deep crenellations ( Fig. 2B View Fig ).
Digestive anatomy ( Fig. 2C, 2F View Fig ): Jaw light brown and corneous with strong vertical ridges. Radular teeth arranged in anteriorly pointed V-shaped rows, each row containing about 206 teeth (102-(17-15)-1-(15-17)-103). Central tooth tricuspid, spatulate, with small ectocones ( Fig. 2D View Fig ). Lateral teeth bicuspid, endocone large with truncated cusp, ectocone larger with curved cusp. From tooth 15 to 17 outwards lateral teeth gradually transformed to tricuspid marginals ( Fig. 2E View Fig ). Marginal teeth asymmetric, endocone medium; mesocone large with curved margins; ectocone small.
Distribution. – The confirmed distribution of this species is currently restricted to the type locality, Pulau Besar, Johor, Malaysia. Species determinations of samples from museum collections with records from a numerous localities, such as Singapore, the Philippines, Borneo and Java (Laidlaw & Solem, 1961: 589; S. Panha, personal observation in collections) require verification. Occurrence in China, as given on the label of ' B. mundus forma β’ cited above, can be ruled out with certainty because China is outside of the geographic range of Amphidromus ( Solem, 1959, 1983; Laidlaw & Solem, 1961; Sutcharit & Panha, 2006a).
| ZMB |
Museum für Naturkunde Berlin (Zoological Collections) |
| RMNH |
National Museum of Natural History, Naturalis |
| RBINS |
Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences |
| ZMUC |
Zoological Museum, University of Copenhagen |
| SMF |
Forschungsinstitut und Natur-Museum Senckenberg |
| R |
Departamento de Geologia, Universidad de Chile |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
|
SubGenus |
Amphidromus |
Amphidromus (Amphidromus) mundus (Pfeiffer, 1853)
| Sutcharit, Chirasak & Panha, Somsak 2011 |
Amphidromus mundus
| Maassen, W 2001: 119 |
| Richardson, L 1985: 31 |
| Pilsbry, H 1900: 174 |
| Fulton, H 1896: 71 |
| Morgan, J 1885: 387 |
Bulimus mundus
| Pfeiffer, L 1856: 261 |
| Pfeiffer, L 1853: 57 |
| Pfeiffer, L 1853: 651 |
Bulimus mundus
| Pfeiffer, L 1853: 57 |
| Pfeiffer, L 1853: 651 |