Rosellinia qiongensis S.H. Long & Q.R. Li, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.552.5.2 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6799416 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/204C87DC-E24B-FF88-95A8-97BCFDEA4C3C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Rosellinia qiongensis S.H. Long & Q.R. Li |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Rosellinia qiongensis S.H. Long & Q.R. Li View in CoL sp. nov. ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 )
MycoBank No GoogleMaps : MB842285
Holotype: — CHINA, Hainan Province, Qiongzhong County (19°7′8.60″N, 109°7′8.60″E), elev. 177 m, on dead branch of bamboo, GoogleMaps 13 November 2020, S.H. Long and Lili Liu QZ 100-1 ( GMB0082 , holotype; ex-type GMBC0082 ); ibid ( KUN-HKAS 122640 , isotype).
Saprobic on a dead branch of bamboo. Sexual morph Subiculum felted cream-colored to light brown, restricted to rim around stromata, persistent. Stromata 560–725 µm high × 525–635 µm diam. (av. = 639 × 582 µm, n = 20), superficial, scattered to gregarious, solitary, globose, with a conical pointed top, dark brown to black, shiny, carbonaceous. Ostioles black, finely to coarsely papillate. Ectostroma 60–80 µm thick, black, carbonaceous. Entostroma black, confined to base. Perithecia not collapsed in the stroma cavity. Asci 108.5–141.5 × 11–24 µm (av. = 126 × 15.5 µm, n = 30) 8-spored, unitunicate, cylindrical, short pedicellate, apically rounded, with a long barrel-shaped, apically flattened, basally attenuated or not, J + apical apparatus in Melzer’s reagent, 6.0–6.8 µm high, 6.6–9.9 µm wide. Ascospores 24.5–31 × 5–8 µm (av. = 27.2 × 6.4 µm, n = 30), biseriate, fusiform, ends rounded, hyaline when immature, slight brown to brown at maturity, straight to curved, with three, 3–9 µm, straight germ slits, without slimy sheathes or appendages. Asexual morph Undetermined.
Culture characteristics: —Ascospores germinated on PDA within 24 hours. Colonies on PDA were white when young, became pale brown, dense, but thinning towards the edge, medium dense, white from above, reverse sides were white at the margin, flesh to pale brown at centre, no pigmentation were produced on PDA medium, no conidia were observed on PDA or OA media.
Habitat/Distribution: —Known to inhabit dead wood, Hainan Province, China.
Etymology: —Refers to Qiong, the abbreviation of Hainan province, where the type specimen was collected.
Other material examined: — CHINA, Hainan Province, Qiongzhong County (19°7′8.10″N, 109°52′21.36″E), altitude: 177 m, dead branch of bamboo, 13 November 2020, S.H. Long, QZ180 ( GMB0083 , paratype, ex-paratype GMBC0083 ) GoogleMaps .
Additional sequences: —GMB0082 (LSU: OM001205 View Materials ); GMB0083 (LSU: OM001206 View Materials ).
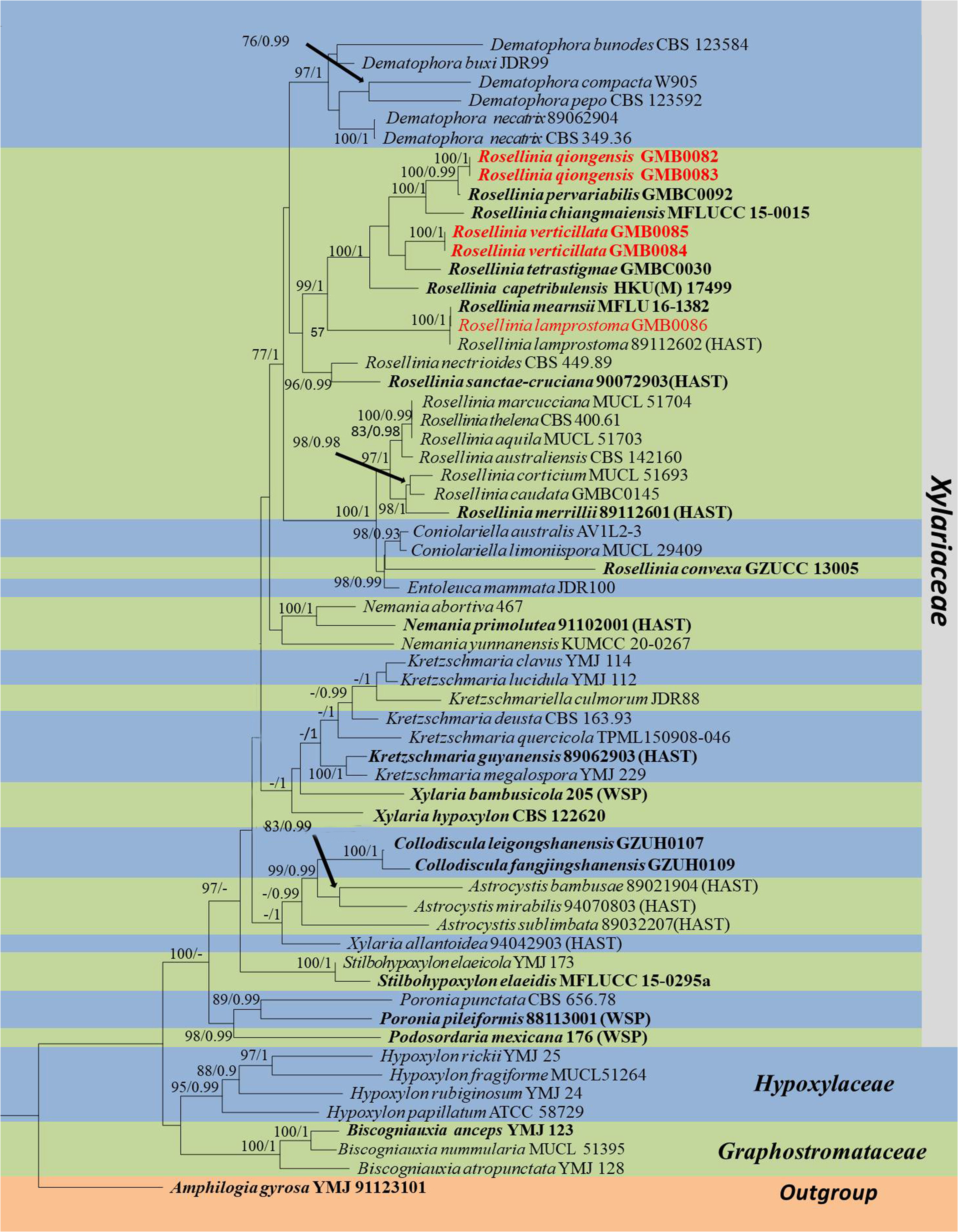
Notes: —Our new strains of Rosellinia qiongensis accommodate as the sister clade to R. pervariabilis Q.R. Li & J.C. Kang in the phylogenetic tree with high statistical supports (100/0.99) ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ). Their ascospores are similar in shape and both are light brown in color, but R. qiongensis had three germ slits on ascospores while R. pervariabilis are lacking them. Moreover, the size of ascospores of R. qiongensis is larger than that of R. pervariabilis (24.5–31× 5–8 µm vs. 19.5–24.5 × 4–5 µm) ( Xie et al. 2019). Rosellinia qiongensis belongs to Rosellinia emergens group and it is also reminiscent of R. dolichospora Syd. & P. Syd. and R. patilii L.E. Petrini , which has fusiform, brown ascospores with three short germ slits ( Petrini 2013). However, R. qiongensis differs from R. dolichospora and R. patilii by its smaller ascospores (24.5–31 × 5–8 µm in R. qiongensis , 29–33 × 6.3– 7.7 µm in R. dolichospora , and 38.6–45.4 × 7.2– 9.8 µm in R. patilii ) ( Petrini 2013).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |