Dephomys eburneae, Heim de Balsac & Bellier, 1967
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6887260 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6868643 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/1E30E275-34BE-FF0F-E181-2F1B751C84F2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Dephomys eburneae |
| status |
|
Ivory Coast Defua Rat
French: Déphomys de Céted'Ivoire / German: Liberianische Defua-Ratte / Spanish: Rata defua de Costa de Marfil
Other common names: Ivory Coast Dephomys, Ivory Coast Rat
Taxonomy. Dephomys eburnae Heim de Balsac & Bellier, 1967 View in CoL ,
Lamto, Ivory Coast.
Dephomys eburneae is distinguished from D. defua on chromosomal and cranial grounds, as well as by lacking cusp t3 on M'. Monotypic.
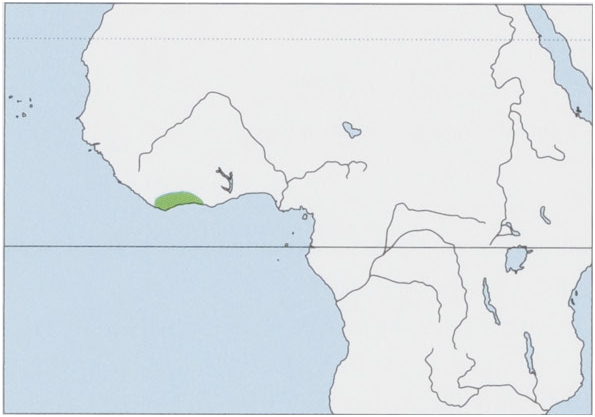
Distribution. E Liberia and S Ivory Coast. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 120-142 mm, tail 182-203 mm, ear 18-20 mm, hindfoot 26-28 mm; weight 47-59 g. Fur is long and sleek, reddish brown and black-flecked above, with brighter orange rump, and gray below. Tail is relatively long (160% of head-body length) and black-colored, with fine scales and bristles. Head is long and thin with dark long vibrissae. Ears are small and rounded, and sparsely haired. Feet are white or light brown above, with four digits on forefoot and five on hindfoot.
Habitat. Presumably similar to the Common Defua Rat ( D. defua ), i.e. pristine rainforest, secondary growth, forest clearings, grassland, and cocoa and oil palm plantations.
Food and Feeding. Presumably similar to that of the Common Defua Rat , feeding on vegetable material and some insects.
Breeding. No information.
Activity patterns. Ivory Coast Defua Rats are presumably nocturnal and possibly partly arboreal.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Not assessed on The IUCN Red List.
Bibliography. Cole (1975), Happold (2013a), Monadjem et al. (2015), Musser & Carleton (2005), Tranier & Dosso (1979), Van der Straeten (1984).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.