Saetheria tylus (Townes)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.177577 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5612516 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0E6487EA-FF8E-7344-FF70-BC2E4218F9F9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi (2016-04-05 14:57:10, last updated 2024-11-27 07:09:05) |
|
scientific name |
Saetheria tylus (Townes) |
| status |
|
Saetheria tylus (Townes) View in CoL
( Figs. 6–7 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 )
Saetheria tylus ( Townes, 1945: 150–151).
Paracladopelma nagaraelongata Sasa, 1989: 65 View in CoL ; Sasa and Okazawa (1992: 43); Inoue et al. (2004: 31); Kondo et al. (2005: 52). Syn. n.
Paracladopelma kisopediformis Sasa et Kondo, 1993: 98 View in CoL . Syn. n.
Parachironomus taishoabeus Sasa et Tanaka, 2001: 46 View in CoL . Syn. n.
Material examined. JAPAN: Gifu Prefecture, Gifu City, Minato-machi, Nagara River, holotype male of Paracladopelma nagaraelongata Sasa , 25.x.1988, M. Sasa (Type No.170:42); Gifu Prefecture, middle reaches of Kiso River, holotype male of Paracladopelma kisopediformis Sasa et Kondo , 15.xi.1988, M. Sasa (Type No. 220:70); Gunma Prefecture, Tone River, Taisho Bridge, holotype male of Parachironomus taishoabeus Sasa et Tanaka , 13.ix.1999, N. Tanaka (Type No. 392:81); Aichi Prefecture, Yahagi River, Toyoda Bridge, 1 male, x.2003, S. Kondo ( CHI 19:56); Gifu Prefecture, Kiso River, Oki, 1 male, 28.v.2001, T. Kobayashi ( CHI 27:24); Gifu Prefecture, Nagara River, Nagaraohashi Bridge, 1 male, 29.v.2001, T. Kobayashi ( CHI 29:77); Gifu Prefecture, Nagara River, Horitsu, 2 males, 2.x.2001, T. Kobayashi ( CHI 29:79, CHI 29:80); Nagasaki Prefecture, Todoroki Valley, 2 males, 25.x.2000, H. Suzuki; Niigata Prefecture, Shibumi River, 3 larvae, 3.viii.2005, N. Shimura ( CHI 43:45–47); Shiga Prefecture, Lake Biwa, 2 larvae, vi.1997, N. Kitagawa (as S. sp. SA, Kitagawa’s code B021–1, B021–2); Hokkaido, Kushiro River, 1 larva, 1993, N. Kitagawa (as S. sp. SB, Kitagawa’s code 8721); Gifu Prefecture, Nakatsu River, tributary to Kiso River, 1 larva, xi.2000, N. Kitagawa (as S. sp. SD, Kitagawa’s code 8547); Okayama Prefecture, Takahari River, 1 larva, 2003, N. Kitagawa (as S. sp. SE, Kitagawa’s code 9113); Nagano Prefecture, Nakatsu River, tributary to Shinano River, 1 larva, 2004, N. Kitagawa (as S. sp. SF, Kitagawa’s code 9306); Nagano Prefecture, Nakabusa River, tributary to Sai River, 1 larva, 2004, N. Kitagawa (as S. sp. SG, Kitagawa’s code 9332); Gifu prefecture, Itadori River, tributary to Nagara River, 1 larva, 17.viii.2004, N. Kitagawa (as S. sp. SH, Kitagawa’s code 9603).
Male (n = 4–8)
Total length 2.3–2.8, 2.6 mm.
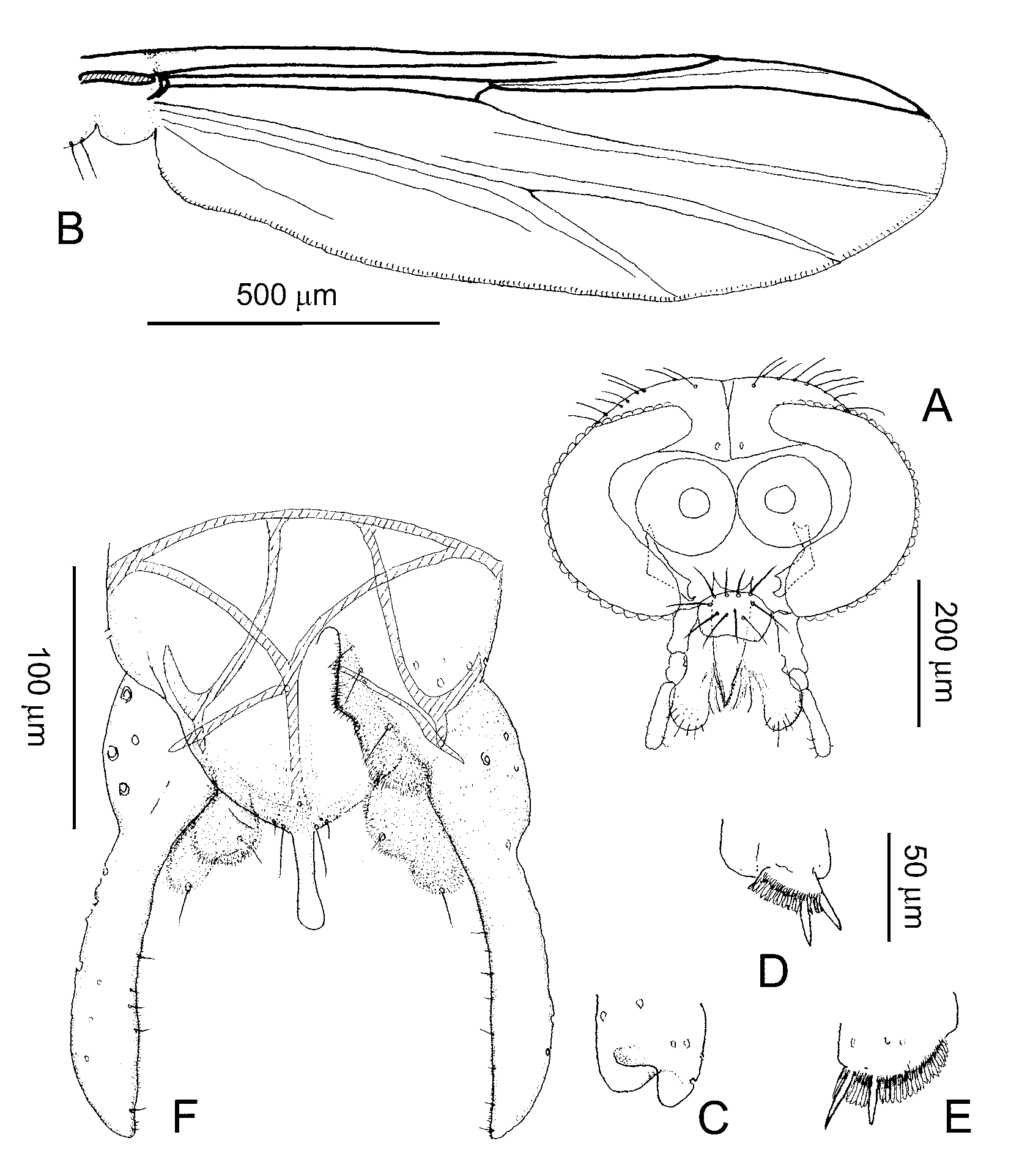
Head ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 A). Frontal tubercles clearly present, but small, c. 8 μm long, 7 μm wide. Antenna with 11 flagellomeres; AR 1.71–2.00, 1.84. Temporals 10–14, 12. Clypeus with 10–17, 12 setae. Tentorium c. 120 μm long, 30 μm wide. Length (in μm) of palpomeres 2–5: 25–40, 31; 95–110, 101; 100–115, 106, 155–180, 167. Thorax. Antepronotals 2–3, 3; acrostichals 7–11, 9; dorsocentrals 8–9, 9; prealars 2–3, 3. Scutellum with 5– 10, 8.
Wing ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 B). Length 1.34–1.60, 1.48 mm. Brachiolum with 0–1 seta. Squama with 2–3, 3 setae.
Legs. Fore tibial scale and mid- and hind tibial combs as in Figures 6 View FIGURE 6 C–E. Pulvilli well developed. Lengths (in μm) and proportions of legs as in Table 3 View TABLE 3 .
Hypopygium ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 F). Anal tergite bands partially fused, Y-shaped. Anal point bare, with rounded apex. Superior volsella bilobed, each lobe with single strong seta. Inferior volsella low, extending along inner margin of gonocoxite, with microtrichia, without setae. Gonostylus gently curved.
Larva (Kitagawa’s code B021, S. sp. SA).
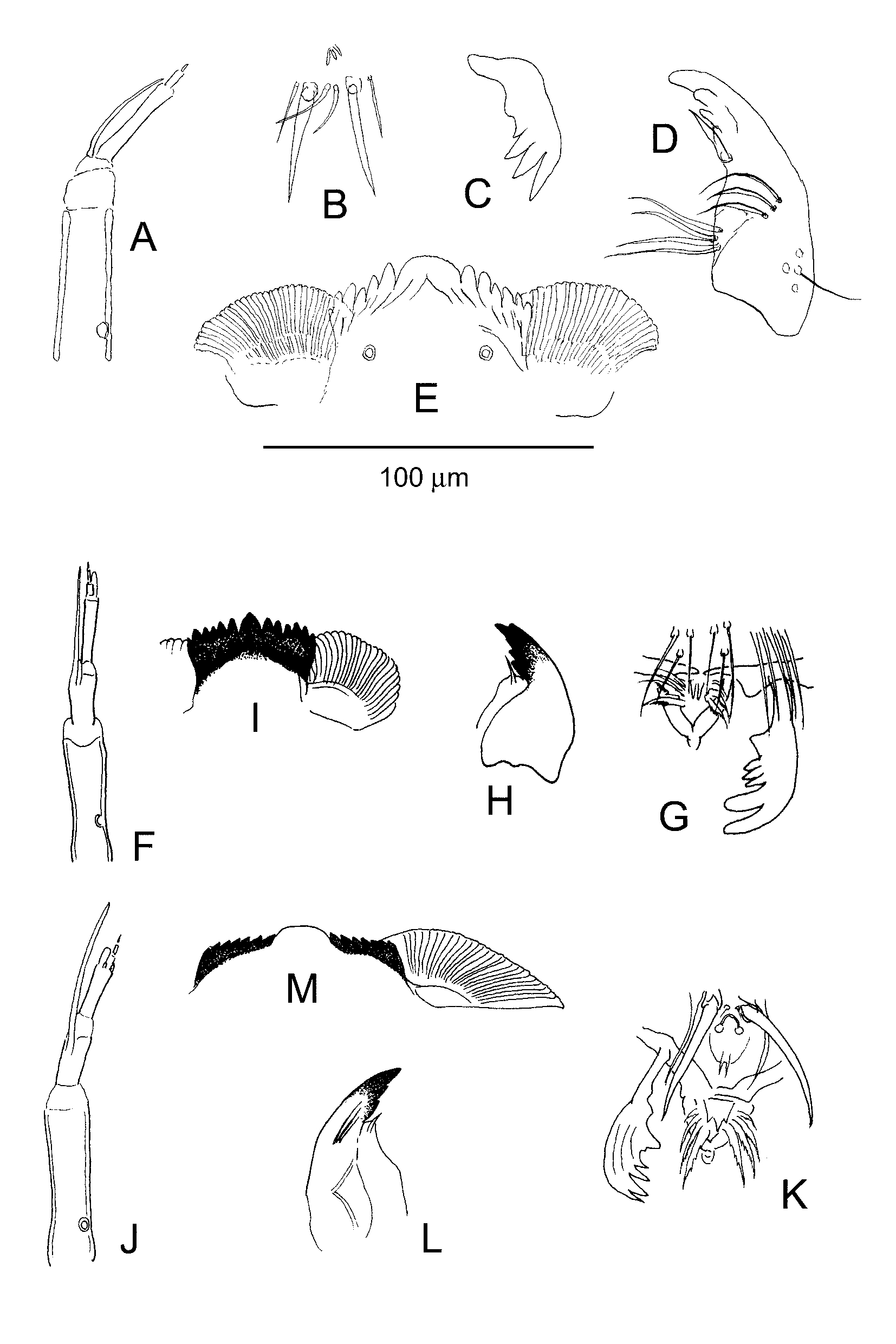
Head. Antenna ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 A) 5 segmented, ring organ in proximal 1/4 of basal segment, blade apically on 2nd segment, extending to near apex. SI seta-like; SII long, broadly blade-like ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 B). Premandible with 4 teeth distally, brush lacking ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 C). Mandible ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 D) with apical tooth and 3 inner teeth; seta subdentalis moderately long, blade-like; seta interna consisting of 4 long serrated lamellae; pecten mandibularis consisting of 3 long lamellae. Mentum ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 E) with narrow median tooth and 6 pairs of lateral teeth; ventromental plates widely separated medially, distinctly striated, about as wide as mentum.
Remarks. The adults of Saetheria tylus differ from S. reissi by the presence of frontal tubercles and in the shape of the superior volsella, which is bilobed in S. tylu s, while it is roughly triangular in S. reissi . The Japanese specimens have small, but distinct frontal tubercles and a bilobed superior volsella, and are thus allotted to S. tylus .
The Japanese Saetheria larvae described by Kitagawa can be split into three groups, mainly based on the morphology of mentum and the ventromental plate. Group A ( Figs. 7 View FIGURE 7 A–E): S. sp. SA (Kitagawa 1977b: 37, Fig. 12), S. sp. SB ( Kitagawa 1998: 187, Fig. 11), S. sp. SD ( Kitagawa 2002: 34, Fig. 18), and S. sp. SF ( Kitagawa 2004: 24, Fig. 9). Group B ( Figs. 7 View FIGURE 7 F–I): S. sp. SE ( Kitagawa 2003: 29, Fig. 11) and S. sp. SH ( Kitagawa 2005: 36, Fig. 15). Group C ( Figs. 7 View FIGURE 7 J–M): S. sp. SG ( Kitagawa 2004: 25, Fig. 10). The three larvae from Shibumi River (CHI 43:45–47) collected by N. Shimura apparently belong to Group B.
Group A resembles the larva of S. tylus (see Jackson 1977: 1354, Fig. 31), having a dome-shaped median tooth. According to Jackson (1977: 1353) the larval antenna of S. tylus is 6 segmented. However, according to Kitagawa (1997b: 37, 2002: 34, 2004: 24) the antennae of S. sp. SA, S. sp. SD, and S. sp. SF appear to be 5 segmented, while the antenna of S. sp. SB ( Kitagawa 1998: 187) is 6 segmented. Group B resembles S. hirta described by Saether (1983). Group C has a broad ventromental plate and shows similarities to Jackson’s (1977) S. sp. 1 and Wang et al. ’s (1991) S. sp. However, the identity of the various larvae can not be decided with certainty as none of the larvae have associated males.
Wang, X., Zheng, L. & Ji, B. (1991) A taxonomic study on Chironominae from China II. (Diptera: Chironomidae). Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Nankaiensis 1, 12 - 16. [In Chinese.]
Inoue, E., Kawai, K. & Imabayashi, H. (2004) Differences in occurrence among lotic chironomid (Diptera: Chironomidae) species in relation to spatio-temporal factors of mountain streams. Journal of the Graduate School of Biosphere Science, Hiroshima University, 43, 25 - 39.
Jackson, G. A. (1977) Nearctic and Palaearctic Paracladopelma Harnisch and Saetheria n. gen. (Diptera: Chironomidae). Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 34, 1321 - 1359.
Kitagawa, N. (1997 b) Chironomid larvae from Lake Biwa. Tansuiseibutsu, 74, 1 - 75. [In Japanese.]
Kitagawa, N. (1998) Chironomid larvae of Hiji River - Thirty-four species. In: Taxonomic studies on Chironomid larvae. N. Kitagawa private publication, Yokkaichi City, Mie Prefecture, Japan, pp. 175 - 212. [In Japanese.]
Kitagawa, N. (2002) Taxonomic studies on Chironomidae larvae (4). Tansuiseibutsu, 87, 1 - 147. [In Japanese.]
Kitagawa, N. (2003) Taxonomic studies on Chironomid larvae (5). Tansuiseibutsu, 88, 1 - 155. [In Japanese.]
Kitagawa, N. (2004) Taxonomic studies on Chironomid larvae (6). Tansuiseibutsu, 89, 1 - 124. [In Japanese.]
Kitagawa, N. (2005) Taxonomic studies on Chironomid larvae (7). Tansuiseibutsu, 90, 1 - 116. [In Japanese.]
Kondo, S., Mano, T., Yamamoto, M. & Kobayashi, T. (2005) Chironomid midges emerging from an Egeria densa community in the middle reaches of the Yahagi River during fall season in 2003. Research of Yahagi River, 9, 49 - 53. [In Japanese.]
Saether, O. A. (1983) Oschia dorsenna n. gen., n. sp. and Saetheria hirta n. sp., two new members of the Harnischia complex (Diptera: Chironomidae). Entomologica scandinavica, 14, 395 - 404.
Sasa, M. (1989) Annex. Chironomid midges of some rivers in western Japan. Research Report from Toyama Prefectural Environmental Pollution Research Center, 1989, 45 - 110.
Sasa, M. & Okazawa, T. (1992) Studies on the chironomid midges (yusurika) of Kurobe River. Research Report from Toyama Prefectural Environmental Pollution Research Center, 1992, 38 - 91.
Sasa, M. & Kondo, S. (1993) Studies on the chironomid midges (yusurika) collected in Toyama and other areas of Japan. Part 7. Additional chironomids recorded from the middle reaches of Kiso River, Aichi. Research Report from Toyama Prefectural Environmental Pollution Research Center, 1993, 98 - 106.
Sasa, M. & Tanaka, N. (2001) Studies on the chironomid midges collected with light traps during the summer season by the bridges of the Tone River, Gunma Prefecture. Annual Report of Gunma Prefectural Institute for Public Health and Environmental Sciences, 33, 41 - 73.
Townes, H. K. Jr. (1945) The Nearctic species of Tendipedini (Diptera, Tendipedidae (= Chironomidae). American Midland Naturalist, 34, 1 - 206.
FIGURE 6. Saetheria tylus (Townes, 1945), male. A – C: Specimen CHI 36: 56. A, head. B, wing. C, tibial scale of foreleg. D – F: Specimen CHI 43: 48. D, tibial combs of midleg. E, tibial combs of hind leg. F, hypopygium.
FIGURE 7. Saetheria spp., larvae. A – E: Saetheria tylus (Townes, 1945), larva. A, antenna. B, SI and SII. C, premandible. D, mandible. E, mentum and ventromental plate. F – I: Saetheria sp. SE, (redrawn from Kitagawa 2003, Fig. 11). F, antenna. G, labrum and premandible. H, mandible. I, mentum and ventromental plate. J – M: Saetheria sp. SG, (redrawn from Kitagawa 2004, Fig. 10). J, antenna. K, labrum and premandible. L, mandible. M, mentum and ventromental plate.
TABLE 3. Lengths (in μm) and proportions of legs of Saetheria tylus (Townes, 1945), male, from Japan.
| fe | ti | ta1 | ta2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1 | 580–650, 619 (7) | 350–420, 379 (7) | 790–850 (3) | 390–450 (3) |
| p2 | 550–630, 590 (6) | 470–550, 510 (7) | 240–300, 277 (7) | 140–170, 154 (7) |
| p3 | 600–700, 646 (7) | 620–725, 671 (7) | 390–470, 430 (6) | 225–260, 246 (6) |
| CHI |
University of Illinois |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Chironominae |
|
Genus |
Saetheria tylus (Townes)
| Kobayashi, Tadashi 2007 |
Parachironomus taishoabeus Sasa et Tanaka, 2001 : 46
| Sasa 2001: 46 |
Paracladopelma kisopediformis Sasa et Kondo, 1993 : 98
| Sasa 1993: 98 |
Paracladopelma nagaraelongata
| Kondo 2005: 52 |
| Inoue 2004: 31 |
| Sasa 1992: 43 |
| Sasa 1989: 65 |
1 (by plazi, 2016-04-05 14:57:10)
2 (by ImsDioSync, 2016-11-28 07:37:58)
3 (by ImsDioSync, 2016-11-28 08:01:00)
4 (by ImsDioSync, 2017-06-21 09:18:07)
5 (by ImsDioSync, 2018-06-30 20:48:09)
6 (by ExternalLinkService, 2019-09-26 21:56:43)
7 (by ExternalLinkService, 2021-10-29 00:36:13)
8 (by ExternalLinkService, 2021-10-29 05:09:07)
9 (by plazi, 2023-10-25 09:33:00)