Ophiocomina nigra (Abildgaard in O. F. Muller, 1789)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.2005.00155.x |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5490146 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0D0A0B06-FFD8-FFE1-618D-863BFC05FE84 |
|
treatment provided by |
Diego |
|
scientific name |
Ophiocomina nigra |
| status |
|
(ABILDGAARD, IN O.F. MÜLLER, 1789)
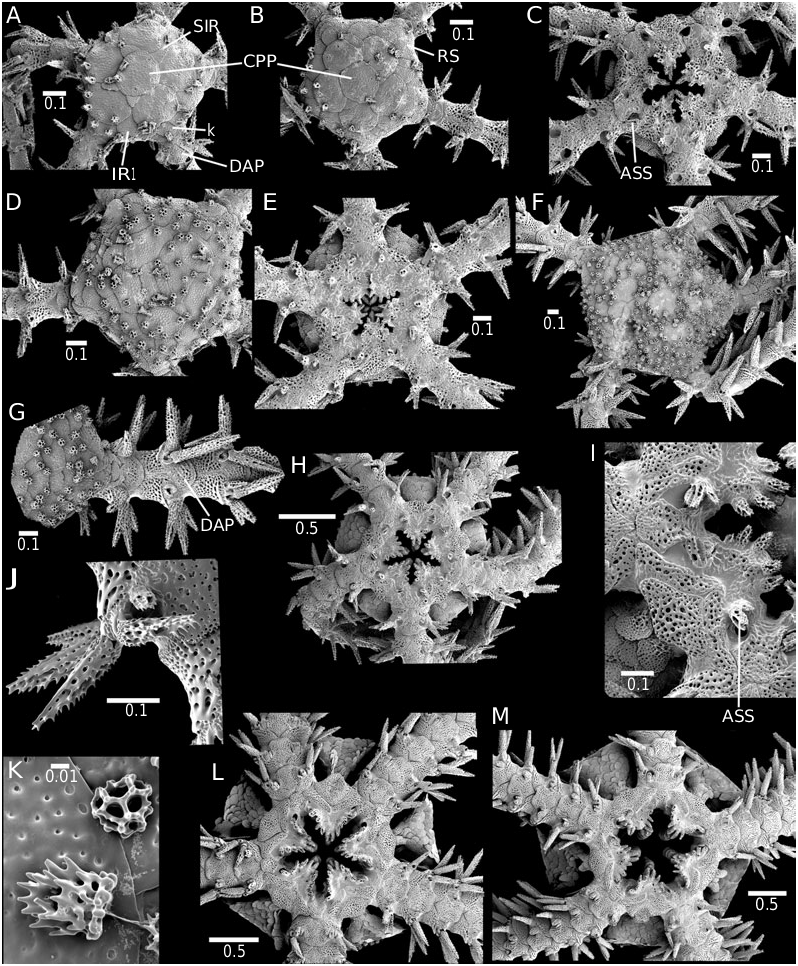
( FIG. 17A–M View Figure 17 )
All stages studied here had a dark brown, almost black colour, which makes them unique among the species found at the Swedish west coast and thus easily identifiable. The smallest specimens available measure 0.7 mm dd with seven arm segments. The dorsal disc is formed by the round CPP and five RPPs, triangular SIRs, IR1 and the round k-plate above the distal ends of the RSs ( Fig. 17A View Figure 17 ). All plates are almost imperforate, except for small holes on their margins particularly under a disc spine. The disc spines are conical and rugose. Each LAP bears three erect serrated spines. The DAP is triangular, slightly wider than long, with strongly convex distal edge, and adjacent plates separated by the LAPs. Another individual of 0.7 mm dd has fewer SIRs, and slightly larger IRs ( Fig. 17B View Figure 17 ). The MP are rugose and spiniform, one on the DP and another on the oral plate, both half as long as the spine-like tooth ( Fig. 17C View Figure 17 ). On some jaws a third lower papilla is present on the distal end of the oral plate. There is a strong, rugose ASS in the middle of the concave edge of the long distally flaring AS. The OS is teardrop-shaped, wrapped around the raised edge of the oral frame. Several round evenly perforated scales form the ventral disc. On the proximal arm segments, the TPo bears a single small rugose scale, which does not cover the pore. The VAPs are longer than wide, with convex distal edge, proximal angle and deeply concave lateral edges. The first VAP is similar to the others except for a convex proximal edge. Adjacent plates are separated by the LAPs.
At 0.9 mm dd, the number of disc scales has increased considerably. Most disc spines are shorter granules, but some are still conical spines, all of which are rugose ( Fig. 17D View Figure 17 ). The oral plates bear two MP, the distal one lower and wider than the proximal papilla ( Fig. 17E View Figure 17 ).
At 1.4 mm dd, the numerous dorsal disc scales are partially obscured by rugose granules ( Fig. 17F View Figure 17 ). There are now four strongly serrated arm spines, the dorsalmost being the longest, longer than an arm segment ( Fig. 17G View Figure 17 ). Of the RSs only the distal edge is visible beneath the disc scales. The MP on the DP have moved closer towards each other, forming an apical pair below the first tooth ( Fig. 17H View Figure 17 ). The TS is flat, oval and covers the pore. Bursal slits are visible above the arm. Numerous round overlapping scales form the ventral disc.
With increasing size, the number of disc granules ( Fig. 17K View Figure 17 ) increases until the dorsal disc is completely covered. At 1.6 mm dd, the ASS has moved to the oral plate and a small papilla has formed on the proximal side of the ASS ( Fig. 17I View Figure 17 ). The ASs are long, pairs forming a wide angle. The OS is twice as wide as long with slightly protruding distal edge. The first VAP is smaller than the others, hexagonal with straight edges. On the first ‘true’ arm segment a second smaller TS has formed. The arm spines are pointed with strongly serrated lateral edges ( Fig. 17J View Figure 17 ).
At 2.4 mm dd, the ASS and its adjacent papilla have been incorporated into the row of lateral MP, thus counting a total of five, with the apical pair close together, ventral to the first tooth ( Fig. 17L View Figure 17 ). The ventral disc is covered with round, imbricating scales with small round perforations, bearing no granules.
At 3 mm dd, additional apical MP can be seen below the apical pair ( Fig. 17M View Figure 17 ), an indication of the apical cluster of the adult, making this the smallest size at which keys for adults can be used. Each TPo bears a pair of one smaller and one larger, flat, oval scale. The VAP are contiguous, slightly overlapping on the proximal segments, with straight distal edge. The AS is long and narrow, almost horizontal to the jaw, bordering the proximal angle of the OS, without separating it from the first LAP. The OS is twice as wide as long, with a low protrusion in the middle of the distal edge.
Remarks: This shallow-water species can easily be identified in all growth stages by its dark brown to black colour, already present in small postlarvae, and its granulated dorsal disc. The genus Ophiocomina has been argued to belong within the Ophiacanthidae instead of the Ophiocomidae ( Wilkie, 1980) , but this has been refuted by Baker & Devaney (1981). The serrated spines and rugose disc granules and mouth papillae certainly bear closer similarities to Ophiacanthidae than to Ophiocomidae . However, small stages of Ophiocomidae were not available for comparison, leaving this question undecided. In addition, the Ophiacanthidae has been suggested to be paraphyletic ( Smith et al., 1995), which makes the systematic status of O. nigra even more difficult to understand. Until this question is resolved it is retained in the Ophiocomidae .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.