Indolipa gansuensis Feng
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.276421 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3509381 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FE87BA-D605-2418-FF1E-976A454FE0E0 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Indolipa gansuensis Feng |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Indolipa gansuensis Feng View in CoL , sp. nov.
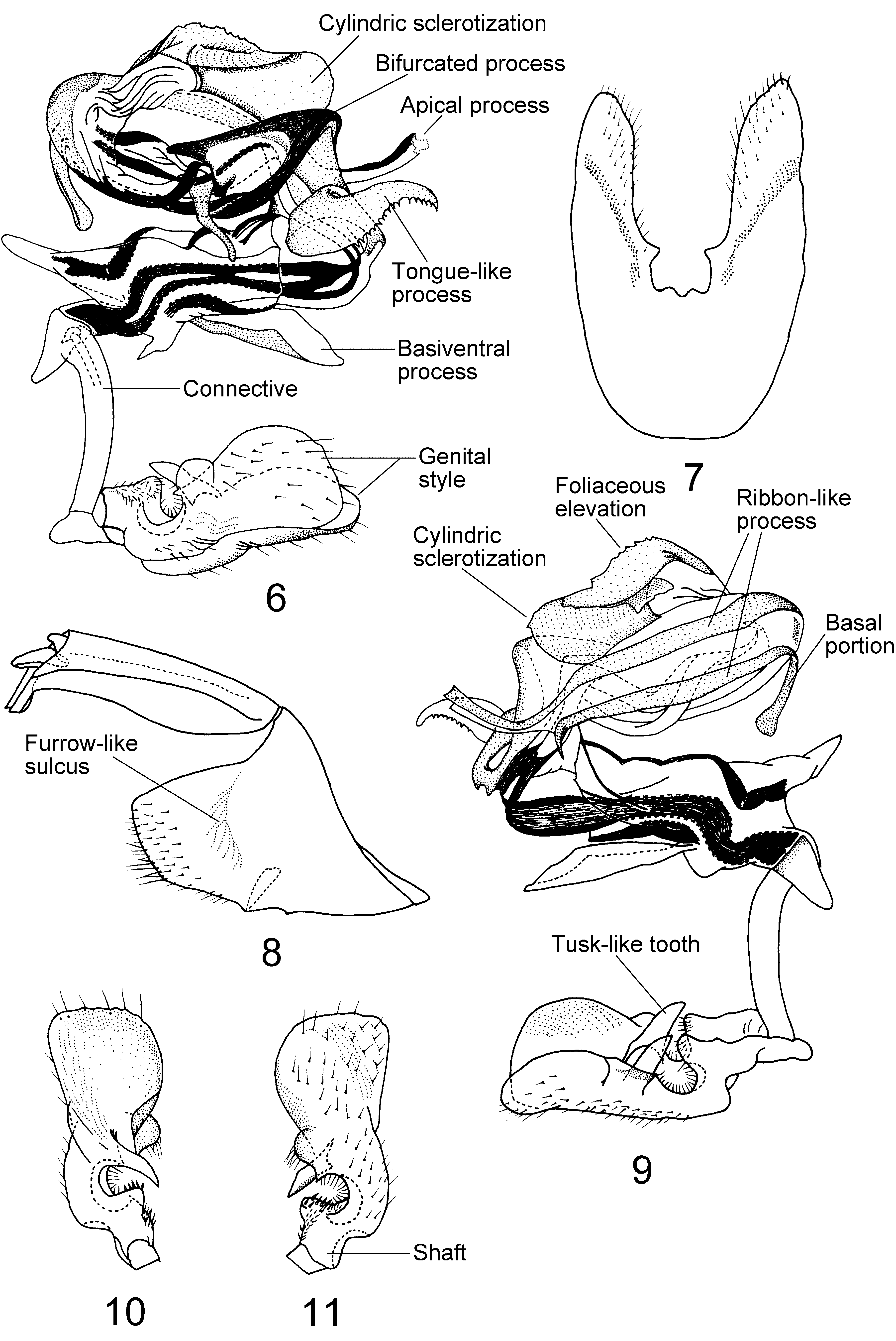
( Figs 1–11 View FIGURES 1 – 5 View FIGURES 6 – 11 )
Description. Body length: 3 5.8 mm.
Head. Head fuscous, carinae and borders concolorous. Frons with median longitudinal carina prominent, forked near apex; frons flat but postclypeus swollen. Vertex about 1.4 times as long as broad, with obtusely angled basal emargination; subapical transverse carina deeply U-shaped, connected with apical border by two small longitudinal carinae; median longitudinal carina absent. Rostrum reaching hind coxae.
Thorax. Pronotum black, carinae and borders testaceous; hind margin obtusely angled. Mesonotum moderately flattened, black, with concolorous carinae. Tegmina whitish-hyaline, 3.0 times as long as broad; veins yellowish with dark brown granules without setae; pterostigma yellow-brown, elongate triangular; RA unbranched, RP apically trifurcated, MA apically bifurcated, MP apically bifurcated, CuA bifurcated; Sc+R forked at same level as fork CuA1+CuA2, r-m crossvein distinctly basad of fork MA+MP; apex with ten cells ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 5 ). Claval veins Pcu and A1 united at centre of clavus ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 5 ). Hind wing with MP and CuA1 complete terminal fusion ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 5 ). Legs with femora brown, tibiae and tarsi yellowish; hind tibia with six apical teeth and three lateral spines. Chaetotaxy of hind tarsomere 7/5.
Male genitalia. Anal segment in dorsal view longer than wide, asymmetrical, right lateral margin more swollen than left lateral margin, apical lobe with ventral margin moderately excavated in middle, and with two convex projections laterally ( Figs 3–5 View FIGURES 1 – 5 , 8 View FIGURES 6 – 11 ). Pygofer with two small lateral protuberances; without ventromedian process ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 6 – 11 ); lateral lobes of pygofer subtriangular, asymmetrical, with several setae along apical margin; outer borders of pygofer with semicircular, furrow-like sulcus near middle ( Figs 4 View FIGURES 1 – 5 , 8 View FIGURES 6 – 11 ). Genital styles greatly dilated apically, thumb-shaped in lateral view; caudal border subtruncate; margin and outer surface setose; shaft short; a deep excavation present between shaft and dilated apex; excavation large, its proximal margin smoothly rounded and bearing short, stout setae, its apical margin (i. e. basal laterodorsal angle of dilated apex (Emeljanov 2001)) with a tusk-like tooth ( Figs 6, 9–11 View FIGURES 6 – 11 ). Aedeagus wound helix-like. Flagellum convoluted with two sinuations, a right lateral one ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 6 – 11 ) and a left lateral one ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 6 – 11 ). Right lateral sinuation of flagellum with dorsal margin sclerotized, foliaceously elevated and terete or cylindric at base ( Figs 6, 9 View FIGURES 6 – 11 ). Aedeagus in total with 6 sclerotized processes. Flagellum with two long subparallel ribbonlike processes on right lateral sinuation, upper one long (broken off apically in the holotype), with apical portion (apical process) curving left-caudodorsally, lower one comparatively short, with apex acute, curving right-laterally, and with basal portion curving left-caudally, slightly dilated and round apically; a somewhat undulate process arising from midway of left lateral sinuation of flagellum; midway of dorsal side of left lateral sinuation of flagellum with a stout, bifurcated process, the upper ramus of bifurcation long and thin, the lower one short and stout. Apex of aedeagus with a big S-shaped process, tongue-like apically, two-thirds of ventral margin of process serrate ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 6 – 11 ). Basiventral process of periandrium scoop-like, directed caudad ( Figs 6, 9 View FIGURES 6 – 11 ).
Female genitalia. Unknown.
Material examined. Holotype 3, CHINA: Gansu Province, Kangxian County, Jincaifeng, 30-VII-1980 (Chun-Hua Yang) ( NWAFU).
Etymology. Named after Gansu, the type locality.
Distribution. China (Gansu).
Remarks. Indolipa gansuensis is similar to I. kurseongensis and I. tappanus in external appearance and male genitalic configuration — the helix-shaped aedeagus; the apex of the aedeagus with a large S-shaped, apically tongue-like process; the uniform shape of the genital styles and the anal segment; and the pygofer without a ventromedian process. I. gansuensis differs from both by the following characters: 1) the processes of right lateral sinuation of the flagellum ( I. gansuensis has two long subparallel ribbon-like processes, I. kurseongensis and I. tappanus have one produced rod-like process); 2) the processes of left lateral sinuation of the flagellum ( I. gansuensis has a somewhat undulate process arising from midway, I. kurseongensis has a Yshaped process arising from the basidorsal area, I. tappanus has no process); 3) the basiventral process of the periandrium (scoop-like in I. gansuensis , spoon-like in I. kurseongensis , but more acute in I. tappanus ); 4) the processes in the basiventral area of the right lateral sinuation of the flagellum ( I. gansuensis without process, I. kurseongensis giving rise to a sclerotized, basally sheet-like process which is divided into three processes and I. tappanus with two spine-like processes).
This new species here represents the first record of the genus Indolipa for the Palaearctic Region (China’s Gansu Province).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.