Microtendipes angustus, Qi, Xin & Wang, Xinhua, 2006
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.171499 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6259455 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FD2A51-FFBD-1838-B808-2E2BFD63FCCF |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Microtendipes angustus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Microtendipes angustus View in CoL sp. n.
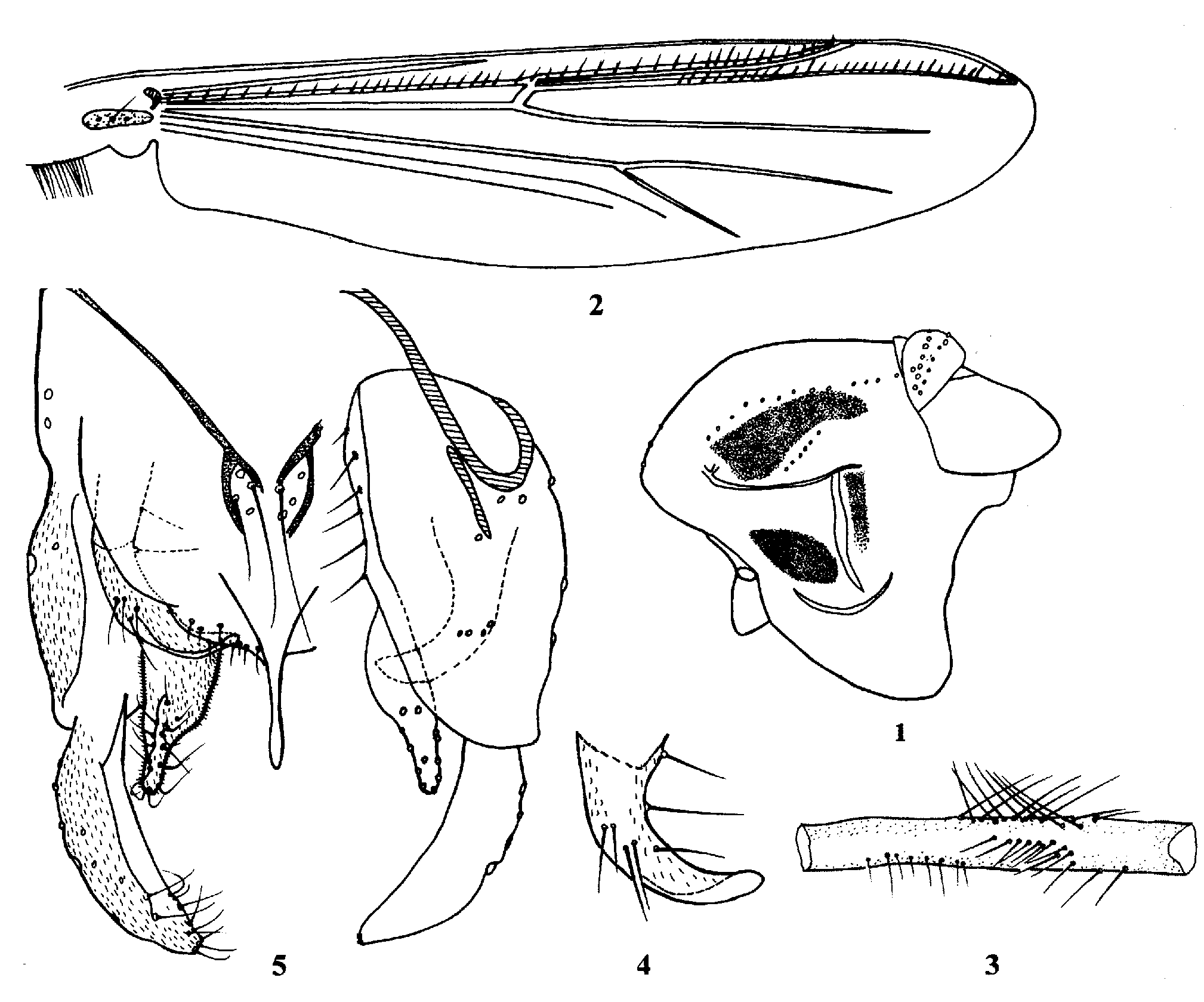
( Figs. 1–5 View FIGURES 1 – 5 )
Type material. Holotype male, CHINA: Fujian Province, Wuyishan City, Qili Qiao, 28.IV.1993, light trap, X. Wang (BDN No.02533). Paratype: 1 male, Guizhou Province, Jiangkou County, 27.V.2002, B. Ji (BDN No.1500).
Diagnostic characters. The new species is similar to M. chloris , but can be separated by the shape of the inferior volsella and the color of the legs. In M. angustus sp. n., the inferior volsella is narrowed apically, but not in M. chloris . The front tibia of M. angustus sp. n. is brown in the apical and basal 1/10 and the remaining legs are greenish yellow. In M. chloris , the front femur is yellowish brown with a narrow apical dark ring, the front tibia and front tarsus I are black, tarsi II and III are brown with basal and apical dark rings, front tarsi IV and V are dark brown, the mid and hind femora are brown with an apical dark ring and the tibia have both basal and apical rings, tarsus I is yellow, and tarsi II to V are brown to dark brown.
Etymology. The species name is from Latin, angustus , meaning narrow, referring to the shape of the inferior volsella, which is narrow in the apical half.
Male imago (n = 2)
Total length 5.25–5.30 mm. Wing length 3.25–3.38 mm. Total length/wing length 1.56–1.63. Wing length/length of profemur 2.24–2.41.
Coloration. Head yellow. Thorax ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 5 ) brownish yellow, scutellum, anterior anepisternum II and epimeron II brown. Abdominal tergites I–IV green, tergites V–X and hypopygium brown. Front tibia brown in apical and basal 1/10, remaining legs greenish yellow.
Head. AR 1.81–2.17. Temporal setae 17–18, including 5–7 inner verticals, 6–10 outer verticals, and 3–4 postorbitals. Clypeus with 35–38 setae. Tentorium 180–190 m long, 50–80 m wide. Palpomere lengths (in m): 60–70, 60–65, 300–325, 340–390, 400–490. L: 5th/3rd 1.33–1.51.
Wing ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 5 ). VR 1.07–1.16. R with 23–25, R1 with 20–21, R4+5 with 27–34 setae. Squama with 10–24 setae.
Thorax. Dorsocentrals 13–20, acrostichals 3–4, prealars 5–6. Scutellum with 26–27 setae.
Legs. Distal half of front femur with 24 proximally directed setae in 2 rows ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 5 ), 225–250 m long. Spur on middle tibia 48–50 m long including 43–50 m long comb, unspurred comb 50 m long, spur on posterior tibia 30–55 m long including 50 m long comb, unspurred comb 45–50 m long. Width at apex of front tibia 70–80 m, of middle tibia 70–75 m, of hind tibia 80– 85 m. Lengths (in m) and proportions of legs: Hypopygium ( Figs. 4–5 View FIGURES 1 – 5 ). Anal point 85–88 m long, apically slightly swollen and rounded. Tergite IX with 8 setae medially and 17 setae along posterior margin. Phallapodeme 30–50 m long; transverse sternapodeme 35–88 m long. Gonocoxite 225 m long. Superior volsella ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1 – 5 ) 100–163 m long, sickle shaped, and apically rounded, with 4 dorsal setae, 2 basal seta. Inferior volsella abruptly narrowed in apical 1/2, 128– 133 m long, with 25 setae. Gonostylus 150–160 m long, with 11 setae along inner margin in distal 1/3. HR 1.41–1.50, HV 3.31–3.50.
Distribution. The species was collected in subtropical mountain areas in Fujian and Guizhou Provinces in Oriental China.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |