Phaesticus Uvarov, 1940
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4965.3.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:145FAB27-536E-4E7E-A435-79816D728E32 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4754550 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FC8783-A521-FFDB-FF3C-C07FFA57FDF2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Phaesticus Uvarov, 1940 |
| status |
|
Genus Phaesticus Uvarov, 1940 View in CoL
( Phaestus Bolívar, 1887 View in CoL ; Lamprauges Blackith, 1992 View in CoL )
= Flatocerus Liang & Zheng, 1984 View in CoL syn. nov.
Type species: Phaesticus mellerborgi ( Stål, 1855) View in CoL
Redescription of generic characteristics
General appearance. Body size small, surface smooth and without humps or wrinkles. Head. Vertex and occiput clearly separated by a ridge (posterior margin of fossulae); vertex extremely shortened, sloping forwards, only restricted between anterior and posterior margins of fossulae; anterior margin narrowest, only reaching the middle of the inner margins of eyes in dorsal view; medial carina and frontal costa not quite developed ( P. mellerborgi and P. moniliantennatus ) or indistinct ( P. hainanensis comb. nov.), lateral carinae indistinct, medial carina extending to occiput; in lateral view, face obtusely angled forwards, facial carinae between antennal grooves strongly arcuate to obtusely angled, vertex and the upper part of face (above antennal sockets) nearly at the same slope ( P. hainanensis comb. nov.) or form a broadly obtuse angle ( P. mellerborgi and P. moniliantennatus ); longitudinal furrow deep, equal to or narrower than the diameter of an antennal scapus. Antennae inserted slightly below the lower margin of eyes (upper margin of antennal sockets and lower margin of eyes nearly at the same level), 13-segmented (or 14- segmented, because the 3 rd segment is usually separated into two short segments), the 11 th and parts of its adjacent segments generally milky white to yellow; subapical segments (generally from 7 th (8 th) to 10 th) considerably broadened and flattened, ovate ( P. mellerborgi ) or long elliptical ( P. moniliantennatus and P. hainanensis comb. nov.). Eyes approximately as high as the top of vertex and not higher than the anterior margin of pronotum, in frontal view with nearly straight inner margins which are slightly contracted upwards. Superior ocelli situated at lower 1/3–1/4 of the inner margins of eyes. Pronotum. Anterior margin projected more or less forwards, broadly arcuate or obtusely angled in dorsal view; median carina distinct and entire, humeral angles broadly arcuate; posterior angel of lateral lobe extending obliquely, downwards and backwards, apex truncated; ventral sinus and tegminal sinus present. Wings. Fore and hind wings normal ( Zha et al., 2016, 2020); hind wings elongated or shortened within the same species, varying with the length of hind pronotal process (detailed in discussion). Legs. Dorsal and ventral margins of fore and mid femora straight or nearly straight; the first segment of hind tarsus approximately as long as the third, apices of three pulvilli obtuse.
Justification of taxonomic placement
Phaesticus can easily be separated from other genera of the family Tetrigidae by the following characteristics: obtusely angled face in lateral view, extremely short vertex sloping forwards, indistinct lateral carinae of vertex, 13-segmented (not considering the separation of the 3 rd segment) antennae with considerably broadened subapical segments, smooth body surface without humps or wrinkles, developed fore and hind wings, directing downwards lateral pronotal lobes with truncated apices, and the first segment of hind tarsus approximately as long as the third. These typical characteristics are somewhat more similar to Metrodorinae and Tetriginae than to the other five subfamilies in Tetrigidae . Skejo (2017) commented its taxonomic placement in detail and speculated that it might belong to Metrodorinae or Tetriginae . We think it might be an independent branch close to Metrodorinae and Tetriginae . Future molecular phylogenetic evidences are needed to confirm its taxonomic placement.
Key to the species of the genus Phaesticus Uvarov, 1940
Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1
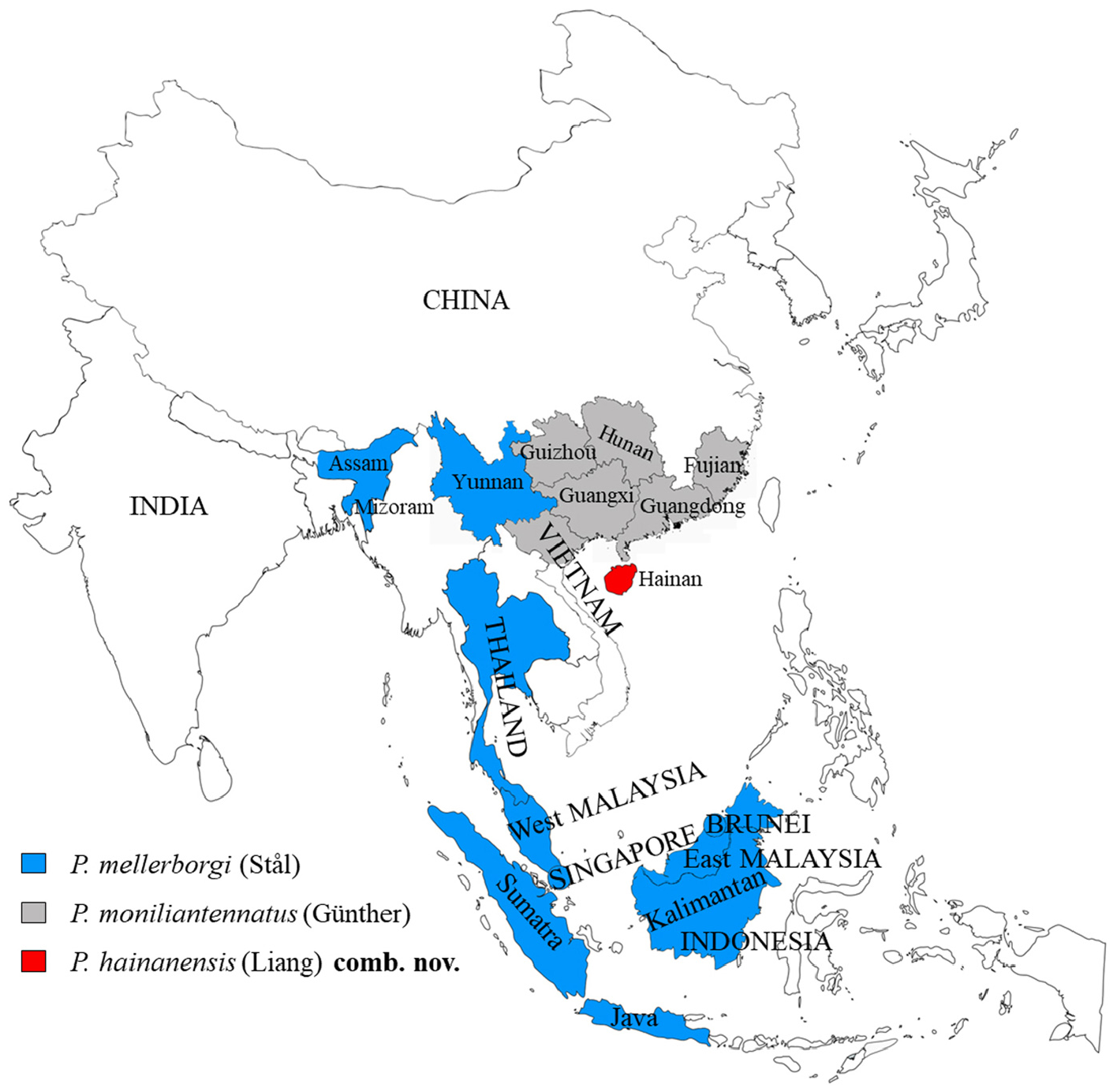
1. Subapical antennal segments from eighth to tenth strongly broadened, ovate, and the widest segment about 1.7–2.4 times as long as it is wide. Distributed in Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Singapore, West Malaysia, Thailand, India ( Assam, Mizoram), PR China ( Yunnan)................................................................. P. mellerborgi ( Stål, 1855) View in CoL
-. Subapical antennal segments from seventh to tenth moderately broadened, long elliptical, and the widest segment is about 3.6–4 times as long as wide.................................................................................. 2
2. Vertex wide, 1.5 times as wide as one eye; pronotum roof-like in front of the shoulders while slightly roof-like behind the shoulders, anterior margin broadly arcuate from dorsal view. Distributed in PR China ( Hainan)........................................................................................... P. hainanensis ( Liang, 1988) View in CoL comb. nov.
-. Vertex narrow, 0.9–1.3 times as wide as one eye; pronotum lamellate, anterior margin obtusely angled from dorsal view. Distributed in northern Vietnam, PR China ( Guangxi, Guangdong, Guizhou, Fujian, Hunan).................................................................................................... P. moniliantennatus ( Günther, 1940) View in CoL
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Phaesticus Uvarov, 1940
| Zha, Ling-Sheng, Skejo, Josip, Mao, Ben-Yong & Ding, Jian-Hua 2021 |
Lamprauges
| Blackith 1992 |
Flatocerus
| Liang & Zheng 1984 |
Phaestus Bolívar, 1887
| Bolivar. Considering 1887 |