Mymarothecioides germanoi Soares and Domingues, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4700.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C10998AB-822A-4B17-8FE1-596DC44C7D6A |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A1E9AC7A-02A8-4699-91D0-57F9D24A0EE4 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:A1E9AC7A-02A8-4699-91D0-57F9D24A0EE4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Mymarothecioides germanoi Soares and Domingues |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Mymarothecioides germanoi Soares and Domingues n. sp.
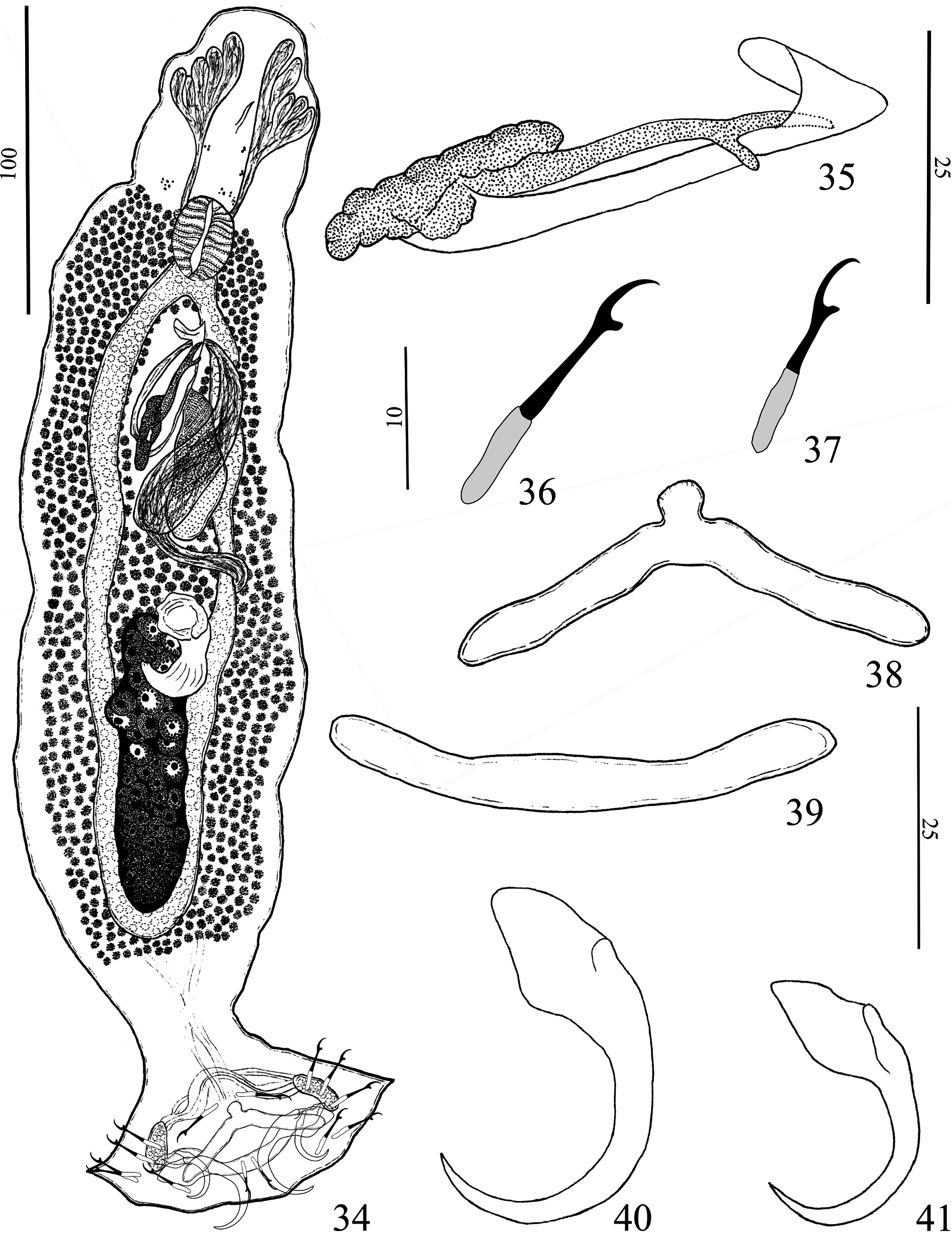
( Figs. 34–41 View FIGURES 34–41 ; 45 View FIGURES 42–45 )
Type host: Hydrolycus armatus (Jardine & Schomburgk) . Site: Gills. Type locality: Volta Grande-Xingu River , municipality of Altamira, Pará State, Brazil (03°21’15,7’’S; 52°11’47,5’’W), collected on June 13, 2015. Prevalence: 100% of three hosts examined. Mean intensity: 1.3 parasites per infected host. Specimens deposited: Holotype MPEG nº 199; 3 paratypes, MPEG nº 200–202. Etymology: The specific name is an homage to the first author’s father (G.B. Soares), Mr. Germano Soares. Zoobank Life Science Identifier: ( LSID) for Mymarothecioides germanoi n. sp. is urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act: GoogleMaps
A1E9AC7A-02A8-4699-91D0-57F9D24A0EE4 Comparative measurements: see Table 3 View TABLE 3 .
Description (based on four specimens, one mounted in Hoyer, three mounted in Gomori’s trichrome): Body fusiform, total length excluding haptor 360 (280–450; n=3) long, total width at level of germarium 98 (97–100; n=3) ( Fig. 34 View FIGURES 34–41 ). Cephalic margin tapered; moderately developed terminal lobes; four to five bilateral pairs of head organs with rod-shaped secretion; cephalic glands unicellular, posterolateral to pharynx (observed only in paratypes). Accessory chromatic granules present in the cephalic area. Pharynx subspherical, 26 (24–32; n= 3) long, 19 (14–24; n=3) wide. Testis fusiform, 63 (47–79; n=3) long, 28 (25–32; n=2) wide (observed only in paratypes); prostatic reservoir saculiform, separated into two zones. MCO, 50 (50–51; n=3) long, with distal portion expanded, bent; base of MCO with broad sclerotized margin ( Fig. 35 View FIGURES 34–41 ; 45 View FIGURES 42–45 ). Accessory piece comprising straight rod, distal portion with subterminal flap with hook, thumb. Germarium fusiform, 73 (51–95; n=2) long, 17 (16–19; n=2) wide. Eggs, seminal receptacle, Mehlis’ glands, ootype not observed. Vaginal aperture midventral, opening at level of vitelline commissure; vaginal vestibule heavily muscular; vaginal canal sigmoid. Uterus delicate; seminal receptacle elongated, with dense musculature. Vitelline follicles dense. Peduncle broad; haptor subhexagonal, 74 (67–80; n=3) long, 98 (82–112; n=3) wide. Anchors similar. Ventral anchor, outer 36 (n=2) long, inner 40 (39–41; n= 2) long, base 16 (n=2); superficial root triangular; deep root poorly developed, rounded; evenly curved shaft and point; point extending just past level of tip of superficial root ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 34–41 ). Dorsal anchor, outer 34 (33–35; n=2) long, inner 32 (n= 2) long, base 12 (n=2); superficial root triangular with slightly depressed tip; deep root elongated; slightly curved shaft and point; point extending to level of tip of superficial root ( Fig. 41 View FIGURES 34–41 ). Ventral bar, 54 (49–62; n=3) long, 9 (6–11; n=3) wide, slightly curved to broadly inverted V-shaped rod with anteromedial projection, rounded ends ( Fig. 38 View FIGURES 34–41 ). Dorsal bar, 55 (54–57; n=3) long, 5 (5–4; n=3) wide, slightly curved rod with anteromedial projection, rounded ends ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES 34–41 ). Hooks similar in shape, with upright thumb, rounded, slightly curved shaft; short point; shank divided into two units, proximal unit compressed, distal unit inflated; filamentous hook loop not observed; hook pairs 1–4, 6–7, 23 (22– 26; n=7) long ( Fig. 36 View FIGURES 34–41 ); hook pair 5, 20 (15–16; n=6) long ( Fig. 37 View FIGURES 34–41 ).
Remarks: Mymarothecioides germanoi n. sp. is similar to M. xinguensis n. sp. based on the morphology of anchor/bar complexes. However, the new species is easily distinguished from M. xinguensis and other congeneric species by possessing a midventral vaginal pore.
TABLE 3. Comparative measurements (in μm) of sclerotized structures of specimens of Mymarothecioides xinguensis n. sp., Mymarothecioides altamirensis n. sp., Mymarothecioides ararai n. sp., and Mymarothecioides germanoi n. sp. from the gills of Hydrolycus armatus (Jardine & Schomburgk) from the Xingu River, Pará State, Brazil.
| Mymarothecioides | N | Mymarothecioides | N | Mymarothecioides | N | Mymarothecioides | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xinguensis n. sp. | altamirensis n. sp. | ararai n. sp. | germanoi n. sp. | |||||
| MCO length | 33 (30–36) | 5 | 27 (26–28) | 2 | 74 (70–77) | 3 | 50 (50–51) | 3 |
| Ventral Bar | ||||||||
| Length | 63 (55–71) | 6 | 72 (70–76) | 3 | 67 (47–87) | 2 | 54 (49–62) | 3 |
| Width | 12 (11–14) | 5 | 13 (11–16) | 2 | 25 (16–35) | 2 | 9 (6–11) | 3 |
| Dorsal Bar | ||||||||
| Length | 51 (44–61) | 5 | 49 (47–50) | 3 | 58 (41–74) | 2 | 55 (54–57) | 3 |
| Width | 6 (5–8) | 5 | 6 (5–6) | 3 | 12 (8–16) | 2 | 5 (5–6) | 3 |
| Ventral Anchor | ||||||||
| Outer | 43 (39–47) | 5 | 48 (47–49) | 3 | 69 (58–79) | 2 | 36 | 2 |
| Inner | 42 (36–47) | 5 | 56 (54–59) | 3 | 45 (43–47) | 2 | 40 (39–41) | 2 |
| Base | 24 (22–25) | 5 | 22 (22–24) | 3 | 55 (47–62) | 2 | 16 | 2 |
| Dorsal Anchor | ||||||||
| Outer | 32 (27–38) | 5 | 33 (28–38) | 2 | 61 (52–70) | 2 | 34 (33–35) | 2 |
| Inner | 34 (30–39) | 5 | 36 (33–39) | 2 | 43 (39–47) | 2 | 32 | 2 |
| Base | 16 (16–17) | 5 | 19 | 2 | 43 (36–49) | 2 | 12 | 2 |
| Hook | ||||||||
| Pair 1 | 25 (20–31) | 4 | 21 (20–25) | 8 | 34 (29–40) | 2 | 15 | 1 |
| Pair 2 | 25 (22–30) | 4 | 23 (22–25) | 6 | 30 (26–35) | 2 | 24 (22–26) | 3 |
| Pair 3 | 30 (30–31) | 2 | 24 (22–26) | 3 | 33 (29–38) | 2 | 23 (22–26) | 3 |
| Pair 4 | 27 (23–33) | 4 | 26 (26–27) | 4 | 33 (30–37) | 2 | 25 (24–26) | 2 |
| Pair 5 | 17 (15–20) | 4 | 20 | 2 | 33 | 1 | 20 (15–16) | 6 |
| Pair 6 | 23 | 1 | 25 (25–26) | 4 | 35 | 1 | 24 (22–26) | 2 |
| Pair 7 | 26 (22–33) | 5 | 28 (28–30) | 5 | 39 | 1 | 23 (22–25) | 2 |
| MPEG |
Museu Paraense Emilio Goeldi |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |