Technomyrmex Mayr, 1872
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.276993 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5689431 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F81D2F-900A-FFB8-FF0B-BD06C65267F8 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Technomyrmex Mayr, 1872 |
| status |
|
Technomyrmex Mayr, 1872 View in CoL
( Figs 5 View FIGURES 1 – 5 , 10 View FIGURES 6 – 10 , 15 View FIGURES 11 – 15 , 22 View FIGURES 16 – 23 , 28 View FIGURES 24 – 28 , 33 View FIGURES 29 – 33 , 38 View FIGURES 34 – 38 , 45 View FIGURES 41 – 45 , 48 View FIGURES 46 – 48 , 54 View FIGURES 52 – 54 , 61 View FIGURES 58 – 61 , 66 View FIGURES 62 – 66 , 71 View FIGURES 67 – 71 , 76 View FIGURES 72 – 76 , 81 View FIGURES 77 – 81 )
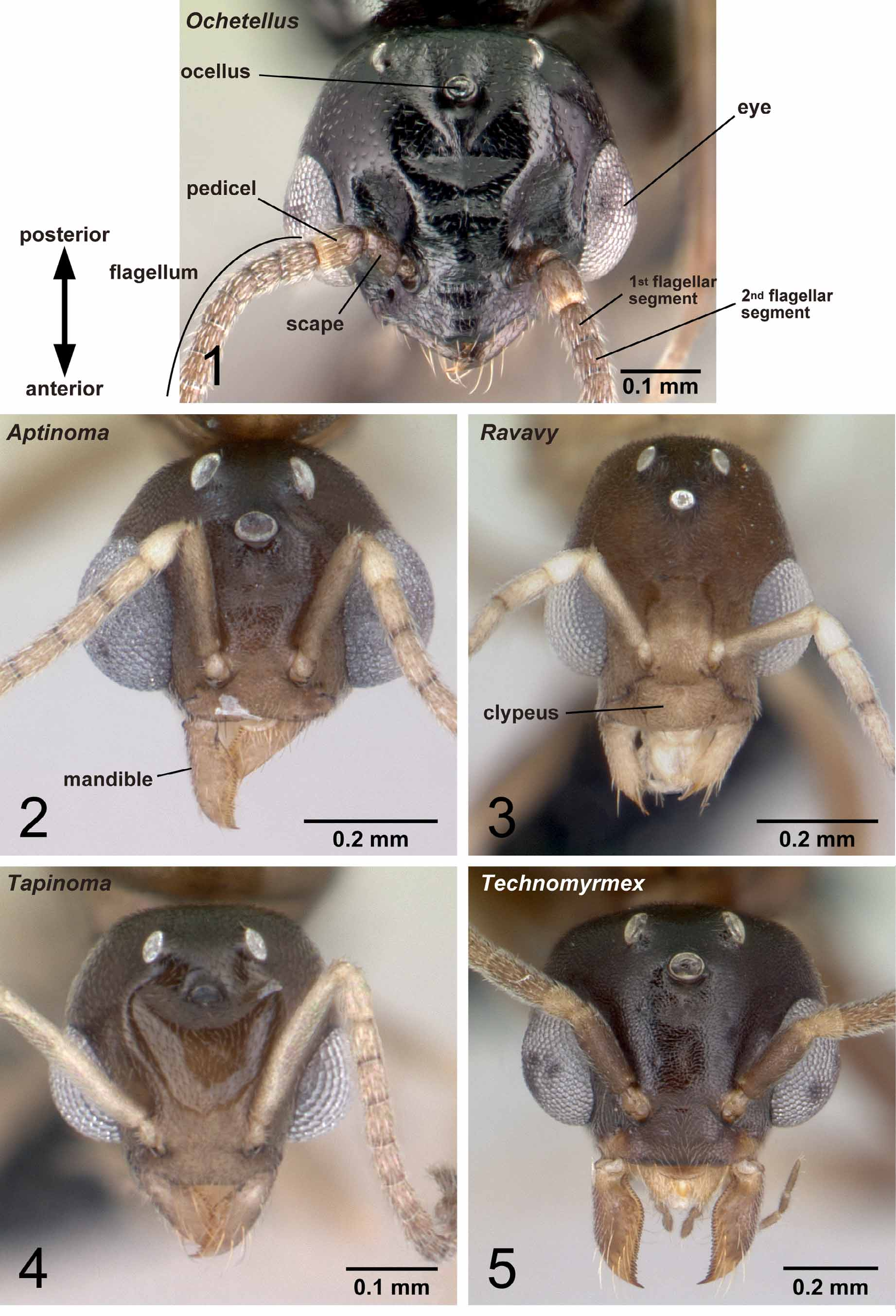
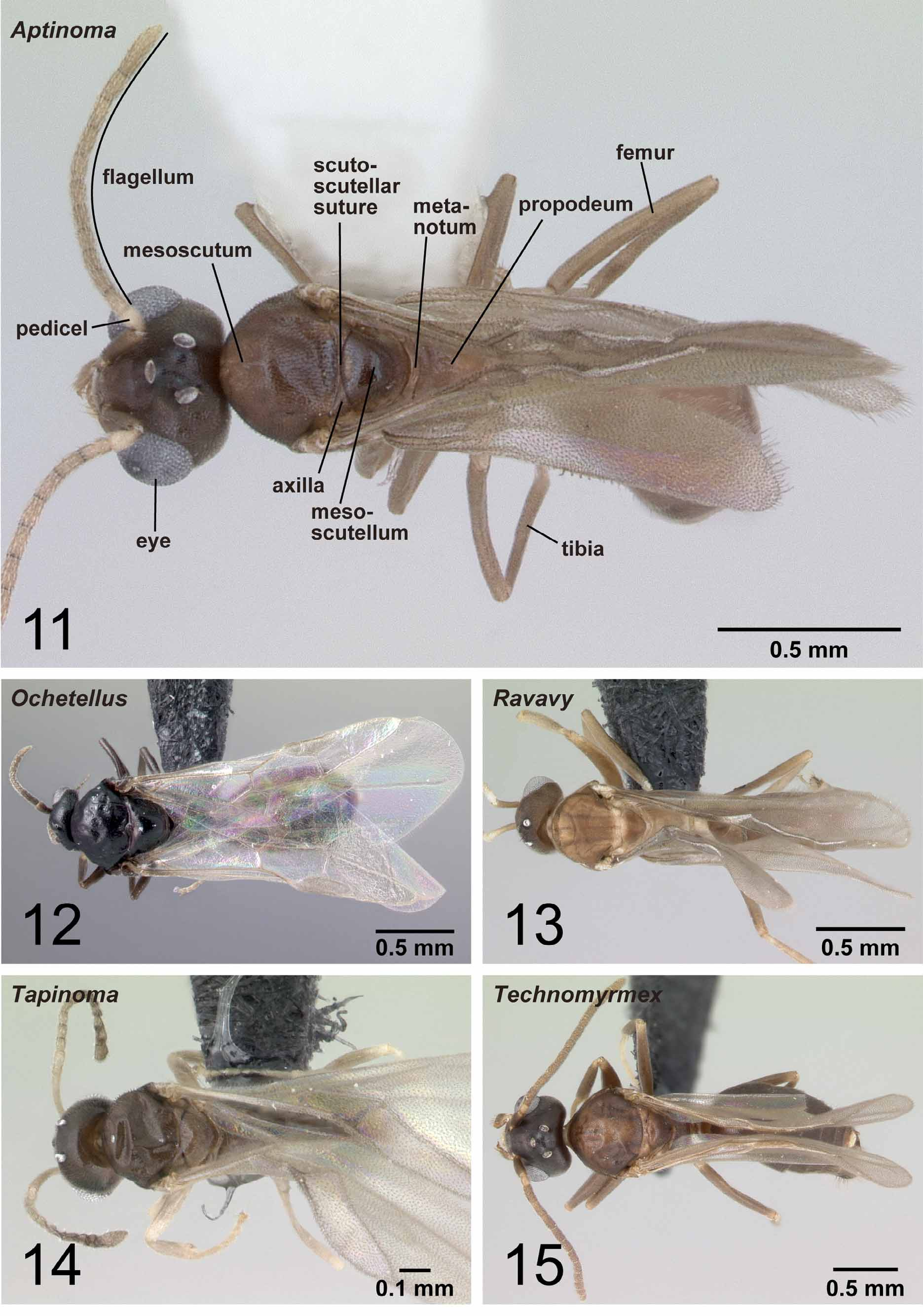
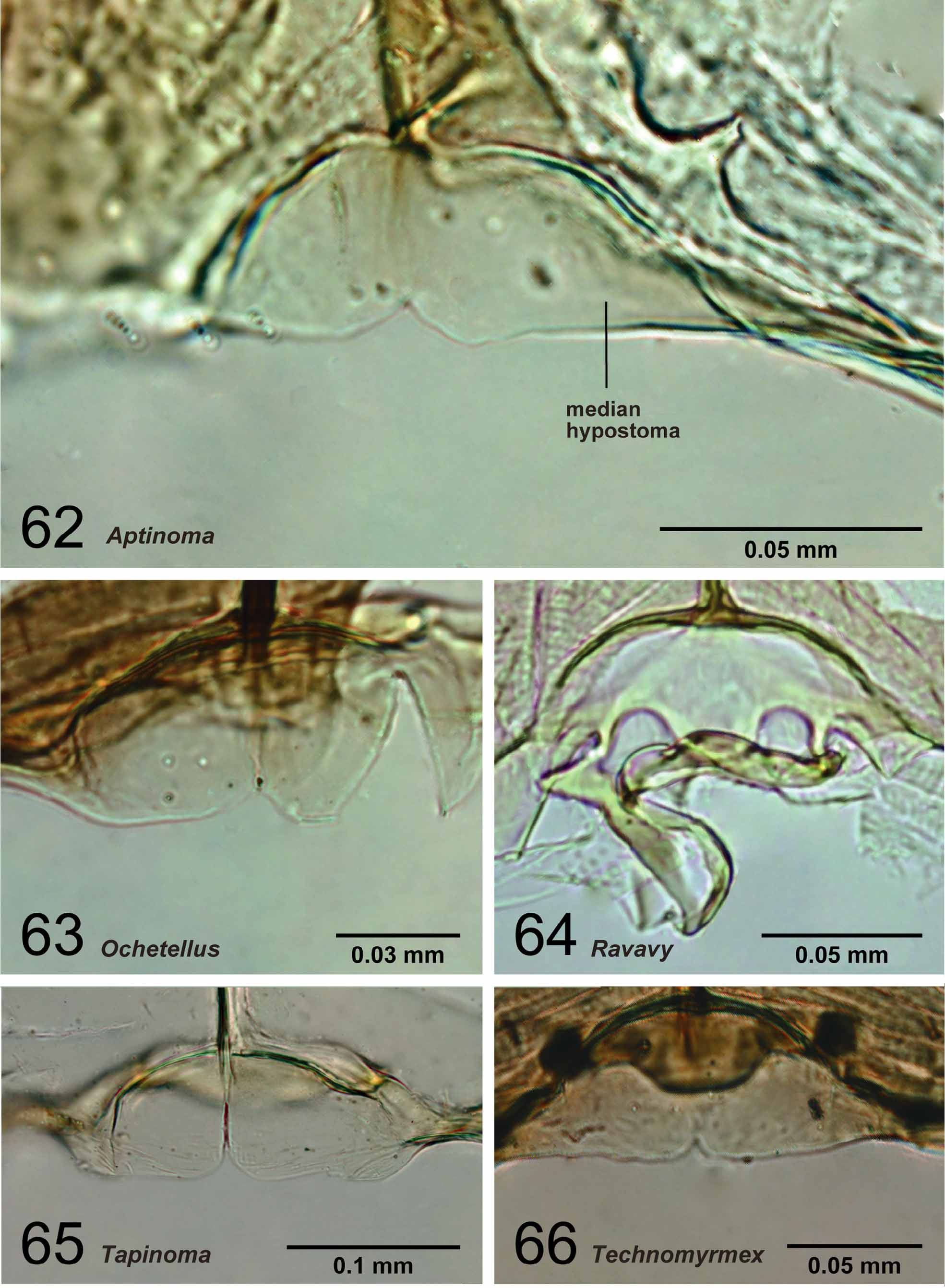
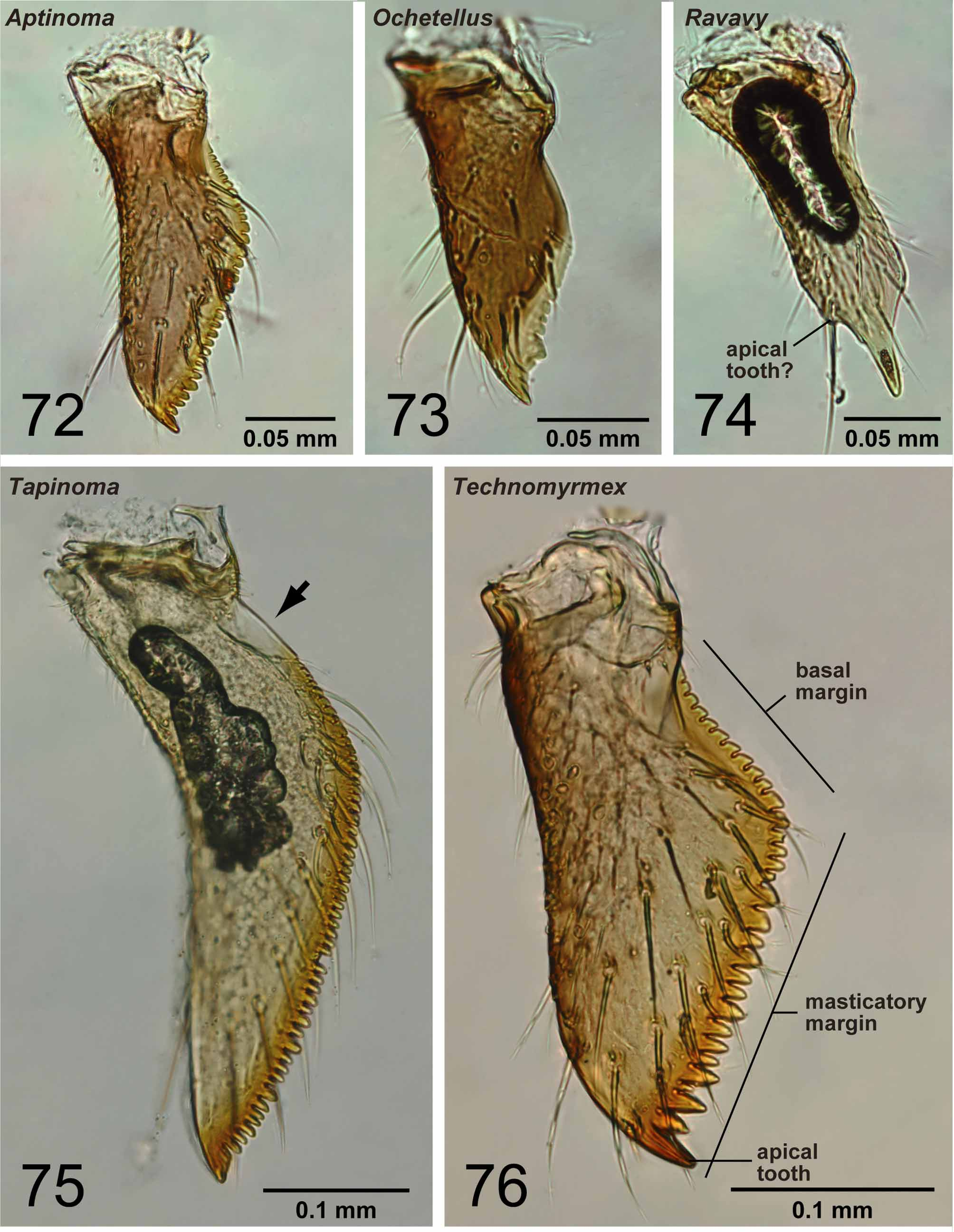
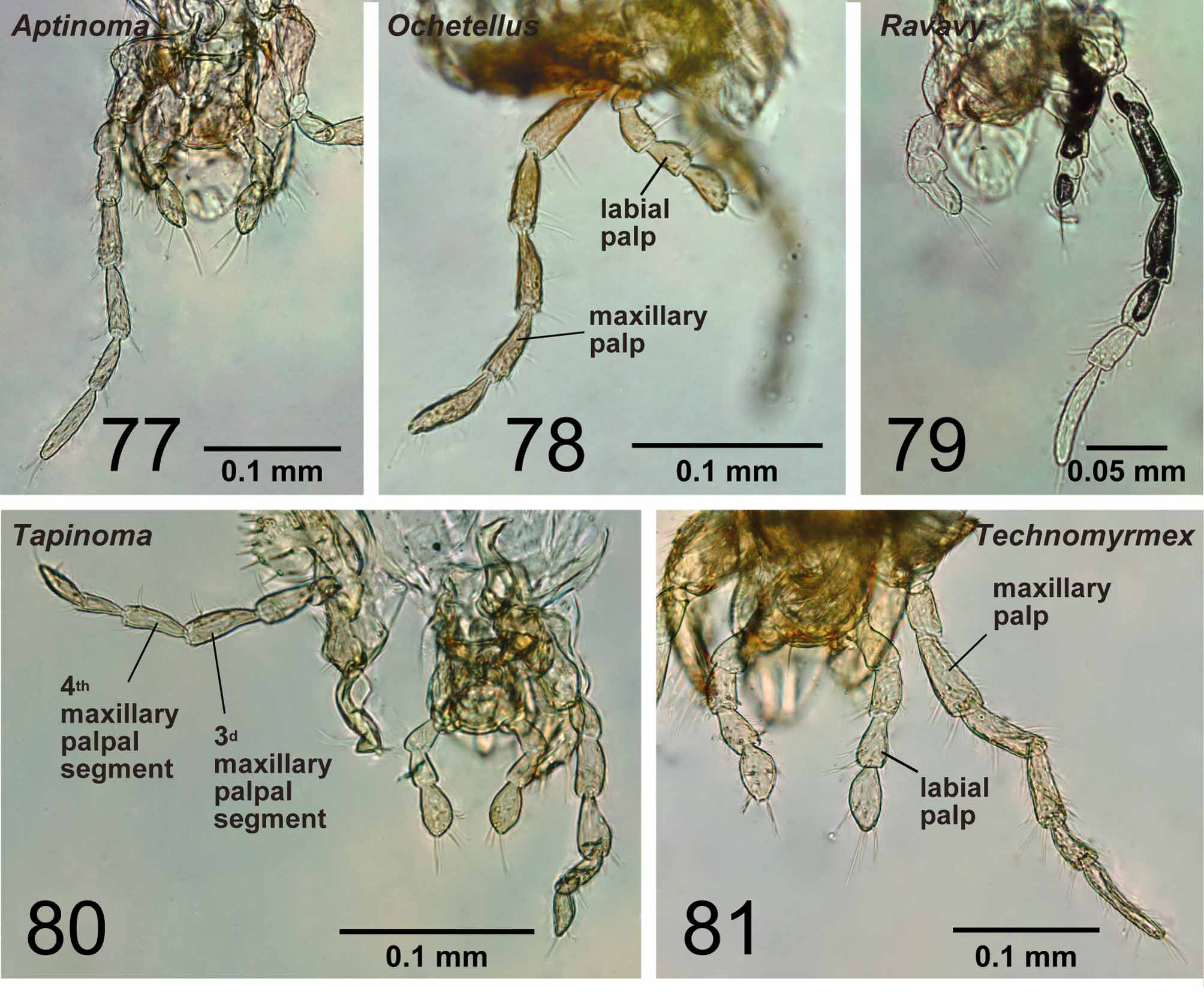
With characters of Dolichoderinae . Ergatoid males known, but all males in Malagasy region alate. Medial hypostoma present ( Fig. 66 View FIGURES 62 – 66 ). Mandible triangular, but its basal angle indistinct. Basal margin and masticatory margin of mandible wholly covered with serrate denticles ( Fig. 76 View FIGURES 72 – 76 ). Apical tooth on masticatory margin longer than subapical one. Palpal formula 6,4 (one specimen of each of eight species dissected: Fig. 81 View FIGURES 77 – 81 ). Third maxillary palpal segment shorter than or as long as fourth. Concavity on distal margin of labrum absent in most cases; when visible, it is much reduced in size and longest setae located distant from apices of lobes ( Fig. 71 View FIGURES 67 – 71 ). Scape excluding its basal condyle shorter than length of flagellar segments 1+2. Pedicel conical ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1 – 5 ). First and second flagellar segments straight. Axillae medially compressed, anterior and posterior margins not parallel. Petiolar node strongly inclined anteriorly, its anterior margin much shorter than posterior margin in lateral view, not much expanded laterally. Petiole narrowly attached to abdominal segment III. Anterior surface of abdominal segment III with indentation that fits posterior surface of petiolar node. Pygostyles present.
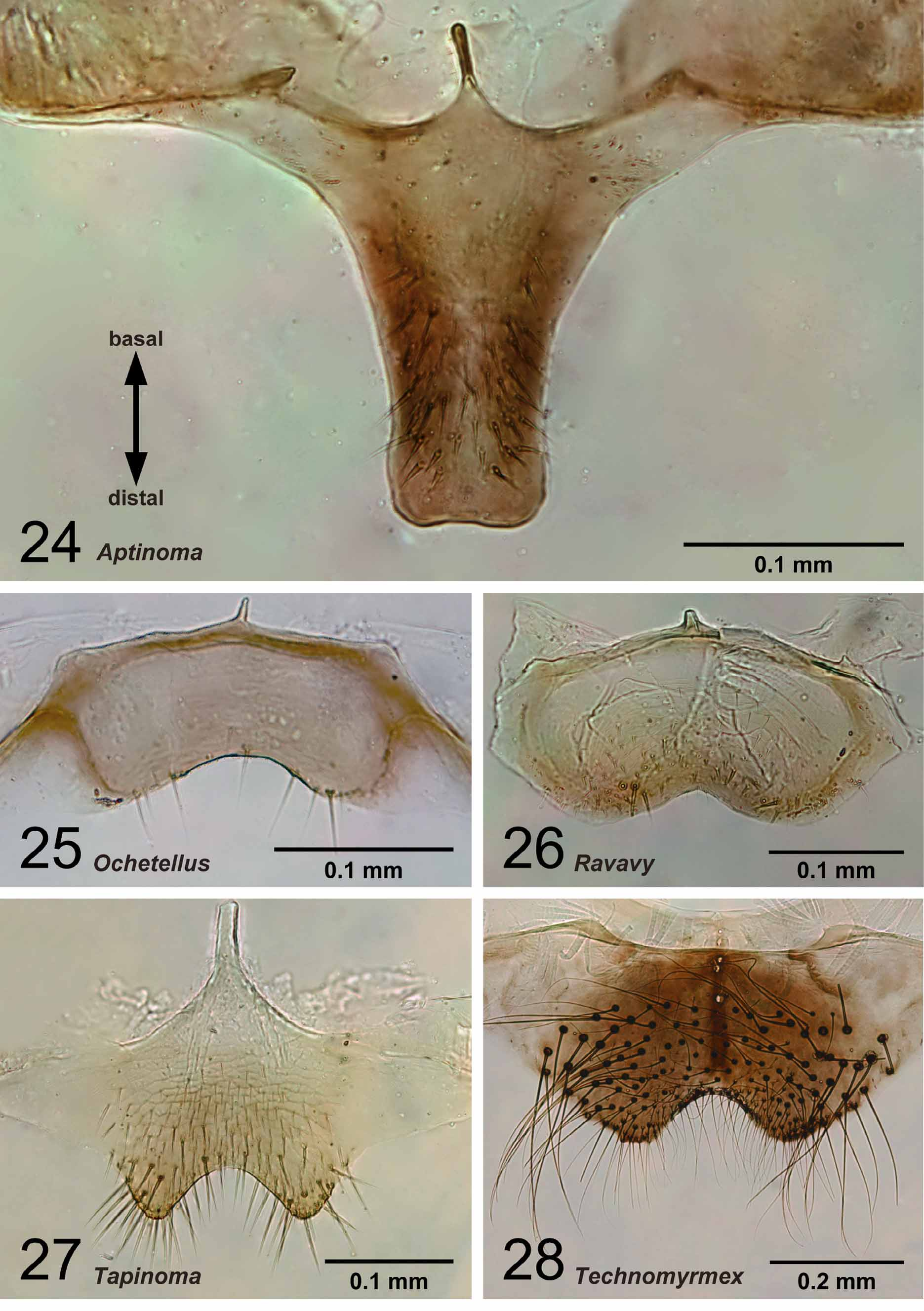
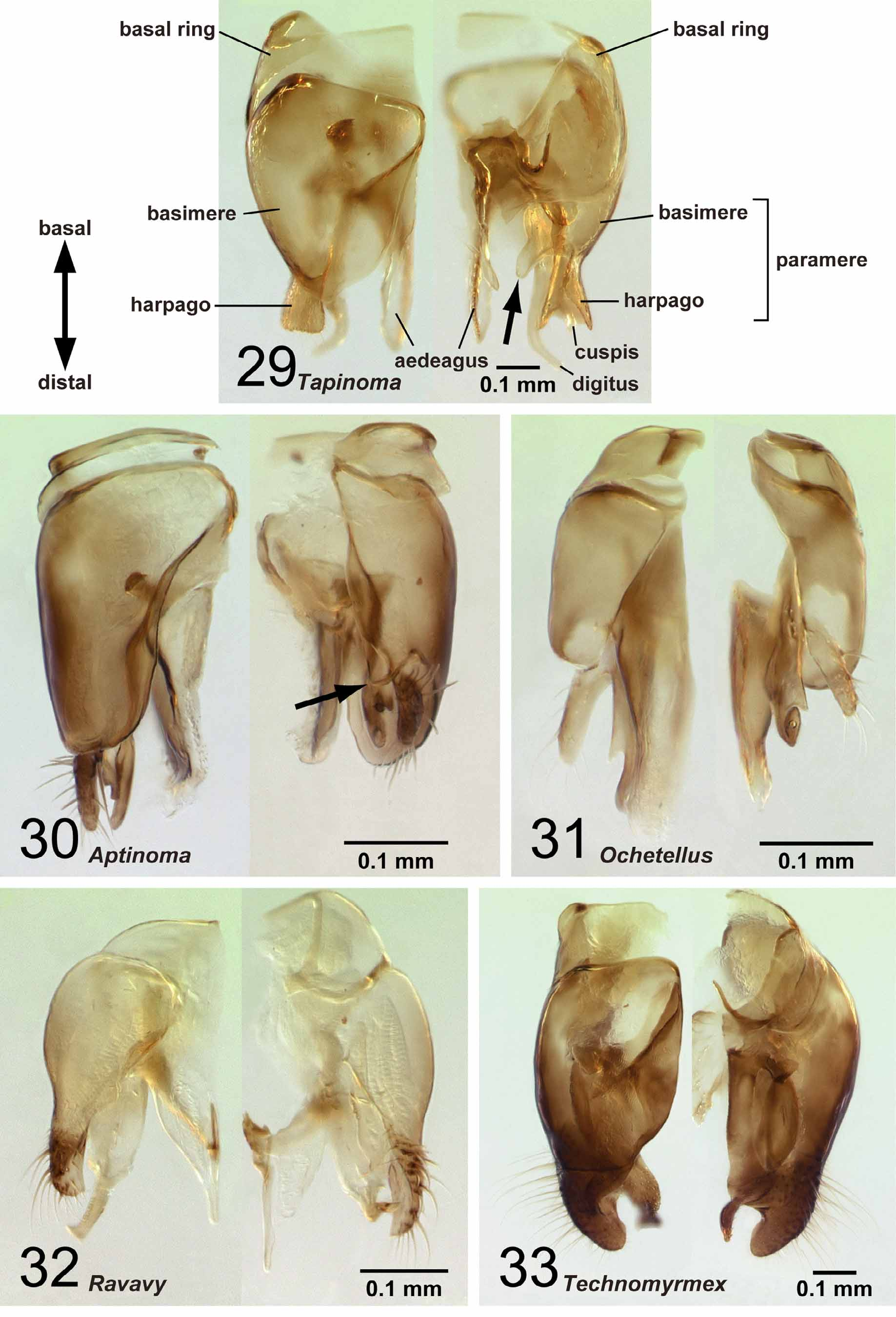
Distal portion of abdominal sternum IX bilobed, its distal margin widely concave ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 24 – 28 ). Apicoventral portion of basimere without projection. Harpago moderate in size, separated from basimere only by suture, without membranous region between them ( Figs 33 View FIGURES 29 – 33 , 38 View FIGURES 34 – 38 ), expanded mesally in ventral view, forming distinct and more or less flat ventral face ( Fig. 22 View FIGURES 16 – 23 ). Basal portion of aedeagus does not bear distinct ventral lobe ( Fig. 45 View FIGURES 41 – 45 ).
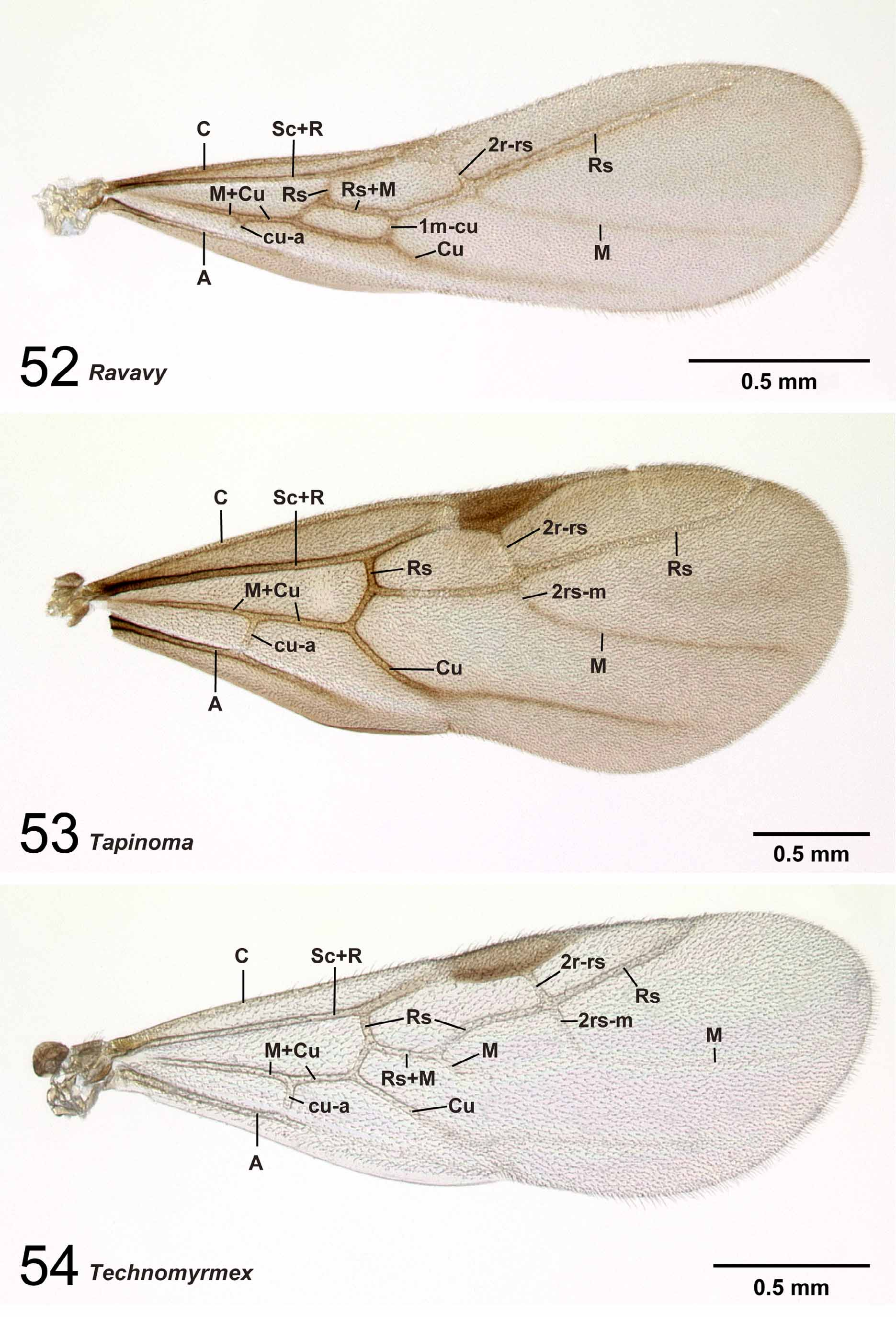
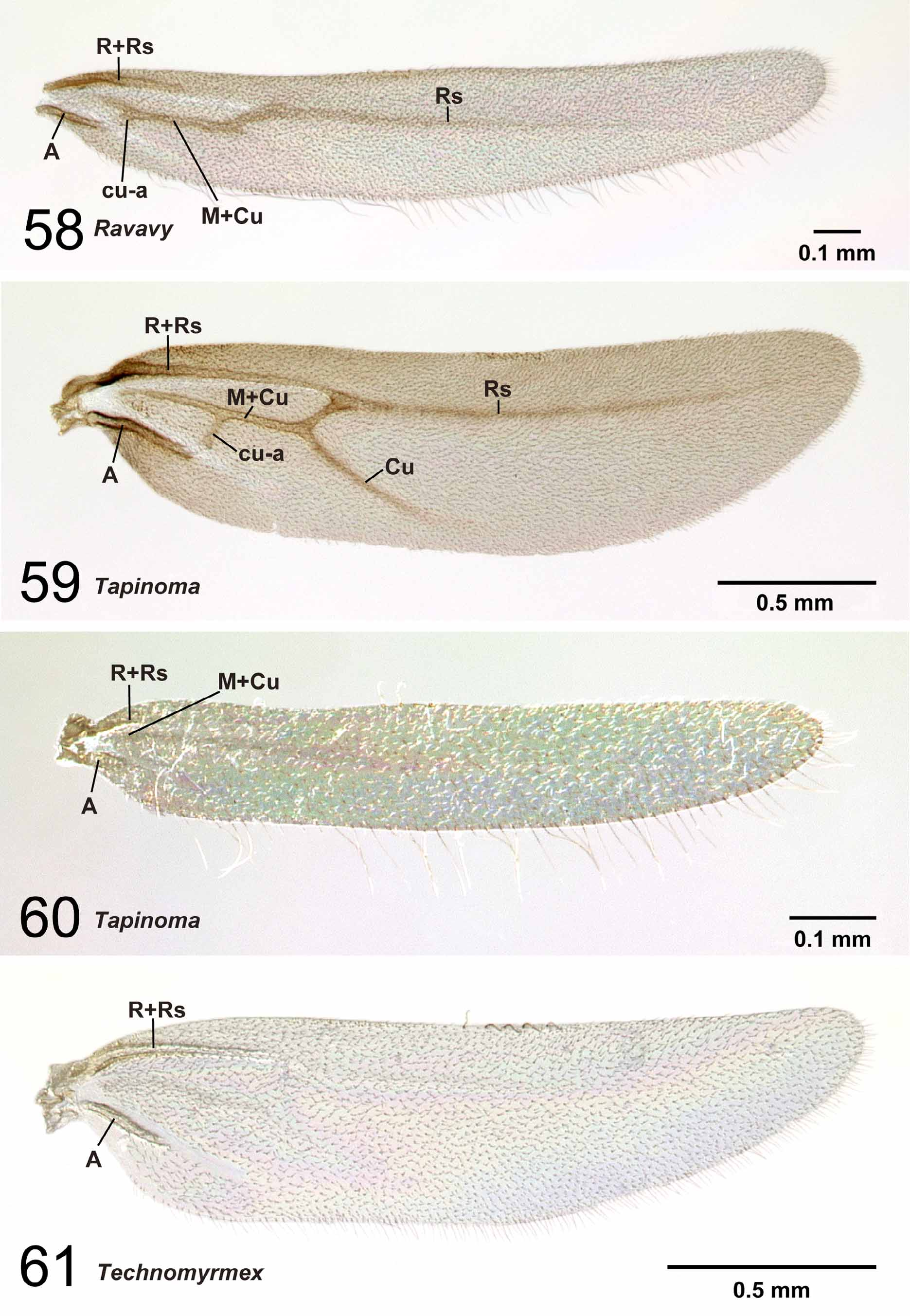
Forewing not extremely elongated apical to wing stigma, its radial sector reaches to costal margin ( Fig. 54 View FIGURES 52 – 54 ), media partially absent between Rs+M and 2rs-m, and 1m-cu absent in many cases. On hindwing, M+ Cu absent , M+1m-cu, free sections of radial sector and cubitus, and cu-a absent ( Fig. 61 View FIGURES 58 – 61 ).
Remarks. Males of nine species were examined. They are distinguished easily from those of the four other Malagasy dolichoderine genera by the ventral portion of the harpago, which is expanded mesally to form a ventral face ( Fig. 22 View FIGURES 16 – 23 ), and the absence of M+Cu on the hindwing ( Fig. 61 View FIGURES 58 – 61 ). Technomyrmex and Aptinoma uniquely share the following characters: the basal margin of the mandible is wholly covered with serrate denticles ( Fig. 76 View FIGURES 72 – 76 ) and the concavity on the distal margin of the labrum is reduced ( Fig. 71 View FIGURES 67 – 71 ). In Technomyrmex and Tapinoma the petiolar node is inclined. The central notch of the labrum is reduced in size or absent , although it is still visible in several males of Technomyrmex . When the notch is visible in Technomyrmex , the longest setae on the labrum are located distant from the apices of the lobes formed by the central notch, while in the other dolichoderine genera with bilobed labrum, the setae are mostly located on the apex of each lobe ( Figs 68–70 View FIGURES 67 – 71 ).
Several of the present results for Technomyrmex disagree with previous studies. A median notch or groove on the anterior margin of the median hypostoma is found in all males of Technomyrmex ( Fig. 66 View FIGURES 62 – 66 ), while the margin in Shattuck (1992a) is regarded as entire. The inner margin of the eye in full-face view is slightly concave in most species, while in Shattuck (1992a) the margin is regarded as flat. The anteromedial margin of the clypeus is not concave in several species ( T. difficilis , T. fisheri , and T. innocens ); the margin of Technomyrmex in Shattuck (1992a, 1995) and Brandão et al. (1999) is treated as broadly concave. The relative length of the first flagellomere compared with its width varies from less than two times to three times (see Table 4), while the length in Shattuck (1992a) is regarded as less than two times. Abdominal segment III does not always cover the petiole completely by overhanging it anteriorly in Technomyrmex (e.g. T. mayri ), although this segment in Technomyrmex in Shattuck (1992a, 1995) is regarded as overhanging the petiole so that the latter is invisible in dorsal view. The cuspis on the volsella is absent in one species ( T. madecassus : Fig. 48 View FIGURES 46 – 48 ), while regarded as present in Technomyrmex by Shattuck (1992a, 1995).
Additional discussion of characters is included in the remarks for Ochetellus .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Dolichoderinae |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Dolichoderinae |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Dolichoderinae |
|
Genus |