Crossodonthina tiantongshana Xiong et al., 2005
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2010.488751 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F687A1-FFC4-A505-8B1C-79869A0FFA22 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Crossodonthina tiantongshana Xiong et al., 2005 |
| status |
|
Crossodonthina tiantongshana Xiong et al., 2005 View in CoL
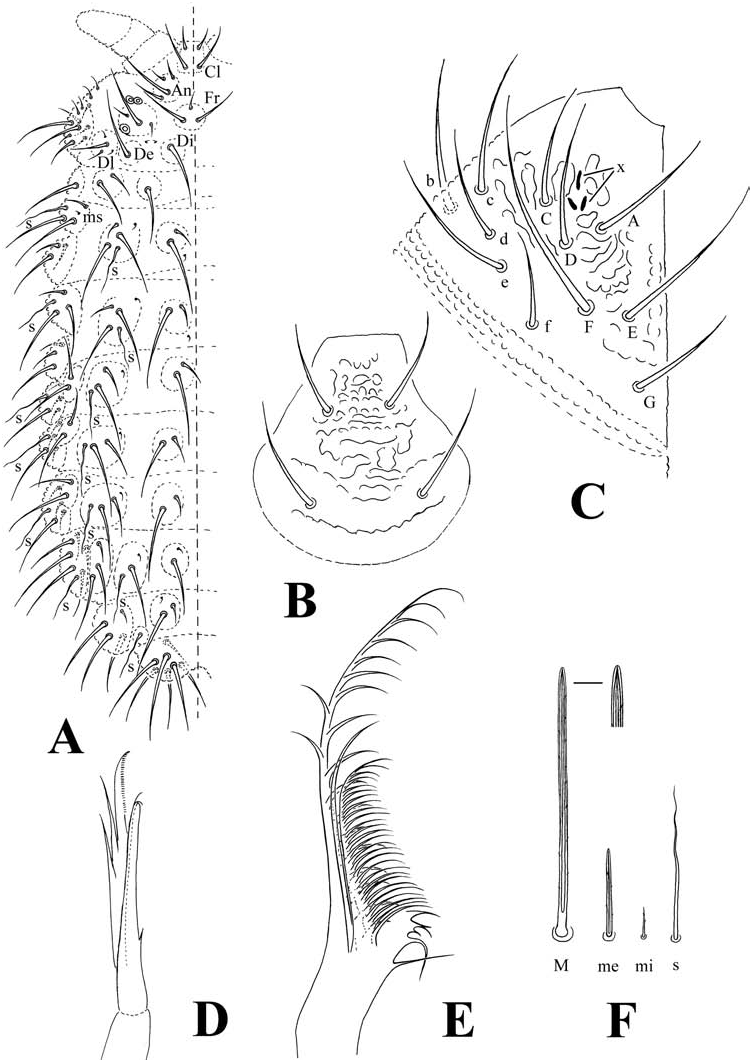
( Figure 2 View Figure 2 , Table 2)
Type locality
China: Zhejiang Province, Mountain Tiantong.
Material examined
Holotype (female) and eight paratypes (seven females, one male), Mountain Tiantong (29°48′N, 121° 47′E, alt. 350 m), Zhejiang Province, China, deposited in SIPPE. GoogleMaps
Redescription
Body length. Up to 3.0 mm.
Colour. Bright red while living, white in alcohol. Head. Eyes 3+3, slightly pigmented, two on anterior and one on posterior part of tubercle Oc ( Figure 2A View Figure 2 ). Ratio of antenna to head as 1:1.2−1.5. Ant. III and IV dorsally fused. Length ratio of antennal segments as I:II:(III + IV) = 1:1.0:2.0. Ant. I and II respectively with 9 and 11 setae. Ant. III with 18 setae and Ant. III organ, 5 sensory setae, including sgd, sgv, ms and 2 strongly curved rods in separate pits. Ant. IV apical bulb trilobed, dorsal chaetotaxy as 8S, i, 12 mou and or. Buccal cone weakly developed. Labrum truncate and granulated, without prelabral seta, setal formula as 0/2, 2 ( Figure 2B View Figure 2 ). Labium with 2(3) x and three setae (A, C, D) on proximal part of palp, four (E, F, G, f) on submentum and four (b, c, d, e) on mentum ( Massoud 1967) ( Figure 2C View Figure 2 ). Mandible head elongate, consisting of two fringed rami, one smooth flagellum and five basal teeth; upper ramus small, pectinate and with simple setae; lower ramus two times length of upper one and with two rows of simple setae; flagellum situated between two rami, longer than upper ramus; third or fourth tooth sometimes bifurcate ( Figure 2E View Figure 2 ). Maxillary head consisting of two rami, inner one with two apical teeth and one inner mid tooth; outer one bifurcated twice into three lamellae, inner one apically ciliated on inner side ( Figure 2D View Figure 2 ).
Cephalic tubercles and chaetotaxy. Dorsal central area with 6 tubercles and 21 setae. Posterior area with 4 tubercles and 8 setae; Di and De respectively with seta Di1 and De1, setae Di2 and De2 situated out of tubercles. In lateral area, tubercle Dl separated with 4 setae, L and So fused with 12 setae ( Figure 2A View Figure 2 , Table 2A). Ventral side respectively with 6 and 10(9) setae in areas Vi and Ve.
Body tubercles and chaetotaxy. Macrosetae serrated, with narrow marginal wings, apically rounded, some on lateral tubercles acuminate ( Figure 2F View Figure 2 ). Th. I with 3+3 tubercles (Di, De, Dl). Th. II− Abd. IV respectively with 4+4 tubercles (Di, De, Dl, L); each tubercle L on Abd. I− IV with one sensory seta besides common setae. Abd. V dorsally with 3+3 tubercles (Di, De, Dl), tubercle De only with one sensory seta; tubercle L ventrally situated. Abd. VI with 1+1 tubercles ( Figure 2A View Figure 2 , Table 2B). S and ms on half terga of Th. II− Abd. V formula as 2+ms, 2/2,2,2,2,1. Each Av with 3(2) microsetae in both sexes. Genital plate with 15−32 and 19 (seen in one specimen) setae respectively in female and male ( Figure 2G View Figure 2 ).
Appendices. Chaetotaxy of legs, ventral tube and furcal remnant shown in Table 2. Tibiotarsi I and II respectively with 19 setae (T1−T4, A1−A7, B1−B7 and M). Tibiotarsus III with 18 setae, B7 absent; B5 very long, about twice length of inner edge of unguis. Unguis ventrally bearing basal granules and medial transverse striae and one inner tooth; inner tooth often with one to three tiny basal denticules. Unguiculus and tenent hair absent ( Figure 2H View Figure 2 ). Ventral tube anteriorly with 1+1 proximal and 3+3 distal setae. Furca reduced to elliptic area with three setae ( Figure 2G View Figure 2 ).
Biotope
Found in forest litter.
Remarks
Chinese species C. tiantongshana is redescribed on the basis of reexamining nine types. Corrections to the original description are the following ( Table 2): mandible consists of two fringed rami, one smooth flagellum and 5 basal teeth rather than only two feathered rami and five basal teeth in the original description; maxillary inner ramus has two instead of one apical tooth, outer ramus is bifurcated twice into three instead of two lamellae; macrosetae are serrated with narrow marginal wings and apically rounded rather than slight serrated, without marginal wings, and apically point; each tergum of Abd. I–III has 4+4 tubercles with tubercle L present rather than absent in the original description. Besides, some additional characters are described added and illustrated, such as the labrum, labium, complete chaetotaxy of antenna, hind leg and ventral chaetotaxy of Abd. I–VI.
C. tiantongshana is similar to the Chinese 3+3-eyed species, C. alatoserrata Yosii, 1965 from Taiwan and C. tridentiens Yue and Yin, 1999 from Shanghai in the antenna, labrum, labium, ventral tube, furcal remnant and macrosetae. However, it is easily distinguished from the latter two by the unique structure of mandible and maxilla as well as tubercle L of Abd. I− IV bearing one sensory seta, Abd. V tubercle De and cephalic tubercle Dl separated, and unguis inner tooth often with one to three denticules.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |