Jakobia densopapillata, Biseswar, 2006
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4689879 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4893229 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F53669-FFE5-FFFA-FF5C-BBCD24C4C4A1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Jakobia densopapillata |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Jakobia densopapillata View in CoL n. sp.
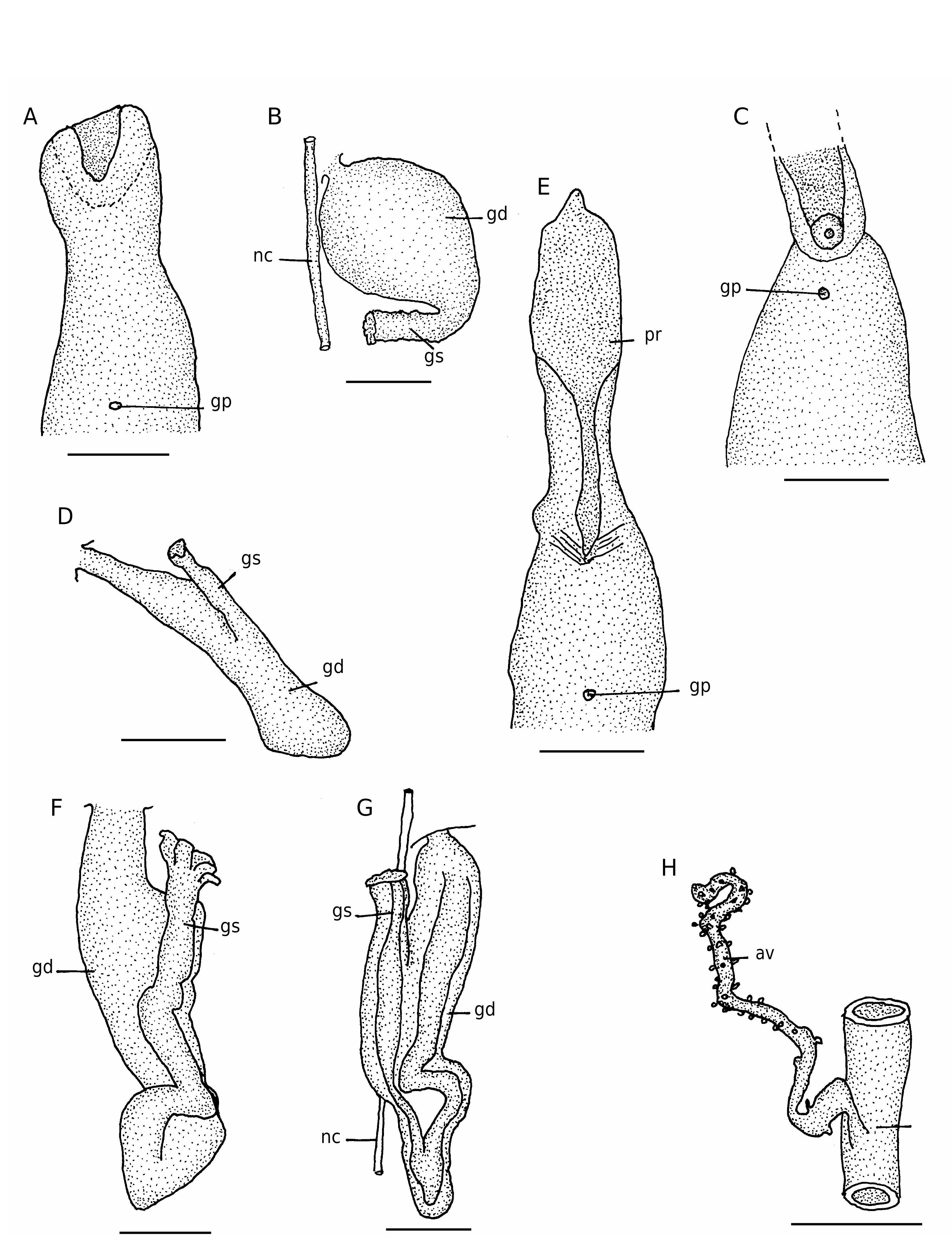
( Fig. 1 View FIG E-H)
TYPE MATERIAL. — Holotype: Porcupine Abyssal Plain, BENGAL 3, Discovery 229, stn 13200#70, 48°51.62’N, 16°31.80’W, 4845 m, 19.III.1998, 1 ♀. GoogleMaps
Paratypes: BENGAL 5, Discovery 231, stn 13368#52, 48°48.3’N, 16°25.97’W, 4839 m, 19.III.1998, 1 ♀.
BENGAL 6, Discovery 237, stn 13627#11, 48°47.82’N, 16°40.37’W, 4847 m, 1.X.1998, 1 ♀.
ETYMOLOGY. — The species name is based on the papillae which are very prominent and densely distributed over entire surface of trunk.
DESCRIPTION
Colour of proboscis is cream, trunk is beige in preserved state. Proboscis of holotype is 30 mm long; distal half is flattened and tapers at tip; in proximal half, lateral margins curl inwards giving it a tubular appearance ( Fig. 1E View FIG ). Mouth is surrounded laterally and ventrally by well developed lips. Probosces missing in both paratypes. Trunk is cylindrical. In holotype trunk is 97 mm in length and 19 mm across broadest part. In larger paratype trunk is 78 mm long and 10 mm at broadest part. Corresponding measurements of smaller specimen are 54 and 12 mm. Body wall is thick and opaque. Papillae densely distributed over entire surface of trunk. Posterior end of trunk covered with raised, rounded papillae; over rest of trunk, papillae are flattened and somewhat elongated. Single gonopore is located a few millimetres away from anterior end of trunk ( Fig. 1E View FIG ). Ventral setae absent.
Single gonoduct is located on right side of nerve cord. Gonoduct consists of two sharply bent sections lying close together and fused to each other ( Fig. 1F, G View FIG ). Muscular tube in gonoduct is also sharply bent to form a V. Gonostome is directed anteriorly with petaloid gonostomal lips ( Fig. 1F View FIG ). Except for anterior part of foregut and hindgut, rest of intestine is missing including blood system. Anal vesicles tubular covered with ciliated funnels. In holotype only left anal vesicle is present ( Fig. 1H View FIG ), right one is missing, probably damaged.
REMARKS
An important distinguishing feature of the genus Jakobia is the presence of a single gonoduct consisting of two sharply bent sections in the form of a V, with arms that lie close together and partly fuse. Two species are currently known in this genus, namely J. birsteini and J. similaris .
The new species, J. densopapillata n. sp. differs significantly from J. birsteini in the structure of the proboscis. According to the description provided by Zenkevitch (1958) the proboscis of J. birsteini consists of a flattened “head” bearing a sensory structure and the stem of the proboscis is oval in transverse section. The new species also differs in the structure of the gonoduct and anal vesicles. In J. birsteini the middle section of the gonoduct, containing the eggs, is distended and the anal vesicles are sac-like structures.
The new species differs from J. similaris in the nature of the body wall and the anal vesicles. According to DattaGupta (1981) the body wall of J. similaris is thin and the anal vesicles are branched. Furthermore, the papillae at the posterior end of the trunk of J. similaris are small.
re
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
SubClass |
Echiura |
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |