Cricotopus van der Wulp Cricotopus (Isocladius) intersectus (Staeger, 1839)Cricotopus (Isocladius) sylvestris (Fabricius, 1794)Cricotopus (Paratrichocladius) skirwithensis (Edwards, 1929)Cricotopus (Cricotopus) tremulus (Linnaeus, 1758)Cricotopus
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4819.2.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:2459A542-6CF2-4545-9E6F-262C68838D99 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4396882 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F487F1-FFAD-FFB5-FF22-FBEFABD5FD2D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Cricotopus van der Wulp Cricotopus (Isocladius) intersectus Cricotopus (Isocladius) sylvestris Cricotopus (Paratrichocladius) skirwithensis Cricotopus (Cricotopus) tremulus Cricotopus |
| status |
|
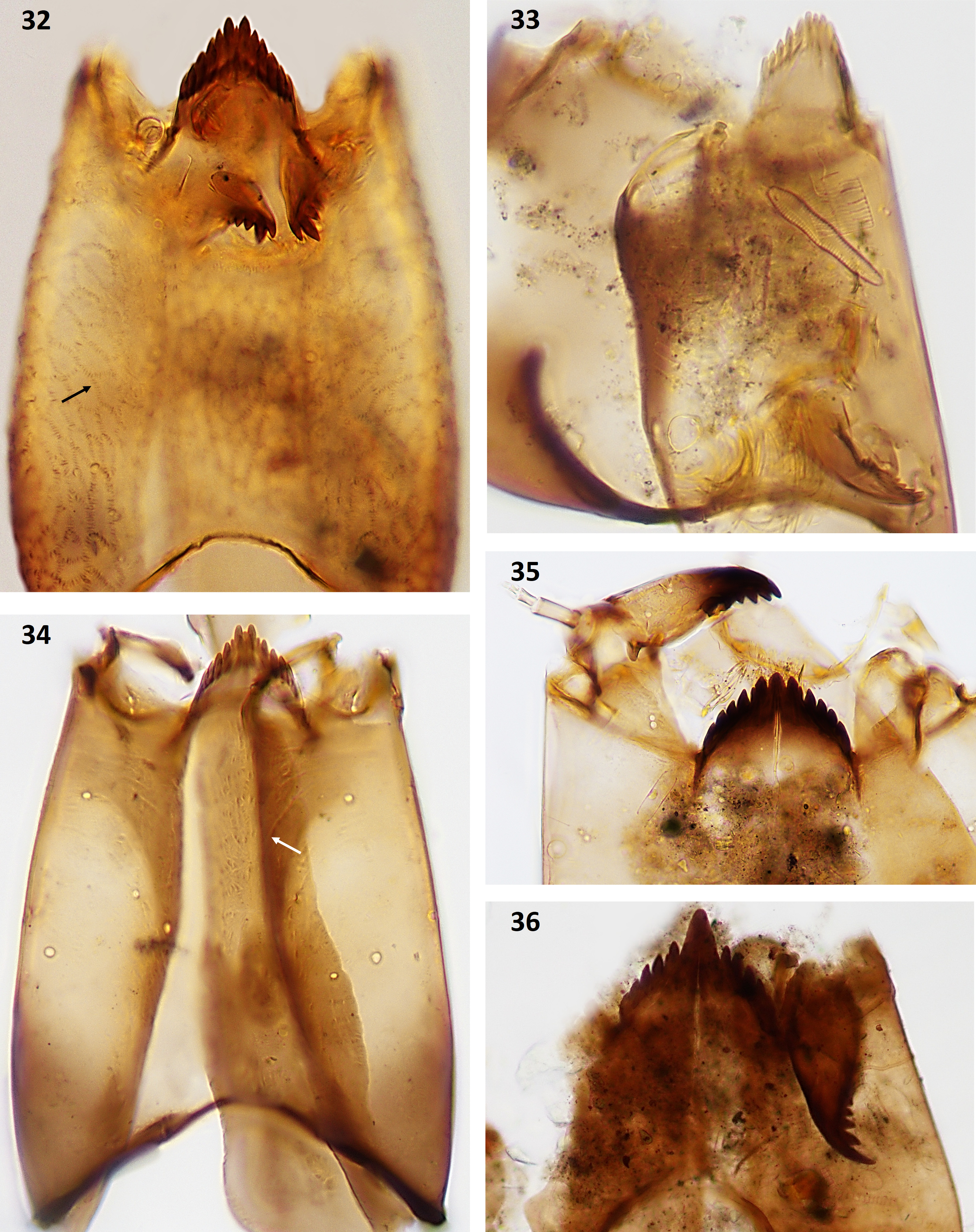
Cricotopus van der Wulp ( Figs 35–40 View FIGURES 32–36 View FIGURES 37–42 )
Head capsule yellow to blackish brown, occipital margin pale to black. Antenna usually 5-segmented. Premandible with one, rarely two apical teeth. Mandible with short apical tooth (shorter than combined width of inner teeth) and 3 inner teeth. Outer margin is usually crenulated, sometimes smooth. Mentum with one median, and usually 6 (rarely 5 or 7) lateral teeth. Ventromental plates narrow.
Remarks: Cricotopus larvae are extremely similar to Orthocladius and Paratrichocladius (recently placed within Cricotopus as subgenus, Cranston & Krosch, 2015).
Tuft of setae on the body segments of most species can distinguish Cricotopus from Orthocladius , however this feature is inapplicable in subfossil material, and the same goes for characters on antennae ( Andersen et al. 2013b). In general, the following characters seem to be more typical for Cricotopus than Orthocladius (though can be present in some Orthocladius as well): outer margin of mandible strongly crenulated, second lateral tooth smaller than first one and/or reduced and fused to first lateral tooth, and outer four lateral teeth forming a distinct group. Brooks et al. (2007) state that lateral teeth of Cricotopus are usually more rounded and pointed apically and the median tooth is relatively narrow, while in general, Orthocladius have lateral teeth more rectangular and median tooth can be broad (>3 times broader than first lateral). Paratrichocladius is usually distinguished by having the first lateral tooth of the mentum constricted at base so that broader in the middle than at the base. This tooth of Cricotopus and Orthocladius is widest at the base.
Cuppen & Tempelman (2018) have proposed a key to recognize Cricotopus subgenera that may be applied to sub-fossil remains. Subgenus Isocladius : Median mental tooth usually rounded, triangular in shape, always <2.5 times as wide as first lateral tooth; second lateral mental tooth strongly reduced and for the largest part fused with the first lateral tooth. Subgenus Cricotopus : Median mental tooth of varying size, either small or up to 3 or 4 times as wide as first lateral tooth, second lateral not reduced (e.g. Fig. 39 View FIGURES 37–42 ).
Up to date, Cricotopus (Cricotopus) pilosellus Brundin 1956 , Cricotopus (Isocladius) perniger (Zettrestedt, 1850) and C. (I.) cf. tricinctus (Meigen, 1818) were identified from pupal exuviae material ( Bitušík 2004; Bitušík et al. 2006a).
Cricotopus was relatively frequently recorded from the lakes situated at lower altitudes.
Five morphotypes were recognized, three of them are not listed in Brooks et al. (2007).
Key to morphotypes:
1 Second lateral tooth of mentum reduced and partly fused with first lateral tooth.................................... 2
- Second lateral tooth of mentum subequal or only slightly smaller than first lateral tooth and not fused with it............. 3
2 Median tooth of mentum prominent, more than twice height of first lateral tooth............... Cricotopus sylvestris- type
- Median tooth of mentum subequal to slightly longer than first laterals....................... Cricotopus intersectus- type
3 Mentum rather horizontal in appearance............................................... Cricotopus / Orthocladius I
- Mentum triangular in shape............................................................................. 4
4 Head capsule light brown; median mental tooth up to 2 times width of first lateral tooth; first lateral tooth rounded, wider in middle than at base; first inner tooth of mandible robust, larger than apical tooth............ Cricotopus skirwithensis- type
- Head capsule dark brown; median mental tooth narrow, equal to or slightly wider than first lateral tooth; inner teeth on meandibe subequal in size............................................................... Cricotopus tremulus- type
Cricotopus (Isocladius) intersectus - type ( Fig. 35 View FIGURES 32–36 )
Head capsule yellow with dark brown occipital margin. Mentum with single broad median tooth taller than the first lateral tooth. Second lateral tooth minute and fused to the first lateral. Median tooth and first two laterals form a distinct group separated from the other laterals.
Cricotopus (Isocladius) sylvestris - type ( Fig. 36 View FIGURES 32–36 )
Head capsule jellow to light brown. Mentum with very large rounded median tooth and 6 pairs of lateral teeth. Second lateral tooth is small and fused to the first one. Premandible apically bifid.
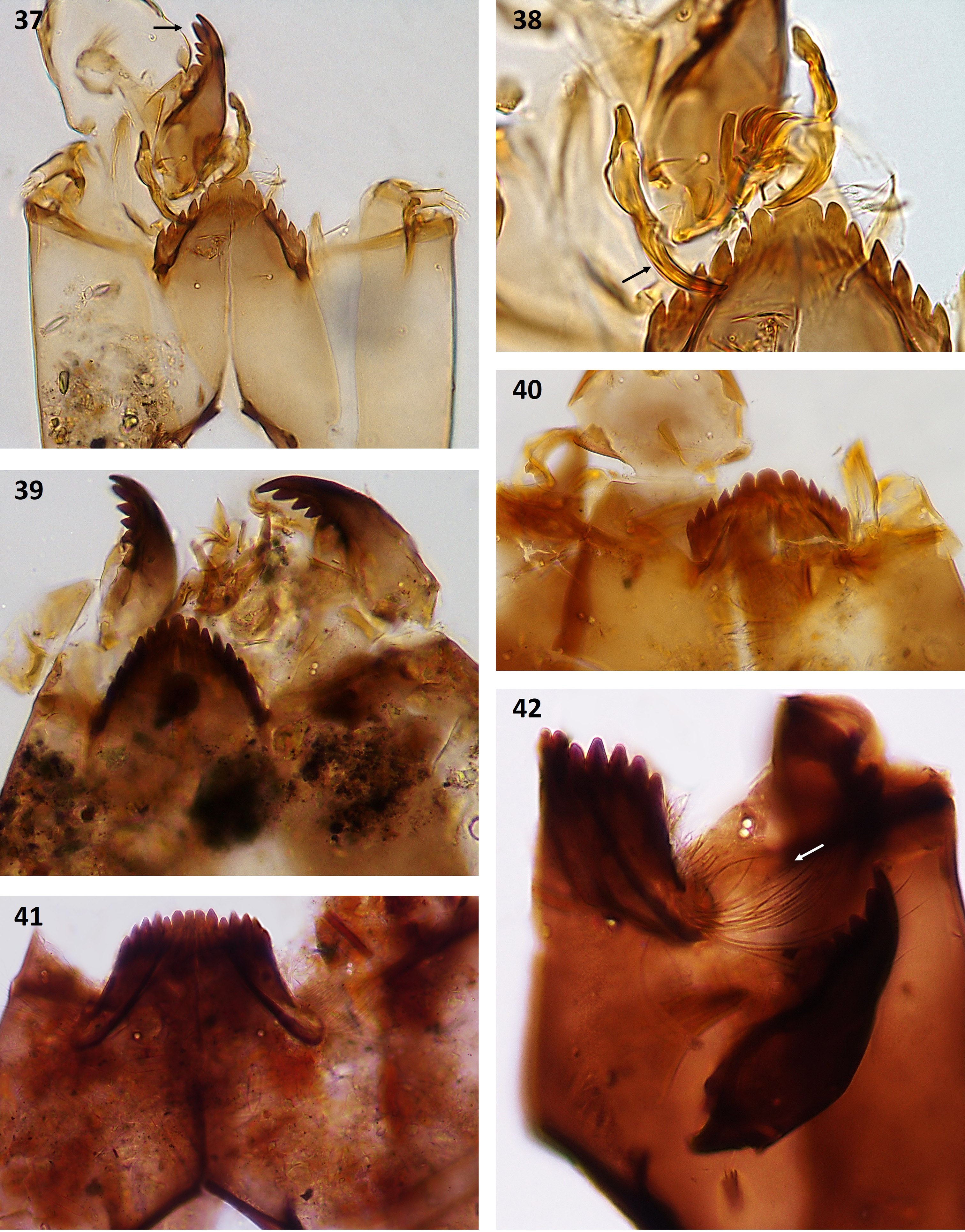
Cricotopus (Paratrichocladius) skirwithensis - type ( Figs 37, 38 View FIGURES 37–42 )
This is a new morphotype, not listed in Brooks et al. (2007).
Head capsule light brown with dark brown occipital margin and mandibular teeth. Mentum triangular in shape with a single median tooth up to 2 times width of first lateral tooth. First lateral tooth of the mentum is clearly rounded, wider in the middle than at the base. Remainder of lateral teeth pointed. First inner tooth of the mandible large, noticeably broader than apical tooth, but not taller ( Fig. 37 View FIGURES 37–42 ); outer margin of mandible smooth or only with a vague indication of crenulation. Setae submenti positioned between the bases of ventromental plates. Premandible with one apical tooth (however, there may be a faint indication of a notch) ( Fig. 38 View FIGURES 37–42 ).
Cricotopus (Cricotopus) tremulus - type ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES 37–42 )
This is a new morphotype, not listed in Brooks et al. (2007).
Head capsule dark brown with black occipital margin and mandibular teeth. Teeth of mentum dark brown to black in colour; single narrow median tooth, equal to or only slightly wider than the first lateral tooth. Mandible with crenulated outer margin. Premandible with single tooth.
Cricotopus /Orthocladius I ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 37–42 )
This is a new morphotype, not listed in Brooks et al. (2007).
Head capsule light brown to yellow in colour. Mentum rather horizontal in shape, all teeth brown. Single median tooth, about 1.5 times width of first lateral tooth; first lateral teeth obviously rounded. Second lateral tooth reduced and partly fused to first lateral. Setae submenti situated below the bases of mentum.
Cricotopus (Isocladius) intersectus - type ( Fig. 35 View FIGURES 32–36 )
Head capsule yellow with dark brown occipital margin. Mentum with single broad median tooth taller than the first lateral tooth. Second lateral tooth minute and fused to the first lateral. Median tooth and first two laterals form a distinct group separated from the other laterals.
Cricotopus (Isocladius) sylvestris - type ( Fig. 36 View FIGURES 32–36 )
Head capsule jellow to light brown. Mentum with very large rounded median tooth and 6 pairs of lateral teeth. Second lateral tooth is small and fused to the first one. Premandible apically bifid.
Cricotopus (Paratrichocladius) skirwithensis - type ( Figs 37, 38 View FIGURES 37–42 )
This is a new morphotype, not listed in Brooks et al. (2007).
Head capsule light brown with dark brown occipital margin and mandibular teeth. Mentum triangular in shape with a single median tooth up to 2 times width of first lateral tooth. First lateral tooth of the mentum is clearly rounded, wider in the middle than at the base. Remainder of lateral teeth pointed. First inner tooth of the mandible large, noticeably broader than apical tooth, but not taller ( Fig. 37 View FIGURES 37–42 ); outer margin of mandible smooth or only with a vague indication of crenulation. Setae submenti positioned between the bases of ventromental plates. Premandible with one apical tooth (however, there may be a faint indication of a notch) ( Fig. 38 View FIGURES 37–42 ).
Cricotopus (Cricotopus) tremulus - type ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES 37–42 )
This is a new morphotype, not listed in Brooks et al. (2007).
Head capsule dark brown with black occipital margin and mandibular teeth. Teeth of mentum dark brown to black in colour; single narrow median tooth, equal to or only slightly wider than the first lateral tooth. Mandible with crenulated outer margin. Premandible with single tooth.
Cricotopus /Orthocladius I ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 37–42 )
This is a new morphotype, not listed in Brooks et al. (2007).
Head capsule light brown to yellow in colour. Mentum rather horizontal in shape, all teeth brown. Single median tooth, about 1.5 times width of first lateral tooth; first lateral teeth obviously rounded. Second lateral tooth reduced and partly fused to first lateral. Setae submenti situated below the bases of mentum.
Andersen, T., Saether, O. A., Cranston, P. S. & Epler, J. H. (2013 b) The larvae of Orthocladiinae (Diptera: Chironomidae) of the Holarctic Region-Keys and diagnoses. In: Andersen, T., Saether, O. A., Cranston, P. S. & Epler, J. H. (Eds.), Chironomidae of the Holarctic Region. Keys and diagnoses. Larvae. Insect Systematics & Evolution, Lund, Supplement, pp. 189 - 386.
Bitusik, P. (2004) Chironomids (Diptera. Chironomidae) of the mountain lakes in the Tatra Mts. (Slovakia). A review. Dipterologica bohemoslovaca 12, Acta Facultatis Ecologiae, Zvolen, 12 (1), 25 - 53.
Bitusik, P., Svitok, M., Kolosta, P. & Hubkova, M. (2006 a) Classification of the Tatra Mountains lakes (Slovakia) using chironomids (Diptera, Chironomidae). Biologia, 61 (18), 191 - 201. https: // doi. org / 10.2478 / s 11756 - 006 - 0131 - 8
Brooks, S. J., Langdon, P. G. & Heiri, O. (2007) The Identification and Use of Palaearctic Chironomidae Larvae in Palaeoecology. QRA Technical Guide No. 10. QRA, London, 276 pp.
Cranston, P. S. & Krosch, M. N. (2015) DNA sequences and austral taxa indicate generic synonymy of Paratrichocladius Santos- Abreu with Cricotopus Wulp (Diptera: Chironomidae). Systematic Entomology, 40 (4), 719 - 732. https: // doi. org / 10.1111 / syen. 12130
Cuppen, H. P. J. J. & Tempelman, D. (2018) Identification key for the 4 th stage larvae of north west European species of Cricotopus (Diptera: Chironomidae: Orthocladiinae). Lauterbornia, 85, 69 - 90.
FIGURES 32–36. Corynoneura arctica-type: 32—head capsule (arrow indicates net-like reticulation). Corynoneura edwardsi- type: 33—head capsule. Corynoneura lobata-type: 34—head capsule (arrow indicates wrinkled sculpturing). Cricotopus intersectus-type: 35—head capsule. Cricotopus (Isocladius) sylvestris-type: 36—head capsule.
FIGURES 37–42. Cricotopus (Paratrichocladius) skirwithensis-type: 37—head capsule (arrow indicates first inner tooth of the mandible). C. (P.) skirwithensis-type: 38—detail of premandible). Cricotopus (Cricotopus) tremulus-type: 39—head capsule. Cricotopus/Orthocladius I: 40—head capsule. Diplocladius cultriger: 41—head capsule. D. cultriger: 42—detail of the head capsule (arrow indicates long and dense beard).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |