Clinotanypus setosus, Oliveira & Silva & Trivinho-Strixino, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2013.825019 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F4605B-C614-FD5E-FE12-FA0F75FEFB95 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Clinotanypus setosus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Clinotanypus setosus View in CoL sp. nov.
( Figures 7–9 View Figure 7 View Figure 8 View Figure 9 )
Type material
Holotype male with pupal exuviae, BRAZIL, SP, São Carlos , Monjolinho Reservoir, 21 ◦ 59 ′ S, 47 ◦ 52 ′ W, 856 m a.s.l., 18 October 2010, S. T. Strixino GoogleMaps . Paratype pharate female with larval exuviae, BRAZIL, SP, Pirassununga , Aquaculture Research
and Training Center – CEPTA / IBAMA, 21 ◦ 55 ′ 44 ′′ S, 47 ◦ 22 ′ 23 ′′ W, 627 m a.s.l., 20 September 2010, S. T. Strixino GoogleMaps .
Etymology
Named after numerous long setae on tergite TIX.
Diagnostic characters
Clinotanypus setosus sp. nov. differs from other Clinotanypus species by the combination of the following characters. Male: TIX with 58 setae, anal point slightly bilobed, gonostylus with 9 setae. Pupa: base of scar with shagreenation, segment VII with 5 taeniae and anal lobe 906 µm long. Larva: shape of mandible and by its row of setae at the lateral outer margin; palp segment and procercus length.
Descriptions
Adult male (n = 1)
Dimensions. Total length 5.30 mm. Wing length 2.43 mm. Total length / wing length 2.18. Wing length / length of profemur 2.17.
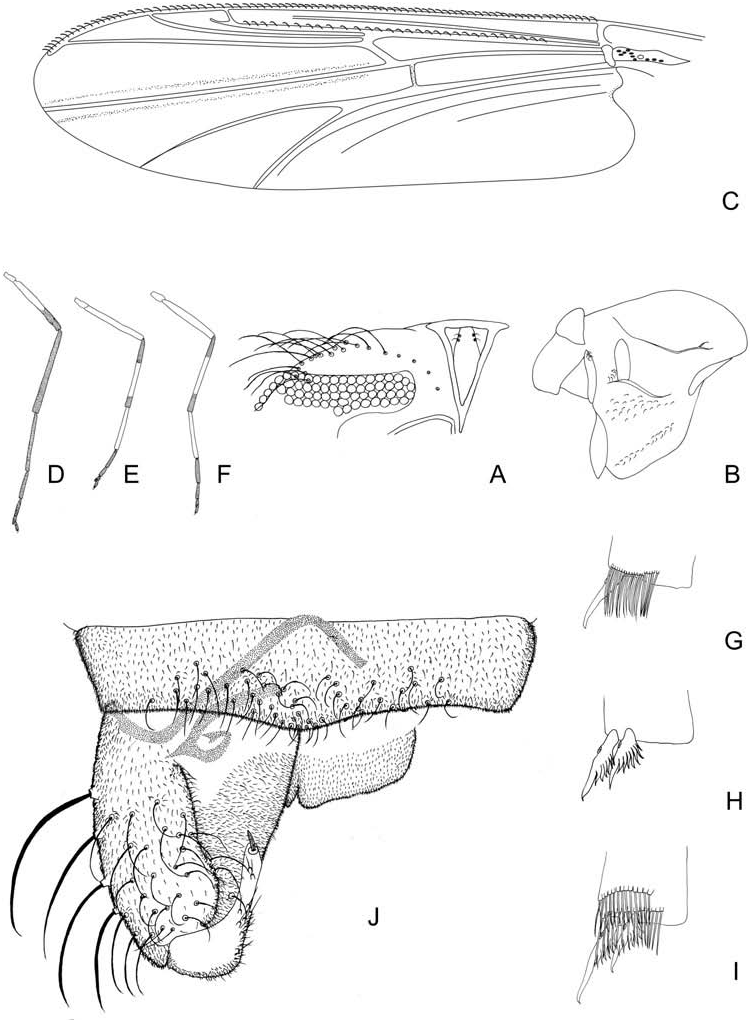
Coloration. Head yellow; pedicel, antenna and maxillary palp brown. Thorax with microtrichia, yellow; antepronotum with two brown vertical spots; scutellum, postnotum, anepisternum and preepisternum brown. Wing membrane transparent without spots, veins brown and macrotrichia on C and R 1 veins. Legs pale brown with dark brown bands as in Figure 7D–F View Figure 7 . Abdomen and hypopygium yellow.
Head ( Figure 7A View Figure 7 ). Antenna with 14 flagellomeres, AR 2.55, flagellum 1644 µm long. Temporal setae 22, multiserial ( Figure 7A View Figure 7 ). Eyes bare, with dorsomedian extension containing 4 terminal facets. Tentorium 253 µm long, stipes not measurable. Clypeus 114 µm long, 145 µm wide at largest part, bearing 22 setae. Cibarial pump with anterior margin concave, 340 µm long. Palpomere lengths 1–5 (in µm): 107; 112; 185, 261; 343.
Thorax ( Figure 7B View Figure 7 ). Antepronotum with 17 lateral setae. Acrostichals biserial; dorsocentrals 44, merging with the acrostichals posteriorly; prealars unobserved; supraalars 1; scutellars 34; postnotals 51; posterior anepisternals II 5; epimerals 6; preepisternals divided in two groups, group I with 23 setae and group II with 20 setae, as in Figure 7B View Figure 7 .
Wing ( Figure 7C View Figure 7 ). Width 0.76 mm long. Costa 2.33 mm long, produced beyond R 4+5. R 1 with 36 setae. VR 0.91. WW 0.31. Brachiolum with 1 seta. Squama with 36 setae.
Legs ( Figure 7D–I View Figure 7 ). Fore leg: tibia one apical spur 79 ( Figure 7G View Figure 7 ). Mid leg: tibia with two apical spurs 65; 49 µm long ( Figure 7H View Figure 7 ); tarsomeres 1–3 each with two pseudospurs 42–49, 33–43 and 33–40 µm, respectively. Hind leg: tibia with two apical spur 108 and 72 µm long ( Figure 7I View Figure 7 ); tarsomeres 1–3 each with one pseudospur 52, 45 and
39 µm respectively; double comb present. All legs with claws pointed. Pulvilli absent. Lengths and proportion of leg segments as in Table 3.
Hypopygium ( Figure 7J View Figure 7 ). Tergite IX with irregular row of 58 dorsal setae. Anal point slightly bilobed. Phallapodeme long and wide, 93 µm long. Sternapodeme curved anteriorly, 154 µm long. Gonocoxite conical, 239 µm long, with slightly concave inner margin. Gonostylus simple, 119 µm long; megaseta 17 µm long. HR 2.01. HV 4.45.
Pupa (n = 2)
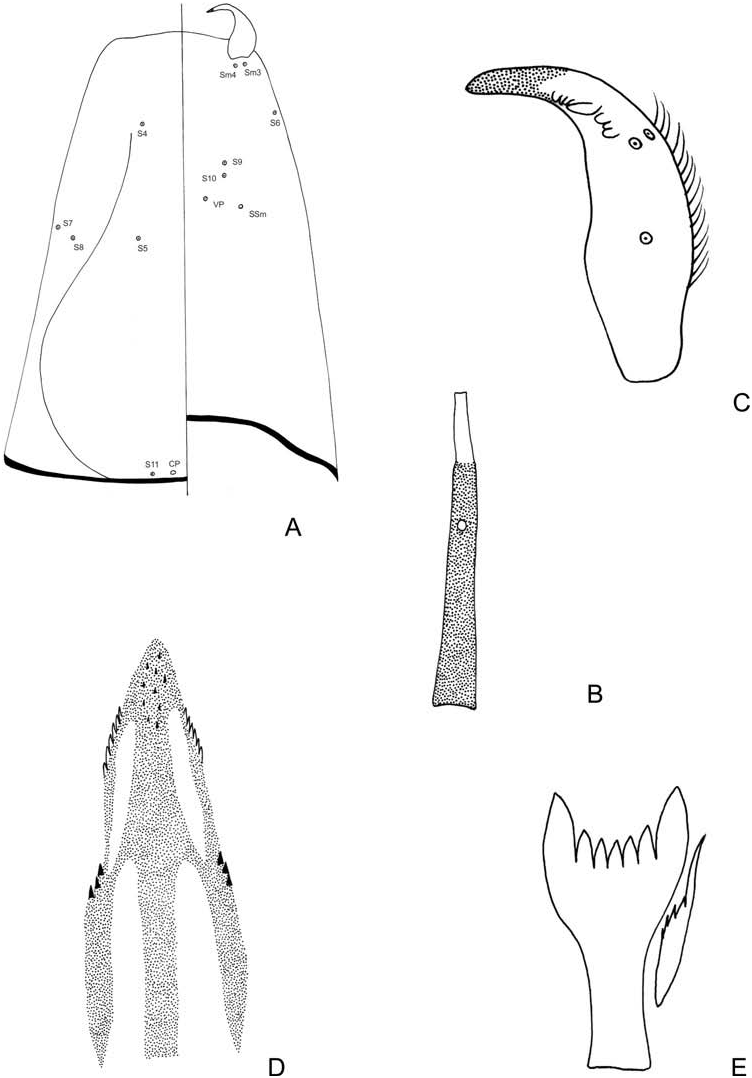
Coloration. Exuviae pale brown with brown spots. Thoracic horn mostly brown.
Cephalothorax ( Figure 8A View Figure 8 ). Wing sheath smooth 1.78 (1) mm long and 0.64 (1) mm wide. Frontal apotome 318 (1) µm wide. Thoracic horn 479–564 µm long and 130–136 µm wide, with few spinules on the surface; plastron plate large, 243–258 µm long ( Figure 8A View Figure 8 ); aeropyle tube 221–321 µm long. Respiratory atrium tubular. Basal lobe present.
Abdomen ( Figure 8B View Figure 8 ) 4.61–4.95 mm long. Tergites I–VII with shagreen consisting of sparse and solitary spinules. T I with pigmented scar, 186–188 µm long, with shagreenation at the base. Dorsal chaetotaxy as in Figure 8B. T View Figure 8 VII with 5 taeniae. T VIII with 5 taeniae. Anal lobe as in Figure 10G View Figure 10 , 906 µm long and 688 µm wide, with two anal macrosetae. Genital sac smaller than anal lobe, with 356 µm long. GS / AL 0.39.
Fourth instar larva (n = 1)
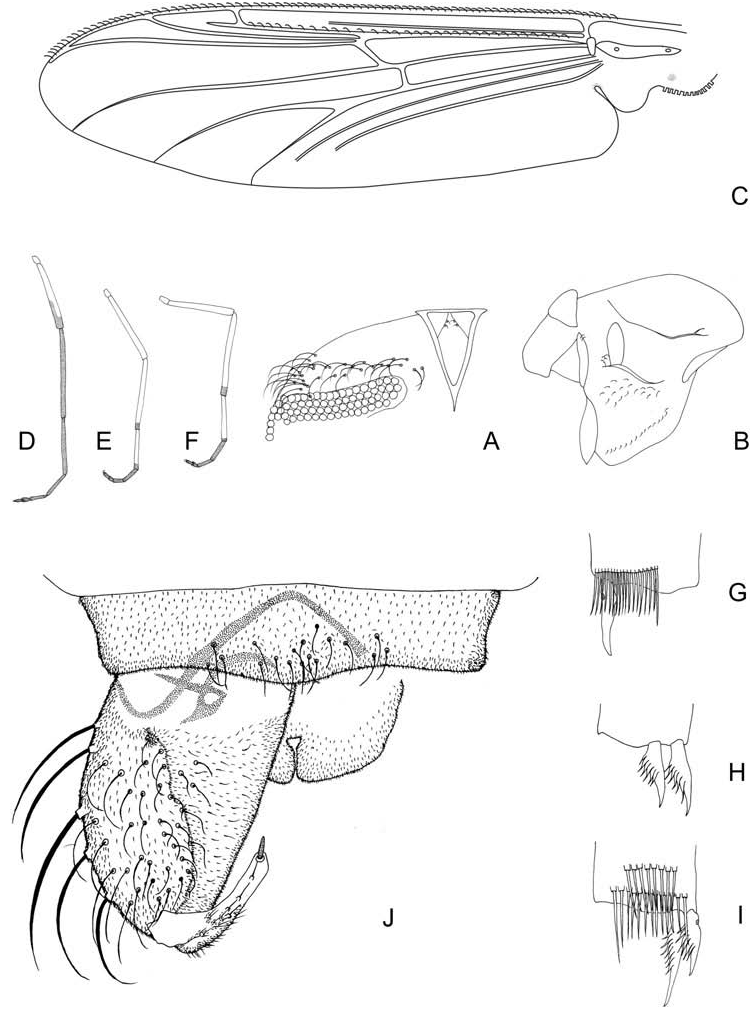
Coloration. Head pale yellow, postoccipital margin brown; antenna pale yellow; apical tooth of mandible brown; ligula pale yellow. Abdomen pale yellow, procercus, anal setae and posterior parapod claws pale yellow.
Head ( Figure 9A View Figure 9 ). Length not measurable. Chaetotaxy as in Figure 9A View Figure 9 . Antenna. Length 727 µm, A 1 667 µm long, with ring organ placed 576 µm from base, A 2 42 µm long. AR 11.
Maxilla ( Figure 9B View Figure 9 ). Palp segment 126 µm long and 12 µm wide, with ring organ 74 µm from base, membranous apex, A 1 / P 1 5.28, A 2 / P 1 0.33.
Mandible ( Figure 9C View Figure 9 ). Length 117, with 3 pairs of lateral setae. A 1 / MD 5.70. Row of setae at the lateral outer margin present.
Mentum and M appendage ( Figure 9D View Figure 9 ). Dorsomentum with 3 teeth; pseudoradula granulate; M appendage with lateral teeth.
Hypopharyngeal complex ( Figure 9E View Figure 9 ). Ligula 94 µm long, maximum width 45 µm, with 7 teeth, anterior toothed margin slightly concave. Paraligula pectinate, 60 µm long. Pecten hypopharyngis with 20 teeth equal in size.
Body. With lateral fringe. Anterior parapods with simple small claws. Procercus 235 µm long, 62 µm wide, with 14 anal setae 833 µm long. L / W 3.83. Supraanal seta 636 µm long. Anal tubules not measurable. Posterior parapod apex with 10 simple and 5 hook-shape claws.
Ecology
The pupa of Clinotanypus setosus was collected in a reservoir associated with the aquatic macrophyte, Myriophylum aquaticum.
| T |
Tavera, Department of Geology and Geophysics |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |