Owenia picta, Parapar, Julio & Moreira, Juan, 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4019.1.20 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9085D431-B770-46AF-95D7-7A9AFBBFD8D6 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6108177 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03F287BF-5226-DC63-4BFA-FB29FD8BF8D9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Owenia picta |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Owenia picta View in CoL n. sp.
( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 D, 2, 7–11)
Material examined. Holotype: AM W.45875, stn. 2.4.2., coarse to medium sand, 4.5 m. Paratypes: AM W.36972, MI QLD 2198, sand, 9 m, fixed in EtOH; AM W.36973, MI QLD 2205, coral rubble, 14.5 m, fixed in EtOH; AM W.36974, MI QLD 2148, sediment, 9 m, in 95% EtOH; AM W.41320, MI QLD 2205, coral rubble, 14.5 m, fixed in EtOH; AM W. 41321, MI QLD 2198 (6 fixed in EtOH), sand, 9 m; AM W.45219, MI QLD 2440, fixed in EtOH; AM W.45403, MI QLD 2441 (2 fixed in EtOH); AM W.45856 (4), medium sand, 3 m; AM.45864, coarse to medium sand, 4.5 m; AM W.45865, medium to fine sand, 18 m; AM W.45868, coarse to medium sand, 4.5 m; AM W.45873, coarse to medium sand, 4.5 m; AM W.45876 (3), filamentous algae, 12 m; AM W.45862, filamentous algae, 12 m; AM W.45917, filamentous algae, 12 m; AM W.47388 (5), sand, 6.5 m; AM W.47385 (3), 2 m; AM W.47390, filamentous algae, 12 m, on SEM stub; AM W.47391, medium sand, 3 m, on SEM stub; AM W.47392, sand, 6.5 m, on SEM stub.
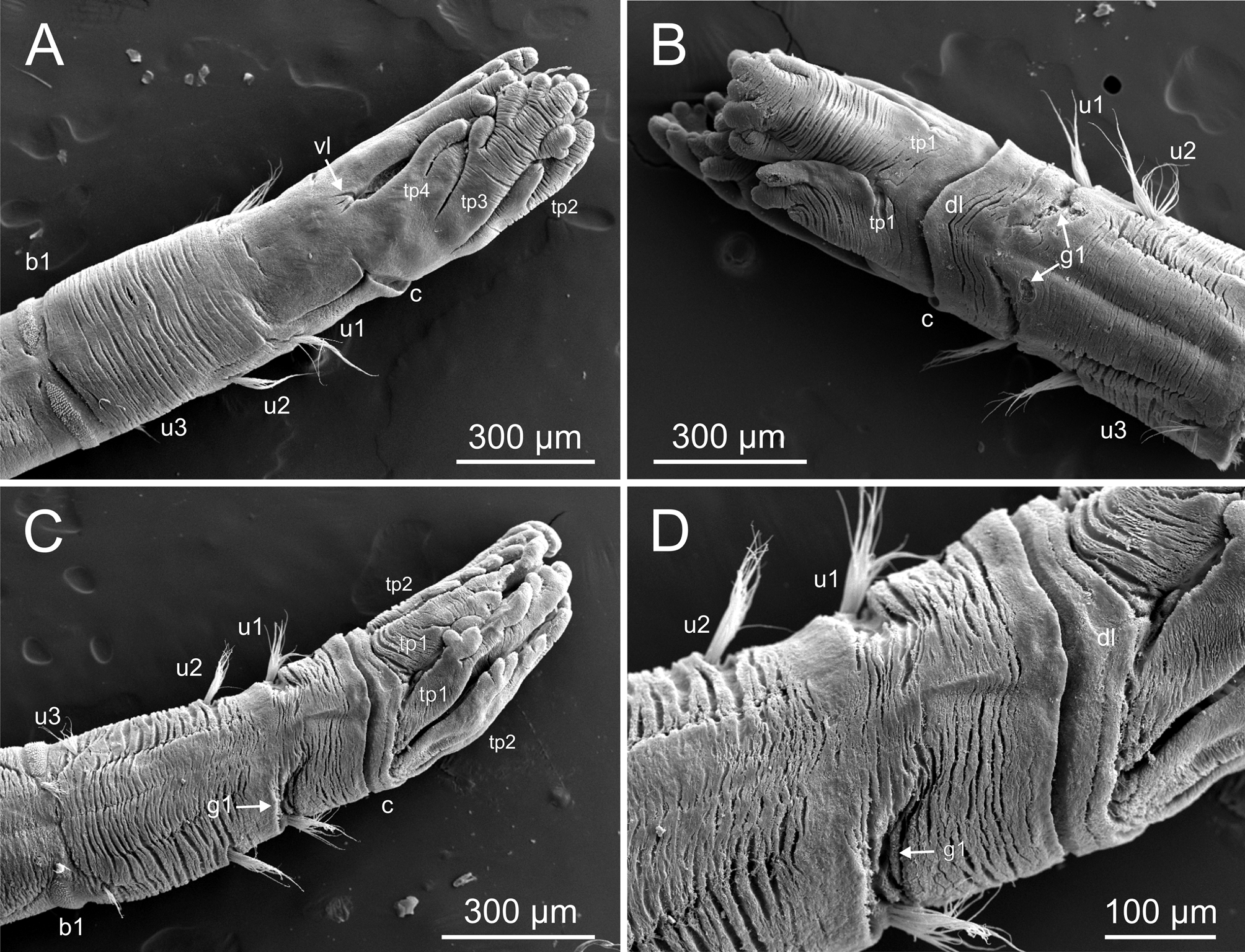
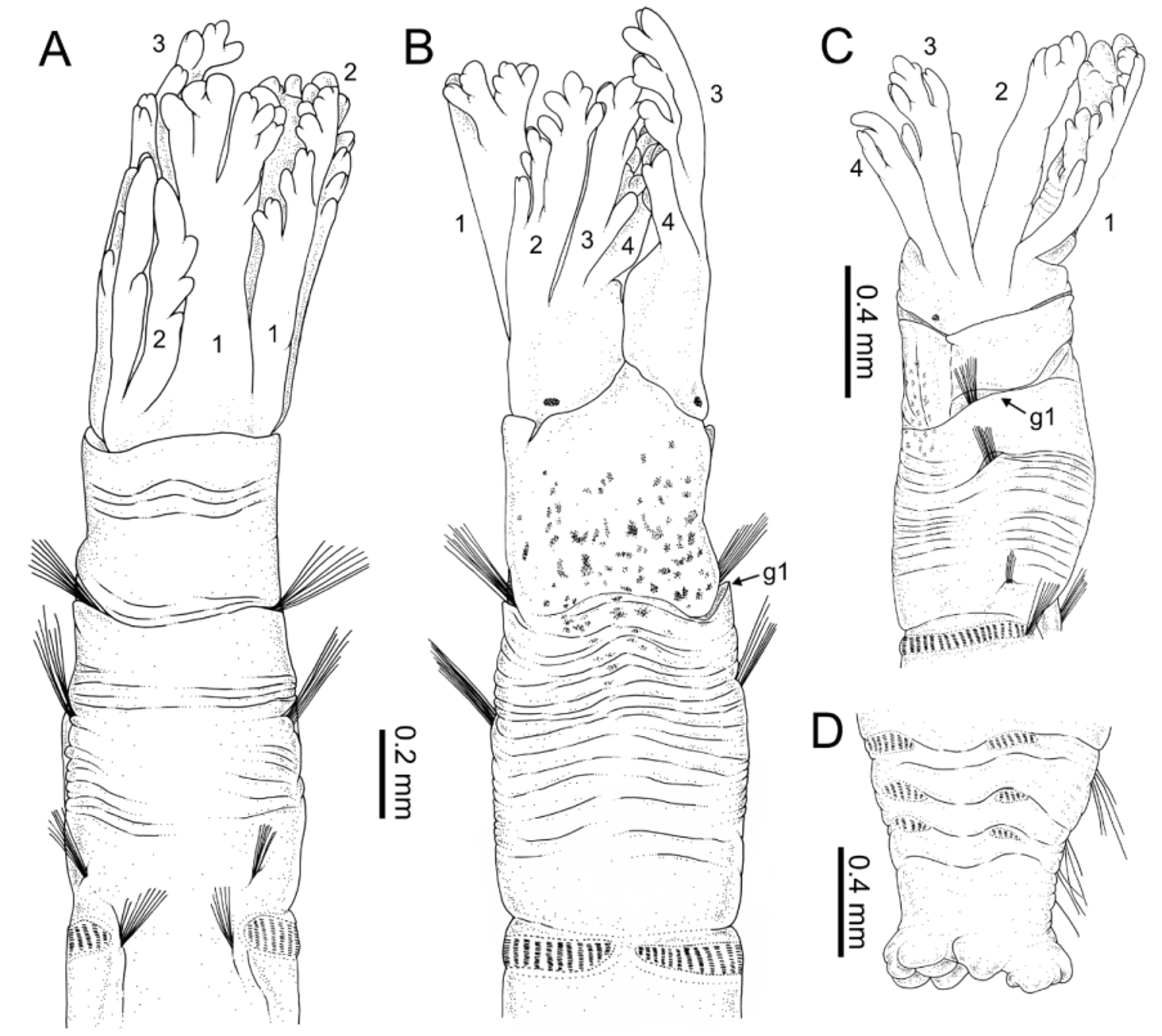
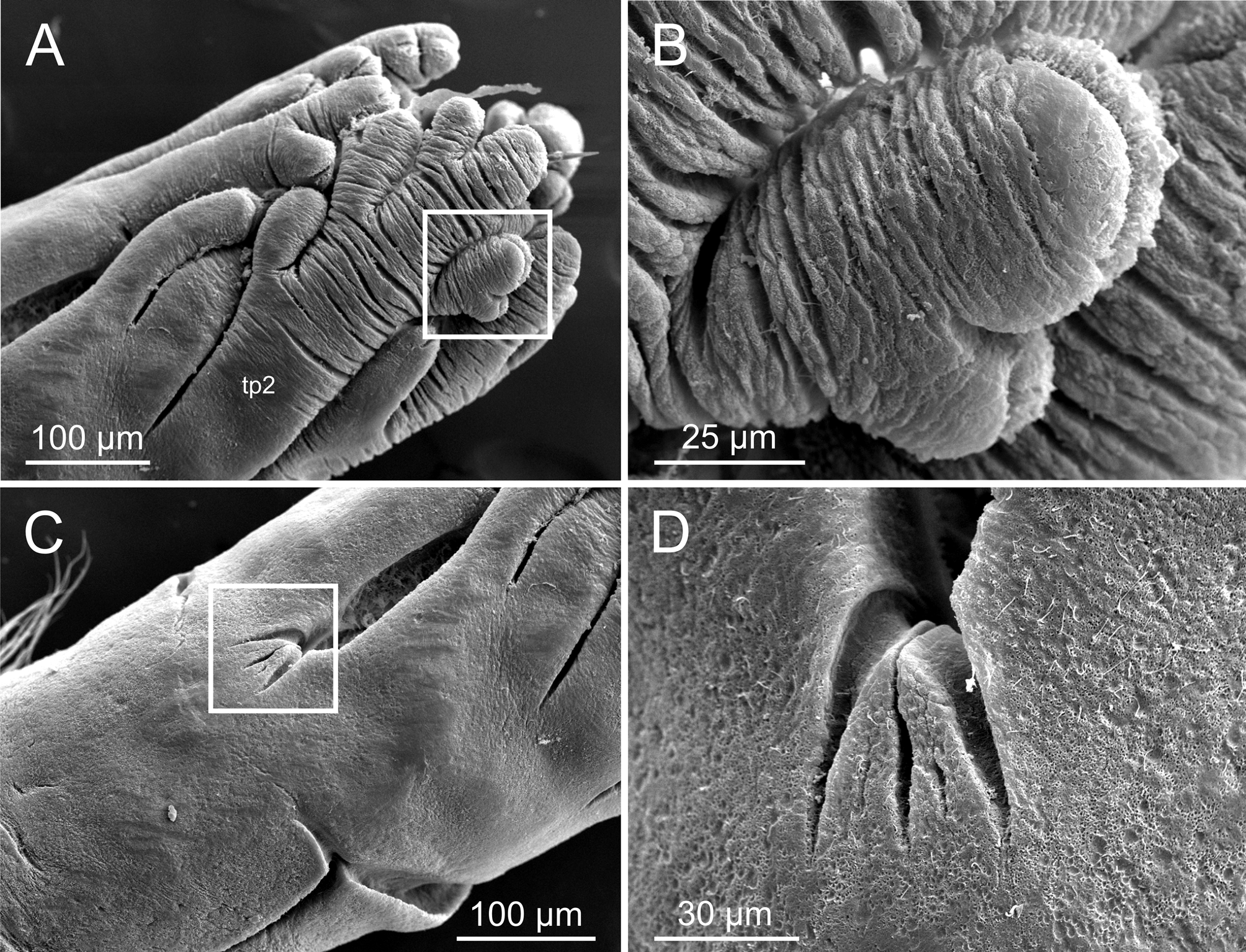
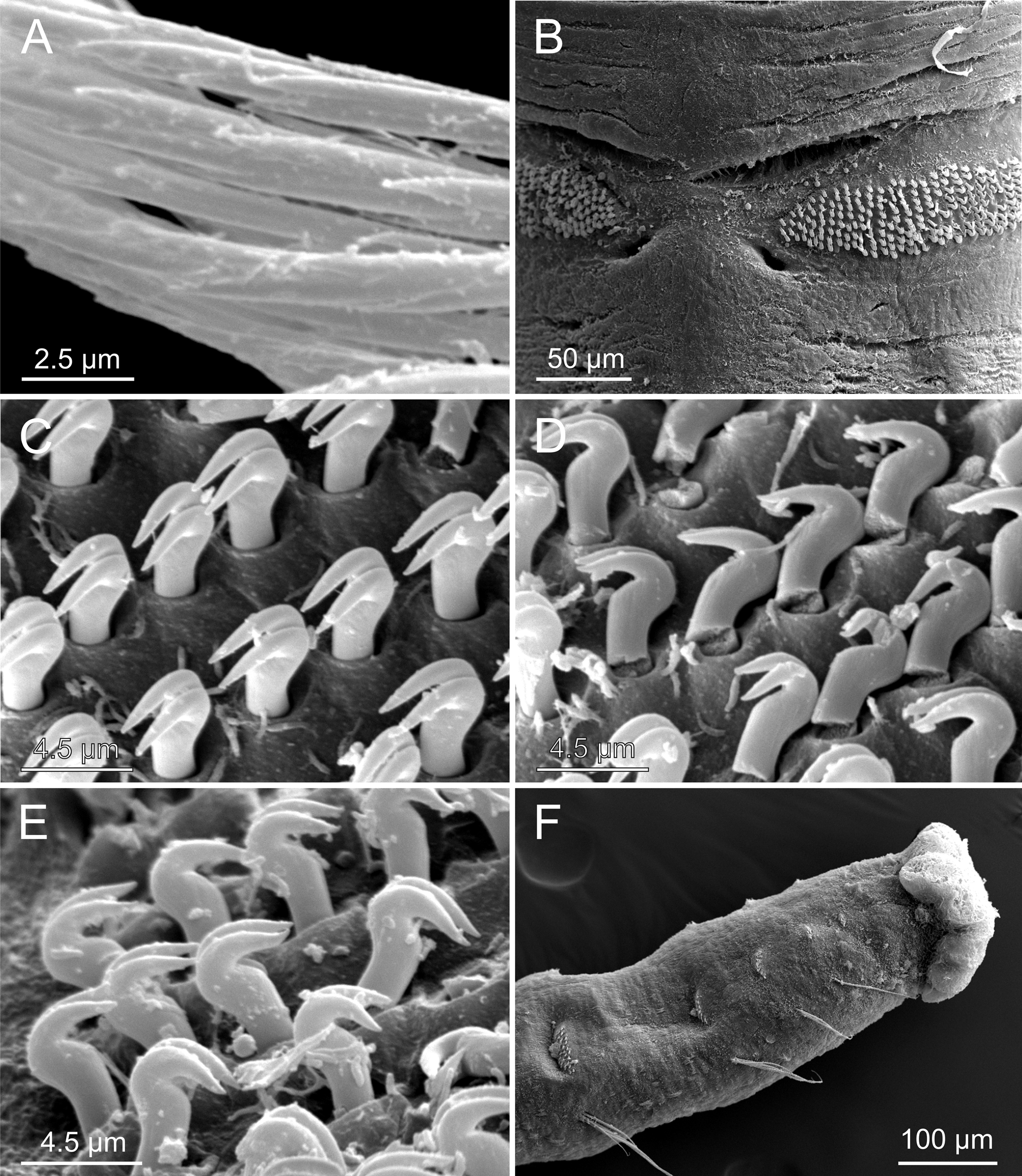
Description. Based on holotype. Body elongated; 26 mm long, 0.5 mm wide, with 22 chaetigers. Branchial crown with four pairs of tentacles ( Figs 8 View FIGURE 8 A, 9A–C). Each tentacle with no major divisions; tips of tentacles with multiple small lobes provided with a distal sulcus ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 A–B) separating inner ciliated side from outer nonciliated side. Crown almost as long as thorax (C/T ratio ≈ 0.85). Pair of pale eye spots at ventral base of crown ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 B). Junction between thorax and tentacle crown marked by a distinct, straight collar closely aligned with body wall, slightly overlapping base of crown. Thorax and crown of similar width. Thorax with three pairs of poorly developed notopodia with capillary chaetae. Collar sometimes expanded in a large dorsal lobe ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 B–D); a short bilobed ventral projection present in all specimens ( Figs 8 View FIGURE 8 B, 9A, 10C–D). RLTS: 1−2.5−0.5. A deep groove at base of first thoracic uniramous chaetiger (u1) present in all specimens ( Figs 8 View FIGURE 8 A–C, 9B–D). Notochaetae with shafts composed of densely packed scales ( Fig. 11 View FIGURE 11 A). Thoracic neuropodia absent. Abdomen of uniform width, with about 16 chaetigerous segments with noto- and neuropodia; width of abdominal segments decreasing posteriorly, being posterior segments short and compact. First abdominal chaetiger (b1) about as long as all thoracic segments (u1–u3) together. Second abdominal chaetiger (b2) about 1.5 times b1; b3 = b4 and both about ¾ of b2; following segments progressively shorter. Abdominal notopodia poorly developed with capillary chaetae similar to thoracic notochaetae. Abdominal notochaetae arranged dorsally. Neuropodia consisting of wide sessile podia with several rows of neurochaetal hooks ( Fig. 11 View FIGURE 11 B); tori almost encircling body except on dorsal surface between notochaetal bundles. Neurochaetal uncini similar through, consisting of hooks with shaft ending in two teeth side by side ( Fig. 11 View FIGURE 11 C–D). Pygidium multilobed ( Figs 8 View FIGURE 8 D, 11F).
Preserved animals creamy white with distinctive pigment marks consisting of diffuse brown speckles covering most of ventral part of peristomium and anterior part of first thoracic chaetiger (u1) ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 B). Tube coated by quartz grains and shell fragments.
Variations. One paratype of sample W.45403 is complete measuring 6 mm in length, 0.3 mm in width with 15 abdominal chaetigers. In one specimen of W.41321, RLTS is 1–3–0.5. Some paratypes show pigmentation more extended than in the holotype. For instance, in W.45219 coloration is also present dorsally in the peristomium and u1, but less marked than in the dorsal area. In paratype W. 36972 there is also coloration in the base of the branchial crown. One paratype of W.45856 shows the anterior end in process of regeneration; in the other the total length of the branchial crown is similar to that of thorax (C/T ratio ≈ 1.0).
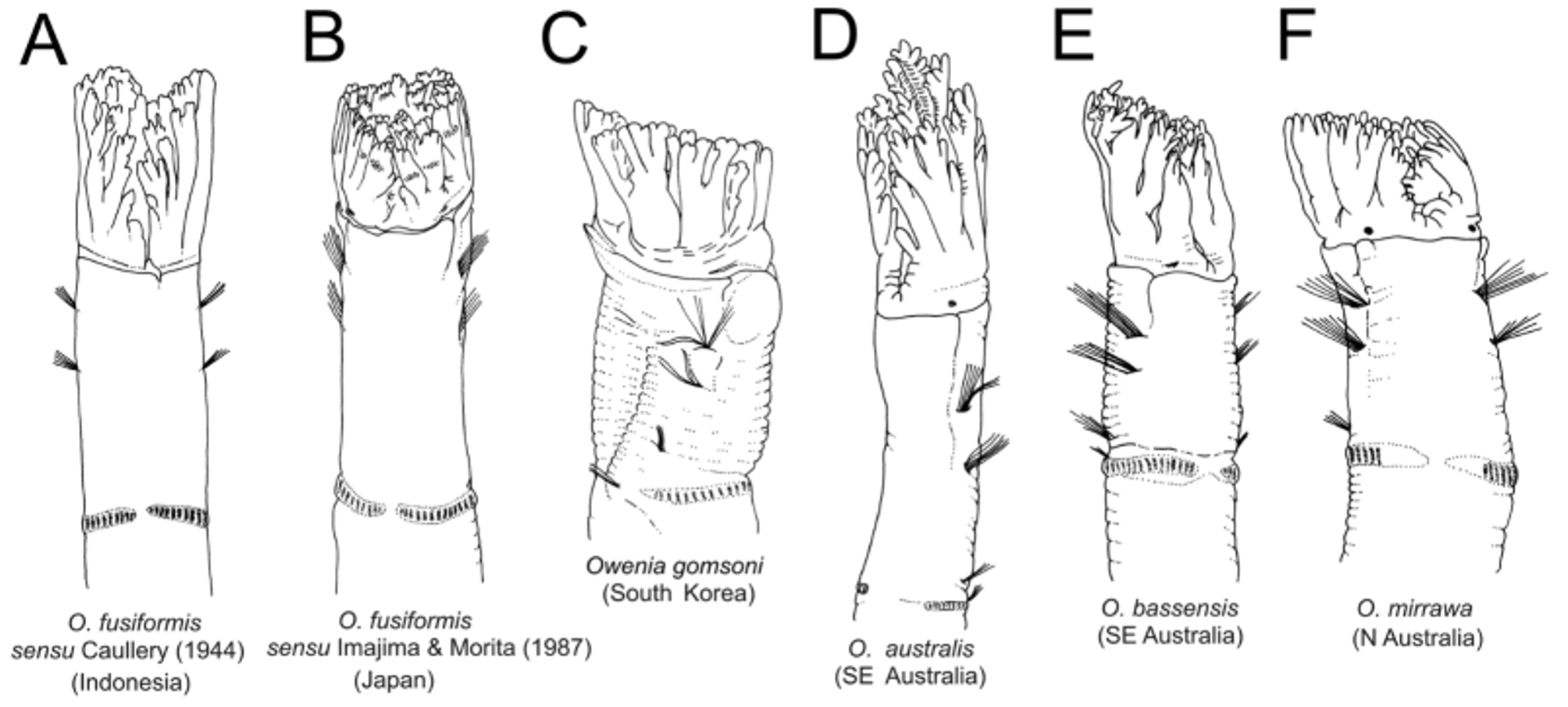
Remarks. Owenia picta n. sp. mostly resembles O. australis from SE Australia ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 D); both differ from any other Owenia in the region by the following features: 1) the larger size of the branchial crown when compared to the thorax (C/T ratio ≈ 0.85), 2) four pairs of branchial lobes, and 3) by lacking conspicuous major ramifications in the crown. However, O. picta n. sp. differs from O. australis in having conspicuous coloration in the anterior end and a deep dorsolateral groove behind notochaetal bundle of u1, which has not been reported in O. australis .
Specimens from Indonesia identified by Caullery (1944) as O. fusiformis ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 A) show likewise a large branchial crown but of a lesser C/T ratio. According to the description and illustrations by Caullery (1944), its length is about half of the thorax length, about 5/8 of the distance from the base to the first uncinigerous torus (C/T ratio ≈ 0.63; Caullery 1944). Furthermore, O. picta n. sp. and O. fusiformis sensu Caullery differ from each other in the pattern of branchial coloration; in O. fusiformis sensu Caullery , there are whitish spots in the tips of the branchial ramifications (see Fig. 41A–C in Caullery 1944) and dorsal white spots sometimes (not explicitly mentioned or illustrated in the description). Caullery (1944) also states that the lateral sides of thorax are uniformly reddish brown. On the contrary, in O. picta n. sp. the branchial and thoracic coloration is reddish and the pattern of pigmentation in the branchial crown is different.
Other oweniid species show a smaller C/T ratio (0.6) than that of O. picta n. sp., namely O. bassensis ( Australia) , O. mirrawa ( Australia) , O. petersenae ( New Zealand) and O. gomsoni ( South Korea) ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ). Furthermore, O. bassensis has three branchial lobes instead of four as it happens in O. picta n. sp., O. mirrawa has conspicuous major divisions in the branchial crown close to its base, O. petersenae has major divisions in the branchial crown only at the distal end, and O. gomsoni has white dorsolateral bands of coloration in u1 and u2.
The Pacific species Owenia johnsoni Blake, 2000 , from the Gulf de California, has also a high C/T ratio ≈ 0.75. However, this species is colourless and the branchial crown has only one major ramification and each lobe end is divided in several (4–5) fine slender bifid tips of same length (see Fig. 5.10. in Blake 2000).
Etymology. The species name (“ picta ”) refers to the conspicuous brown pigmentation present in the anterior part of the body.
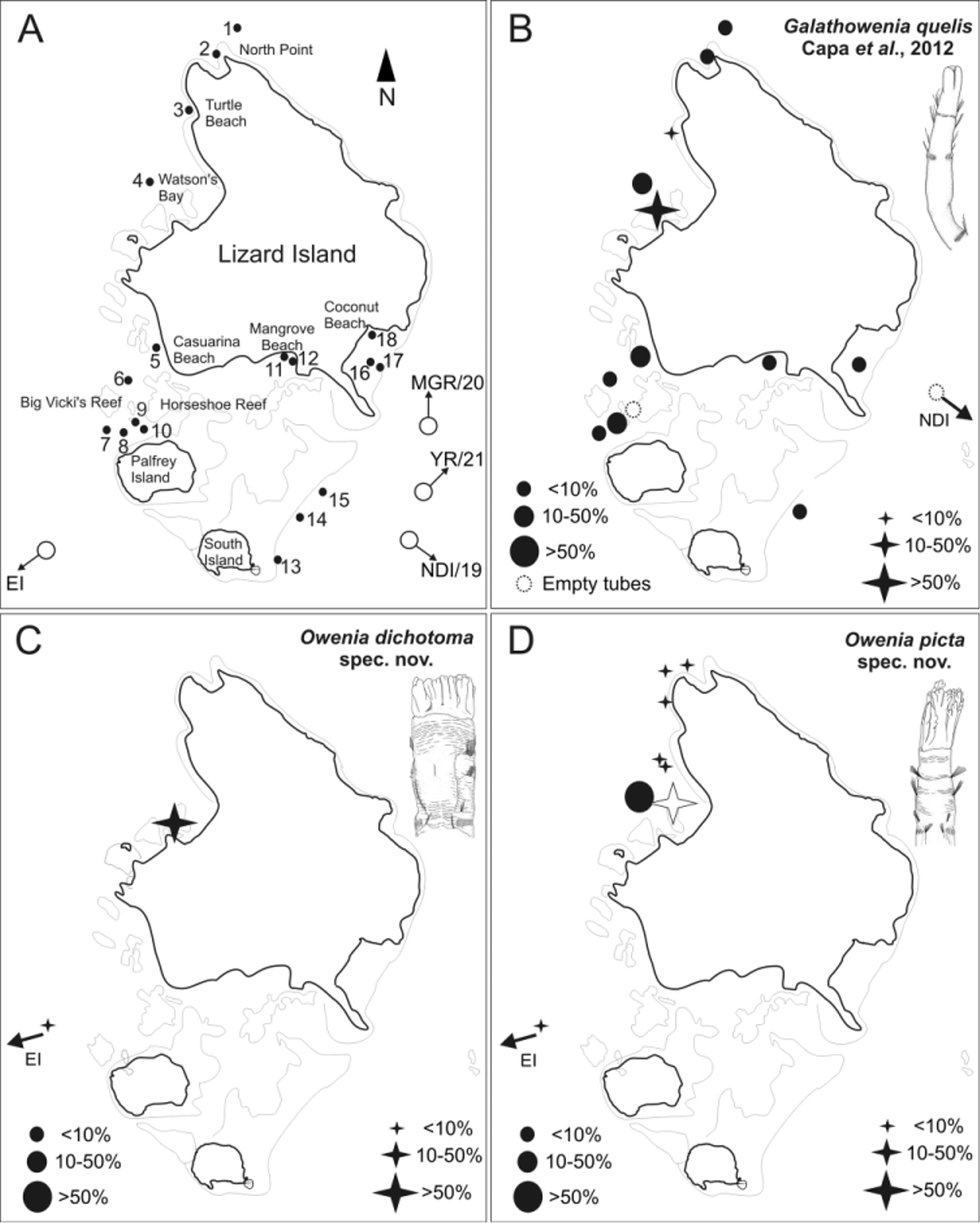
Habitat / Distribution. Species apparently restricted to NW of Lizard Island, Watson’s Bay to North Point from 3 to 15 m depth, on sandy bottoms ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 D). Three specimens were found at 5 m depth at Eagle Island, about 4 nautical miles SW from LIRS.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.