Cothornobata Czerny, 1932
|
publication ID |
https://dx.doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4006.2.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:B154E526-0C08-4A92-868E-A36E45F2F1A1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03ED4575-FFCC-FF9A-759D-FE71DE6E77A5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi (2016-04-21 02:15:48, last updated 2017-01-14 11:17:41) |
|
scientific name |
Cothornobata Czerny, 1932 |
| status |
|
Genus Cothornobata Czerny, 1932
Cothornobata Czerny, 1932: 267 . Type species: C. striatifrons Czerny (= Trepidaria cyanea Hendel, 1913 ) (monotypy). Sphaericocephala Czerny, 1932: 291. Nomen nudum; genus-group name proposed after 1930 without designation of type species from five included species.
Sphaericocephala Steyskal, 1977: 12. Type species: Trepidarea cyanea Hendel, 1913 (original designation). Nomen nudum; genus-group name proposed in synonymy after 1960.
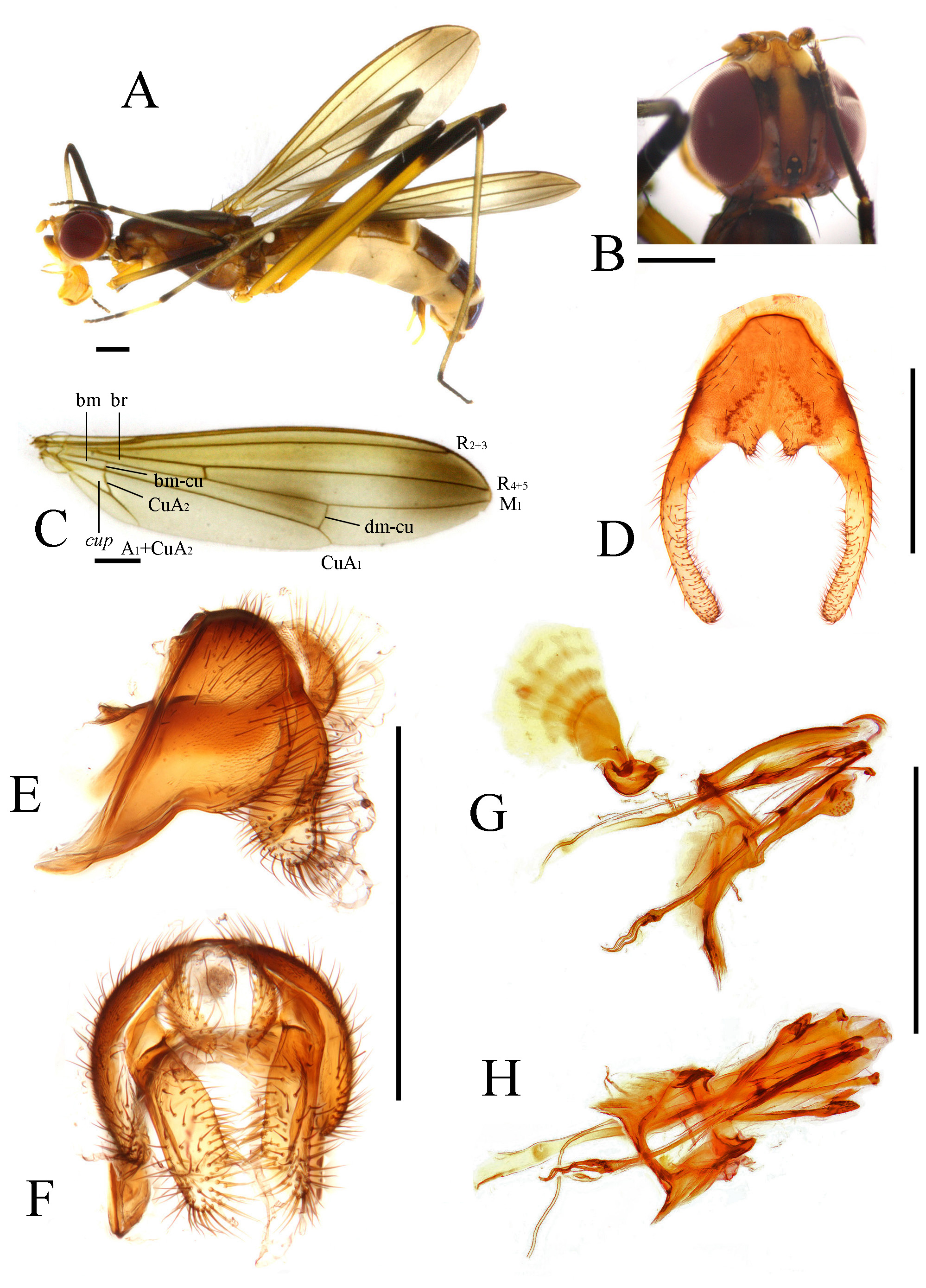
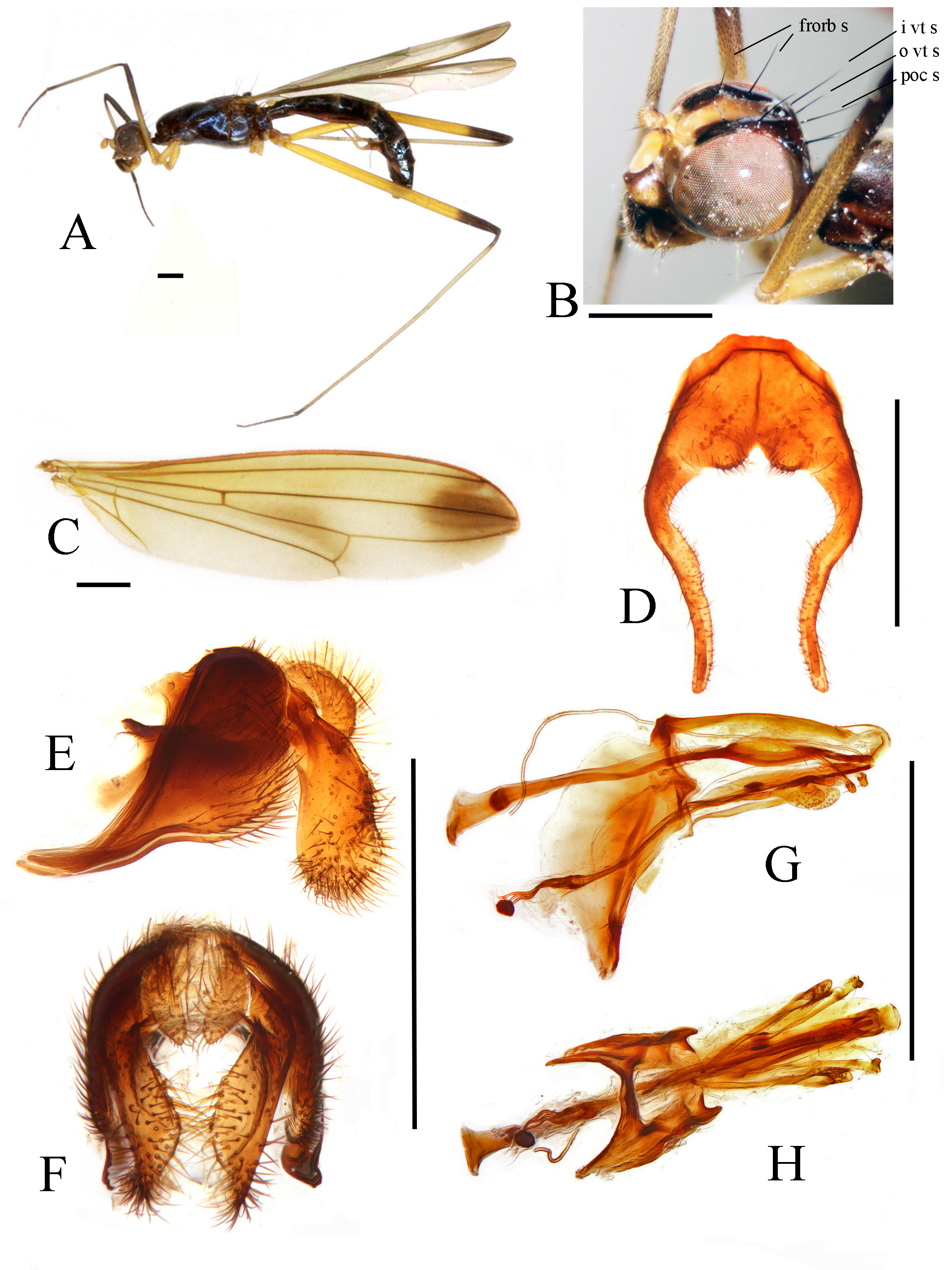
Generic diagnosis. Postmetacoxal bridge absent. Mesonotum elevated, convex anteriorly and without transverse depression between postpronotal lobes. Distiphallus with long terminal filaments.
Generic description. Body colour black to yellow. Frons slightly pitted. Head usually with 1 postocellar seta (postocellar seta absent in the Australian species C. atra McAlpine ), 1 inner vertical seta, 1 outer vertical seta, 1 frontal seta, 0 to 1 orbital seta ( Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 B, 14 B). Orbital plate glossy. Postocellar setae usually subparallel (often slightly convergent in the Australian species C. alta McAlpine ). Clypeus large, often glossy; palpus moderately developed. Arista usually bare or almost so, sometimes pubescent to short-plumose on basal half only.
Thorax entirely pruinose, thorax with 2 notopleural setae, 1 dorsocentral seta, 1 supra-alar seta, 1 postalar seta, 1 apical scutellar seta; katepisternum with 2–4 strong setae ( Fig. 25 View FIGURE 25 B). Mesoscutum dark, concolorous or almost so. Mesoscutum strongly gibbous anteriorly, anterior margin of scutum bent at a near right angle, ending in sunken pronotum. Legs pale yellow to dark brown; mid and hind femora of Oriental species other than C. viriata mostly yellow, with an extensively brown to black apex ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 A). Hind femur little longer than mid femur, mid femur about twice as long as fore femur; mid and hind tibiae sometimes with anterior longitudinal groove in basal quarter (more extensive in some Australian species); hind tibia with 3–5 dorsolateral preapical spines and a bare dorsoapical area. Setulae and setae on legs black. Wing pigmentation relatively conserved among northern Oriental species: generally infuscated except for pale strip posterior to CuA 1 and incomplete pale postdiscal band (posterior to R 2 + 3); distal band often distinct (incorporating the preapical and apical bands which are not separated by pale subapical band), discal band small and only slightly darker than base of wing in northern Oriental species (variable from nearly hyaline to broad and dark in Australian species). CuA 2 slightly sinuate, anal cell pointed posteriorly; vein A 1 +Cu 2 reaching wing margin ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 C). Distal part of axillary sclerites with dense fascicle of short setulae.
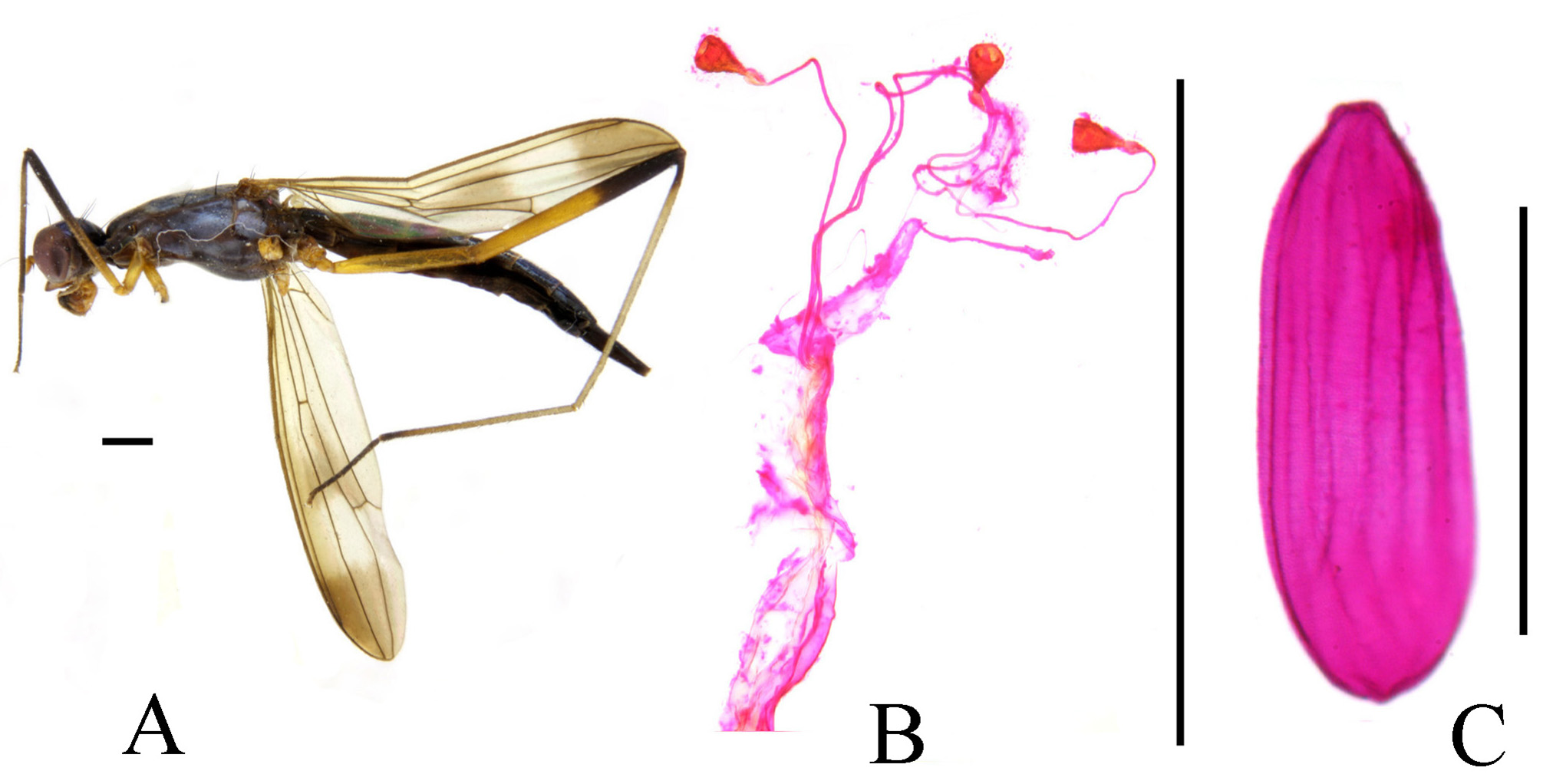
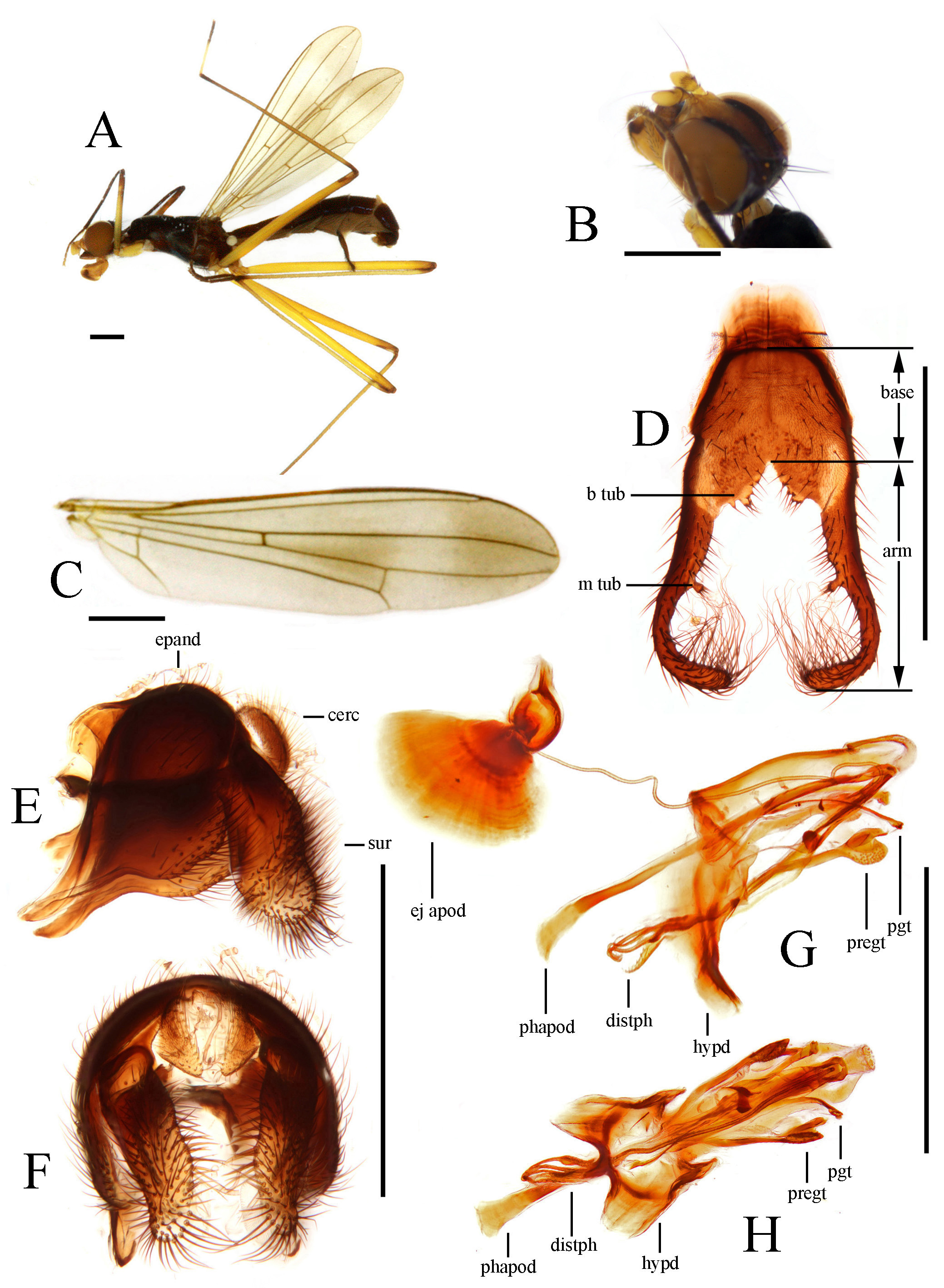
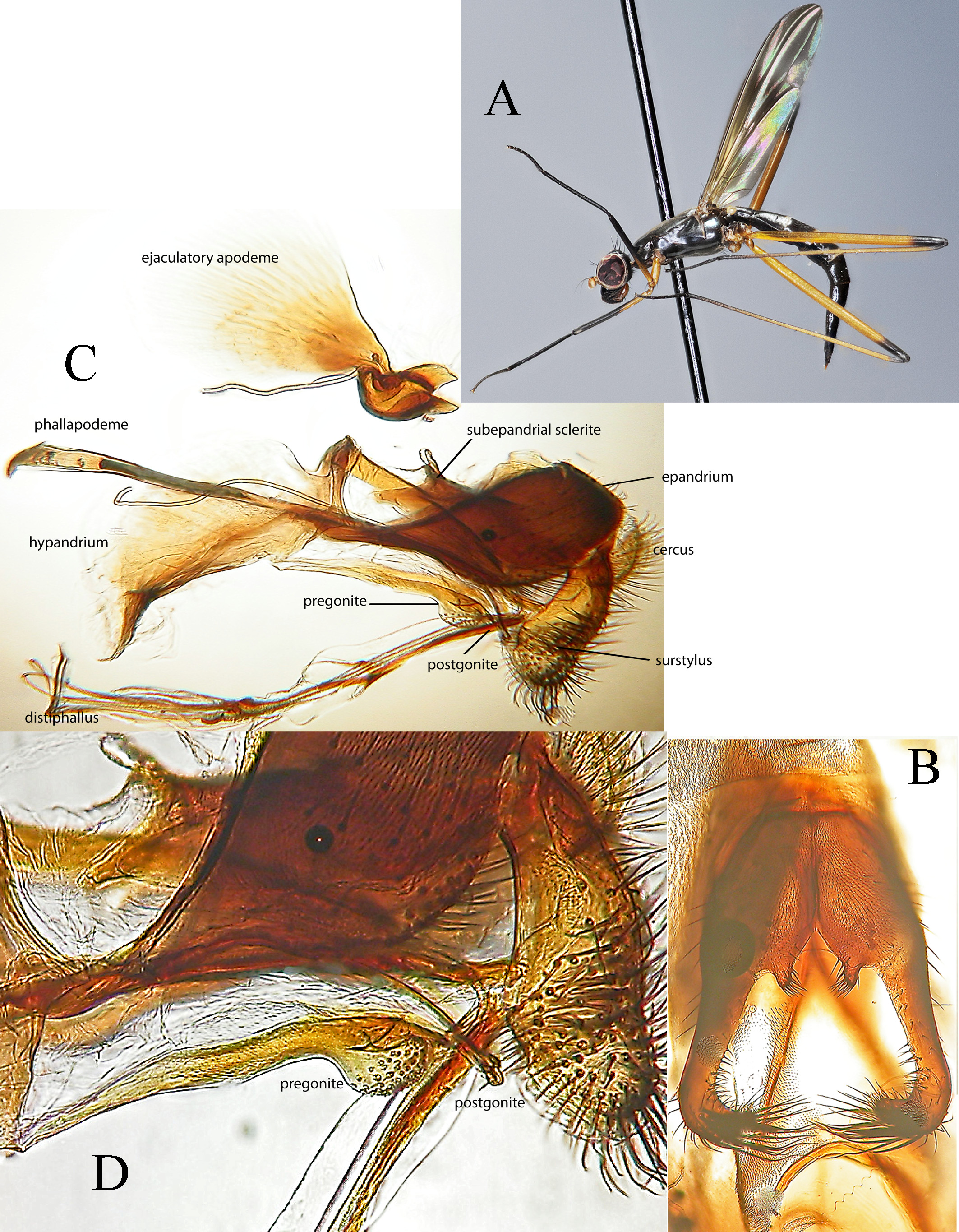
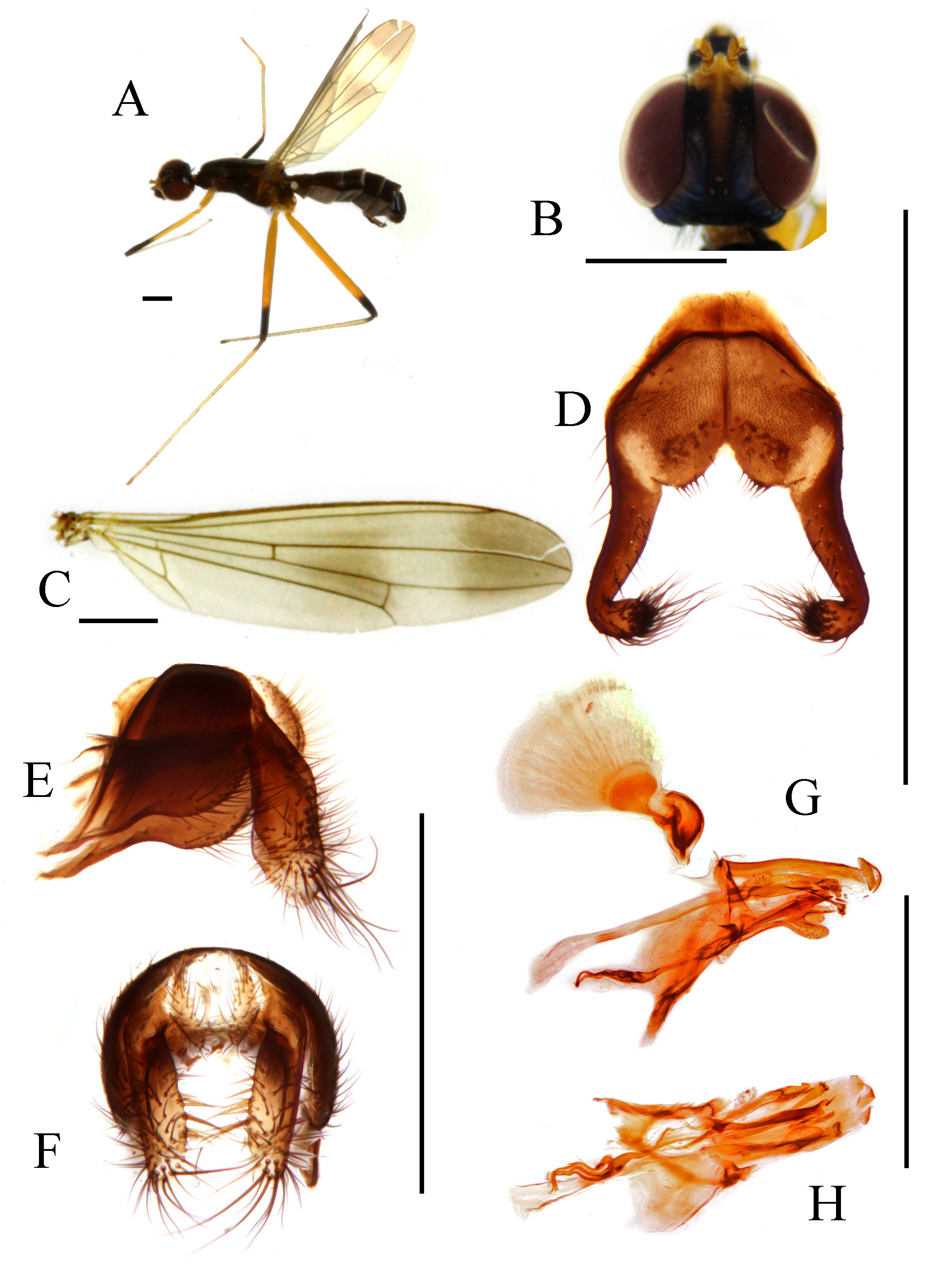
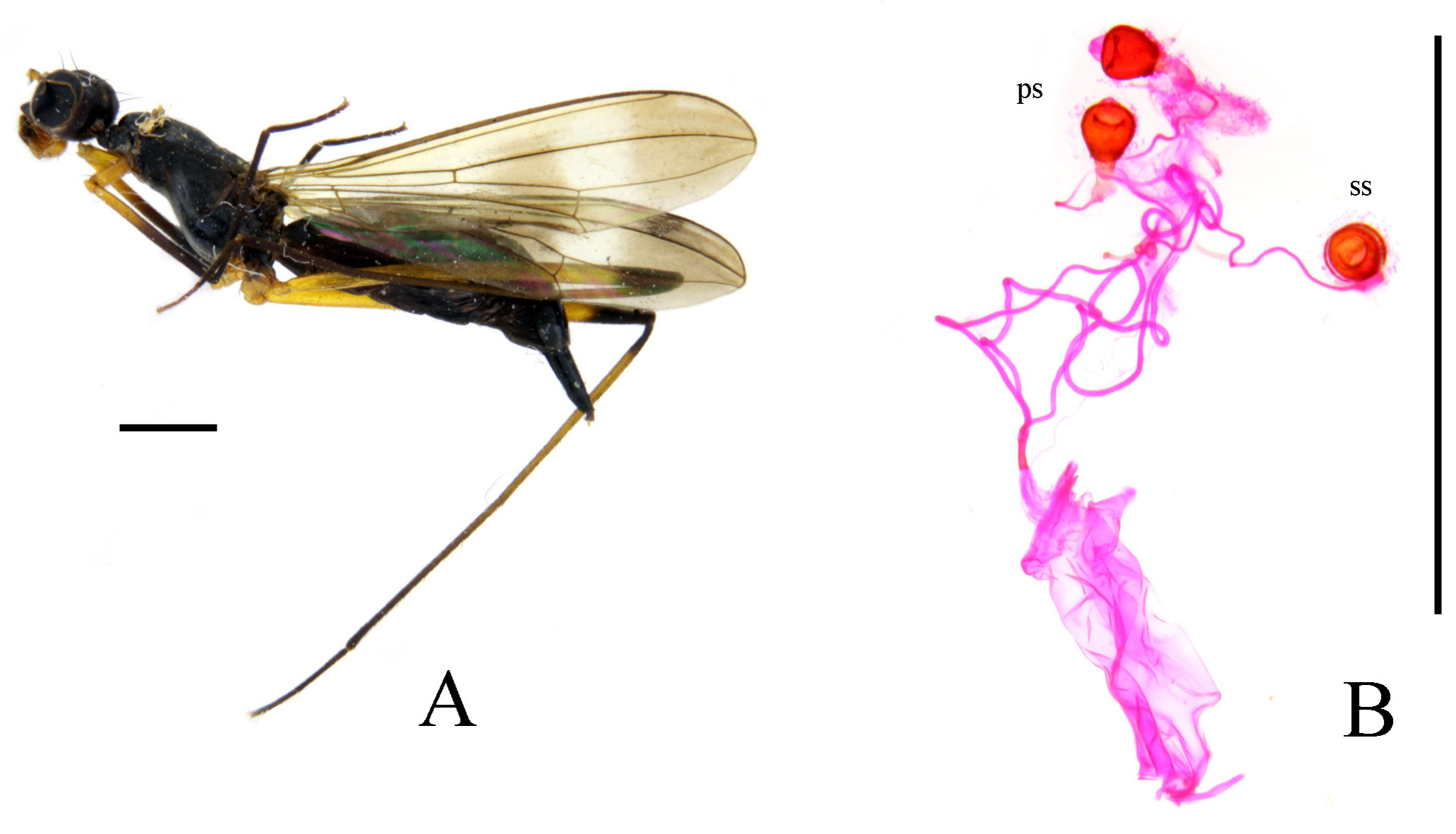
Abdominal tergites mostly dark and pubescent. Setulae on abdomen black to blackish-brown. Genital fork of male sternite 5 highly modified, usually armed with modified basal and medial tubercles ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 D), apex sometimes inflated ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 D). Abdominal membrane pale to dark gray, usually without pigmentation patterns on preserved specimens. Epandrium elongate and pointed anteroventrally, with sparse dorsal setae and long lateral ventral setae, moderately short on dorsal part, elongated and pointed anteroventrally ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 E), anteroventral epandrial arms long and pointed, articulating with posteroventral hypandrial arms ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 C). Surstylus well developed, with long apical and lateral setae. Cercus rounded, densely setulose. ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 E, F). Ejaculatory apodeme of sperm pump usually plate-like, very broad ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 G) (relatively small in C. ingensfurca sp. nov.). Distiphallus with trifurcate or paired terminal filaments. Pregonite ventrally setulose at apex ( Fig. 9 View FIGURE 9 D). Postgonite with 0–1 apical seta ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 G). Female oviscape over 1.2 X length of tergite 6 ( Fig. 17 View FIGURE 17 A). Three (2 + 1) small subspherical, somewhat bell-shaped spermathecae on long, unmodified ducts ( Fig. 17 View FIGURE 17 B).
Eggs (obtained from female abdomen of Cothornobata shuimanensis sp. nov.) about 1.4 mm in length, nearly 2.4 X as long as wide, with longitudinally elongated oval stripe ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 C).
Similar genera. Cothornobata most closely resembles Crepidochetus Enderlein, 1922 , but differs in having subparallel postocellar setae, a longitudinally striped or (usually) concolorous mesoscutum, mid femur with the basal half not notably thickened, and a distiphallus with long terminal filaments. In Crepidochetus , the postocellar setae are strongly convergent (generally crossed), the mesoscutum has a complete transverse grey-pruinose band immediately in front of the transverse suture, the mid femur is thickened on the basal half and the distiphallus lacks terminal filaments. Moreover, the contour of the mesoscutum in Oriental Cothornobata (as described above) is intermediate between the form typical of Metopochetus and Crepidochetus . In Metopochetus , the mesoscutum is strongly convex anteriorly and overhangs the pronotum, with the anterior margin of scutum forming an angle of less than 90 °. In Crepidochetus , the mesoscutum is only slightly convex anteriorly and gradually slopes towards the pronotum, with the anterior margin of scutum forming an angle of more than 90 ° (the Australian Cothornobata grallina McAlpine and C. levis McAlpine somewhat resemble Crepidochetus for this character). The scutellum in Oriental Cothornobata varies from flattened to slightly inflated, but it is less inflated than in Crepidochetus or Australian Cothornobata .
Relationships within Cothornobata . McAlpine (1998) characterized Cothornobata as a “diverse and widely distributed genus, which is poorly studied morphologically and may not be monophyletic”. We agree that Cothornobata as a whole is weakly supported as a monophyletic group, however the northern Oriental Cothornobata species appear to form a single clade (including the type species of the genus) based on the following characters: thorax elongated (length twice as long as height), tibiae without longitudinal grooves beyond basal quarter, genital fork large and with relatively strong and hirsute tubercles on inner surface, and distiphallus with trifurcate terminal filaments. The Sumatran speices C. viriata is inadequately known to assess as part of this clade, and the Australian Cothornobata species differ from the Oriental species in that the thorax is relatively short (length 1.5 X height); the inner surfaces of the genital fork have at most only weak, membranous tubercles and the distiphallus has paired terminal filaments.
Six species groups were established within the northern Oriental clade, as follows:
The C. uniseta group (including: C. atra sp. nov., C. curva sp. nov., C. elegantula sp. nov., C. longigonite a sp. nov., C. mentogensis sp. nov., C. nigrigenu ( Enderlein, 1922) , C. uniseta sp. nov.) was considered to be the basal clade, with following synapomorphies: only 1 strong fronto-orbital seta; distiphallus usually distinctly longer than phallapodeme, filaments relatively straight; pregonite not lobed apically; postgonite without apical seta.
The C. longifurca group ( C. cyanea (Hendel) and C. longifurca sp. nov.), is characterized by a genital fork that is distinctly elongate, reaching sternite 7 and with an elongate arm nearly twice as long as the base of genital fork.
The C. breviseta group ( C. breviseta sp. nov., C. fusca sp. nov., C. shuimanensis sp. nov.) is characterized by a genital fork with only short setulae on the arm, and a vestigial medial tubercle.
The C. pugnoa group ( C. paieroi sp. nov., C. pugnoa sp. nov., C. zhanga e sp. nov.) is characterized by genital fork that is divergent basally and strongly convergent apically like that of the C. uniseta group, but with the medial tubercle absent.
The C. vietnamensis group ( C. bubengensis sp. nov., C. vietnamensis sp. nov.) has a slender genital fork 1 / 5 as wide as base, with arms inflated and apically not strongly convergent.
The C. ingensfurca group (including only C. ingensfurca sp. nov.) differs markedly from other species by its huge genital fork with the basal tubercle of the arm indistinctly convex and the medial tubercle absent.
Czerny, L. (1932) Tyliden und Neriiden des Zoologische Museums in Hamburg. (Diptera). Stettiner Entomologische Zeitung, 93, 267 - 302.
Enderlein, G. (1922) Klassifikation der Micropeziden. Archiv fuer Naturgeschichte Berlin Abt A, 88 (5), 140 - 299.
Hendel, F. (1913) H. Sauter's Formosa-Ausbeute. Acalyptrate Musciden (Dipt.) II. Supplementa entomologicae, 38, 37 - 51.
McAlpine, D. K. (1998) Review of the Australian stilt flies (Diptera: Micropezidae) with a phylogenetic analysis of the family. Invertebrate Taxonomy, 12 (1), 55 - 134. http: // dx. doi. org / 10.1071 / IT 96018
Steyskal, G. C. (1977) Family Micropezidae. In: Delfinado, M. D. & Hardy, D. E. (Eds.), A catalog of the Diptera of the Oriental region, 3, pp. 13 - 20. [The University Press of Hawaii]
FIGURE 2. Cothornobata breviseta sp. nov., male. A, left lateral; B, head; C, wing; D, genital fork; E, genitalia, left lateral; F, genitalia, posterior; G, aedeagus and associated structures, left lateral; H, aedeagus and associated structures, ventral. Scale bars = 1 mm.
FIGURE 4. Cothornobata shuimanensis sp. nov., male. A, left lateral; B, head; C, wing; D, genital fork; E, genitalia, left lateral; F, genitalia, posterior; G, aedeagus and associated structures, left lateral; H, aedeagus and associated structures, ventral. Scale bars = 1 mm. Abbreviations: frorb s, fronto-orbital setae; i vt s, inner vertical seta; o vt s, outer vertical seta; poc s, postocellar seta.
FIGURE 5. Cothornobata shuimanensis sp. nov., female. A, left lateral; B, spermathecae and associated structures; C, egg. Scale bars = 1 mm.
FIGURE 7. Cothornobata cyanea (Hendel, 1913), male. A, left lateral; B, head; C, wing; D, genital fork; E, genitalia, left lateral; F, genitalia, posterior; G, aedeagus and associated structures, left lateral; H, aedeagus and associated structures, ventral. Scale bars = 1 mm. Abbreviations: arm, arm of genital fork; base, sternite 5 anterior to arm; b tub, basal tubercle; cerc, cercus; distph, distiphallus; ej apod, ejaculatory apodeme; epand, epandrium; hypd, hypandrium; m tub, medial tubercle; pgt, postgonite; phapod, phallapodeme; pregt, pregonite; sur, surstylus.
FIGURE 9. Cothornobata paieroi sp. nov. A, female, left lateral; B, genital fork; C, aedeagus and associated structures male terminalia, left lateral; D, details of aedeagus and associated structures, showing pregonite and postgonite, left lateral.
FIGURE 10. Cothornobata pugnoa sp. nov., male. A, left lateral; B, head; C, wing; D, genital fork; E, genitalia, left lateral; F, genitalia, posterior; G, aedeagus and associated structures, left lateral; H, aedeagus and associated structures, ventral. Scale bars = 1 mm.
FIGURE 17. Cothornobata longigonitea sp. nov., female. A, left lateral; B, spermathecae and associated structures. Scale bars = 1 mm. Abbreviations: ps, paired spermathecae; ss, single spermatheca.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Cothornobata Czerny, 1932
| Li, Xuankun, Marshall, Stephen A. & Yang, Ding 2015 |
Cothornobata
| Czerny 1932: 267 |
| Czerny 1932: 291 |
1 (by plazi, 2016-04-21 02:15:48)
2 (by ImsDioSync, 2017-01-14 11:15:00)
3 (by ImsDioSync, 2017-01-14 11:17:41)
4 (by ImsDioSync, 2017-06-21 06:45:39)
5 (by ExternalLinkService, 2019-09-26 11:20:04)
6 (by ExternalLinkService, 2022-01-30 01:28:20)
7 (by ExternalLinkService, 2022-02-15 19:31:21)
8 (by plazi, 2023-10-29 17:42:05)