Atanycolus tangmargensis Ahmed, I. & Kazmi, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5124.4.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1199ECE1-C313-459A-B046-9856B5A62631 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6413739 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6744F72C-7A94-4520-96B5-3962402099CF |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:6744F72C-7A94-4520-96B5-3962402099CF |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Atanycolus tangmargensis Ahmed, I. & Kazmi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
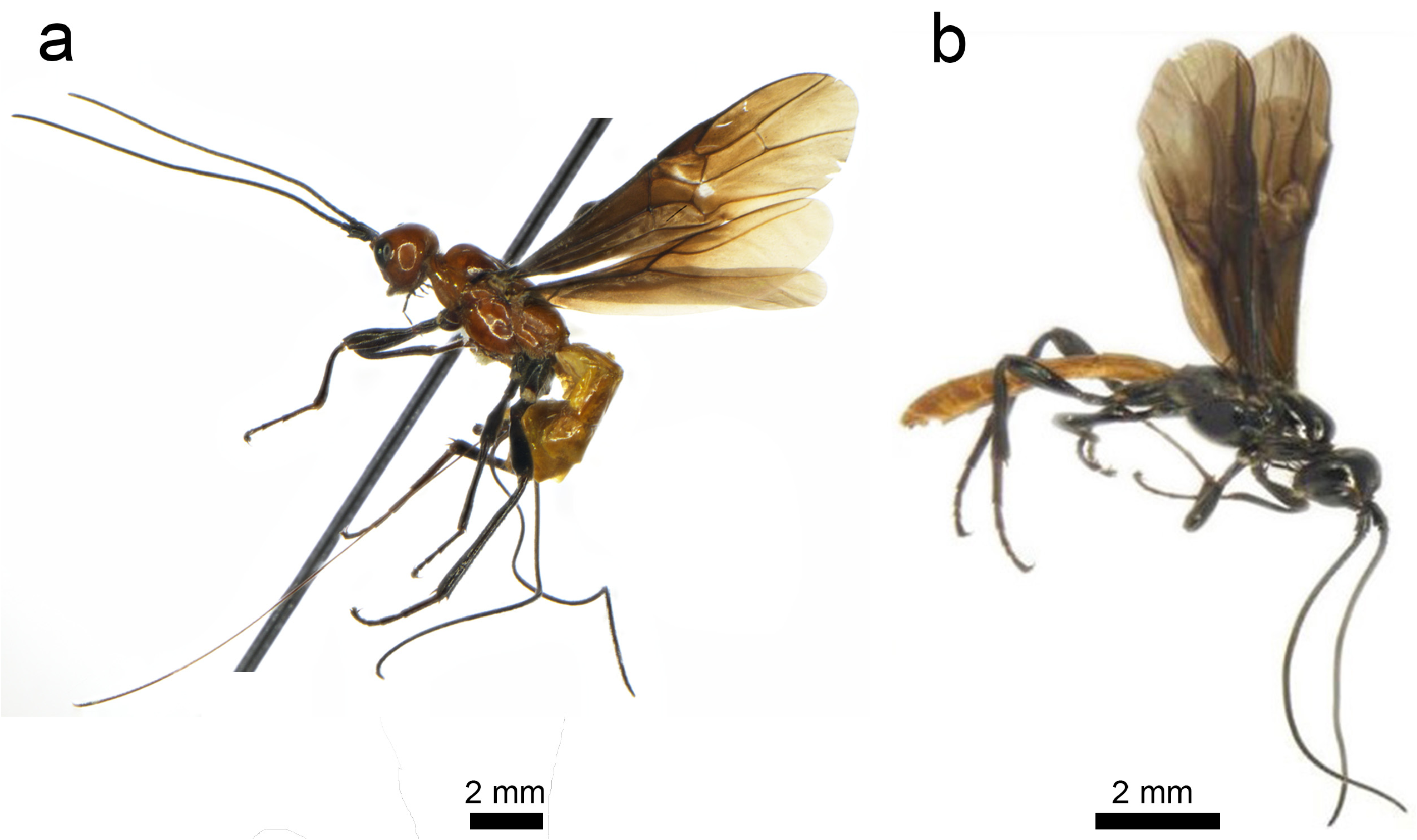
Atanycolus tangmargensis Ahmed, I. & Kazmi sp. nov. ( Figs. 2a–k View FIGURE 2 )
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:6744F72C-7A94-4520-96B5-3962402099CF
Type material: Holotype; ♀ (reg.no. 26125/H3), Tangmarg, Baramulla, Jammu and Kashmir, INDIA. coll. Z. Ahmed. 22.vii.2018. collected from pine logs by sweep net . Paratypes: 2♀♀ and 5♂♂ (reg.no. 26126/H3-26132/H3) collection data similar to holotype. All types deposited in National Zoological Collection ( NZC), Zoological Survey of India, Kolkata .
Description: Holotype: ♀, body length 13.1 mm; fore wing 11.2 mm; ovipositor sheath 14.9 mm.
Head: ( Figs. 2a–c View FIGURE 2 ) 1.6× wider than long dorsally, without any drop shaped black spot on stemmaticum, temples strongly expanded behind eyes, gena with sparse long hairs posteriorly, antenna slightly shorter than the fore wing, sub equal to body length, 54 antennomeres, the length of basal and apical flagellomeres about 2× their respective basal width, F1 slightly longer than F2, length of middle segments 1.5–1.6× the width, scape 2.3× as long as its maximum width, pedicel as long as its maximum width; the ration of width of mandibles: the distance between the inter-tentorial pits: the distance between the inter-tentioles and the compound eyes = 7:12:10; clypeus small narrow concave with few especially long hairs at its ventral raised margin; malar space 1.6× as long as basal mandibular width and more than half the eye length; face 1.6× as wide as long, smooth shiny medially, sparsely setose laterally and dorsally, eyes glabrous, dorsal eye length about half the temple; frons strongly concave medially with a longitudinal carina, vertex smooth, shiny with few hairs at posterior margin; length of maxillary palp 0.6× height of head; malar suture with some short setae; clypeus height: inter-tentorial distance: tentorio-ocular distance = 2: 4: 5.
Mesosoma: ( Figs. 2d, e View FIGURE 2 ) 1.6× as long as wide; mesoscutum with smooth and shiny notauli without any crenulations; scutellum triangular with small marginal hairs, scutellar sulcus narrow crenulated, not much deep; metanotum smooth, shiny; propodeum smooth, sparsely setose laterally; mesopleuron smooth, shiny with some setae posterior-ventrally; metapleuron sparsely setose.
Wings: ( Fig. 2f View FIGURE 2 ) Fore wing: Pterostigma 3.5× as long as its maximum width, SR1: 3-SR: r=5: 26: 6; 1-SR+M vein slightly curved, about 1.3× the length of vein 1-M; 2-SR: 3-SR: 1rm=12:23:10; m-cu straight, about 2.5× the length of 2-SR+M; cu-a interstitial. Hind wing: SC+R1:2-SC+R: 1r-m =12:1:2, basal posterior lobe with long setae marginally.
Legs: The ration of length of fore femur: fore tibia: fore tarsi; 7:8:14; outer hind tibial spur smaller than the inner one, covered by thick bristles; fore tibia with single sickle shaped spur; tarsomeres with few stout bristles apically; hind femur compressed much longer than wide, hind tibia 1.8× the femur length, telotarsus 2× the length of penultimate tarsomere; length of femur, tibia and basitarsus of hind leg 3.4, 10.4 and 8.3× their maximum width respectively.
Metasoma: ( Figs. 2g –i View FIGURE 2 ) Metasomal tergites entirely smooth, first metasomal tergite slender, with comparatively longer hairs on lateral margins, about 1.6× as long as its apical width, with median raised oval posteriorly widening area; the second tergite 1.5× as long as wide, with a medio-basal smooth triangular area narrowing posteriorly; 2 nd tergite longer than 3 rd, suture separating two smooth laterally and shallowly crenulate medially (fig. 2. H); the third metasomal tergite truncate posteriorly, more than twice as wide as long; hypopygium not extending much behind, ovipositior sheath densely setose, 1.2× the fore wing length, 1.18× the body length; ovipositor with a dorsal nodus and five ventral teeth ( Fig. 2j View FIGURE 2 ).
Colour. Reddish yellow; stemmaticum black; antenna and legs blackish brown, mandibles yellowish medially, black basally and apically, basal half covered with long white hairs, eyes dark brown, maxillary and labial palps dark brown; mesosoma reddish yellow; propodeum yellow, wings infuscate, pterostigma and veins dark brown, small light patch below 2SR+M; metasoma uniformly light yellow, with few very small white hairs; ovipositor yellow, ovipositor sheath brown.
Male: ( Fig. 1 b View FIGURE 1 )
Body length 5.54–6.76mm, fore wing length 3.7–5.96mm; antenna 56– 7.27mm with 46–54 segments, dark brown with scape and pedicel completely black; head and mesosoma black dorsally, propodeum brownish, all appendages uniformly dark brown except fore tarsus and fore coxae which are comparatively light brown; eyes with a yellow stripe around dorsal margin, metasoma light yellow.
Etymology: The species is named after the type locality in India, Tangmarg, Baramulla Jammu and Kashmir.
Distribution: India; Tangmarg, Baramulla, Jammu & Kashmir.
Remarks: The new species differ from the other two Indian species as follows: A. initiator have two parallel longitudinal, crenulated lateral grooves on either side on 2 nd metasomal tergite (absent in new species); whereas in A. hookeri the 2 nd metasomal tergite strongly irregularly striated, malar space 0.25× eye length (2 nd metasomal tergite smooth, malar space more than 0.5× eye length in new species).
The new species is similar in appearance to Chinese species A. lindemani Tobias, 1980 and can be separated from it by combination of following characters: mesosoma reddish yellow (brown in A. lindemani ); black spot on stemmaticum absent ( A. lindemani a large black drop-shaped spot present, extending to the posterior end of head); the suture separation second and third metasomal tergite shallowly crenulated medially (smooth in A. lindemani ); antenna 49–54 antennomeres (32–38 antennomeres in A. lindemani ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |