Hayesomyia triangula, Cheng, Ming & Wang, Xinhua, 2006
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.172093 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6258491 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E4EB34-FF89-3A16-A702-FB67FC50FA15 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Hayesomyia triangula |
| status |
sp. nov. |
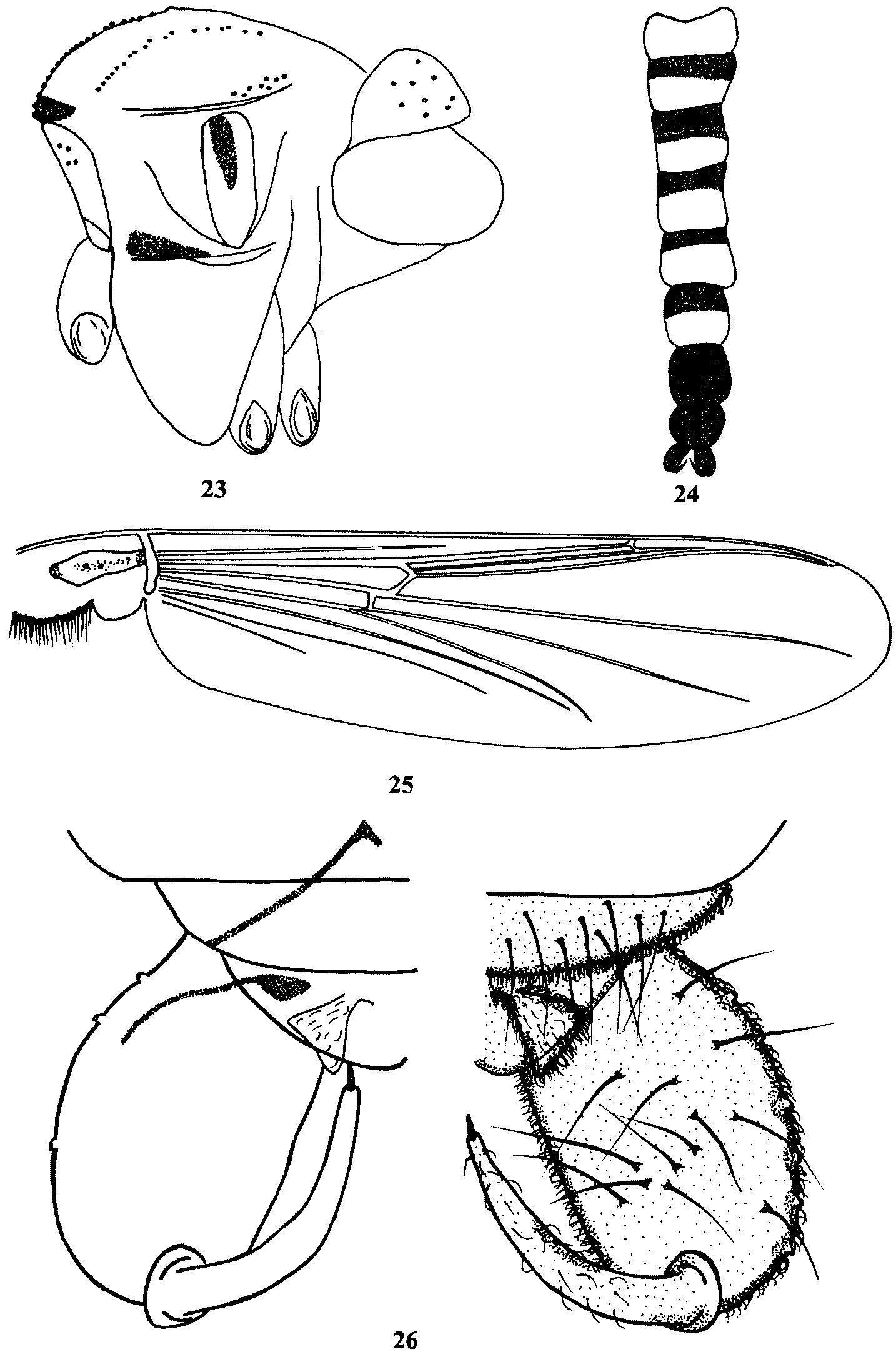
Hayesomyia triangula View in CoL sp. n. ( Figs.23–26 View FIGURES 23 – 26 )
Male imago (n = 2)
Dimensions. Total length 3.35–3.95 mm. Wing length 1.58–2.08 mm. Total length/ wing length 1.90–2.12. Wing length/length of profemur 1.98–2.13.
Coloration. Head yellow. Ground color of thorax yellow, brown pigmentation confined to narrow band on anteanepisternum II along anapleural suture, 1/4 of median anepisternum II and anterior border of scutum ( Fig. 23 View FIGURES 23 – 26 ). Tergites II–VI yellow, each with broad brown basal band; tergite VII–VIII entirely brown ( Fig. 24 View FIGURES 23 – 26 ). Hypopygium brown. Wings without dark markings. ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 23 – 26 )
Head. AR 1.4. Temporal setae 14; including 10 verticals and 4 postorbitals. Clypeus with 26 setae. Tentorium 195 µm long, 50 µm wide. Palpomere 1–5 lengths (µm): 50; 88; 180; 200; 340. (Head of No. 24452 was lost).
Wing ( Fig. 25 View FIGURES 23 – 26 ). VR 0.78–0.92. Brachiolum with 2 long setae. Squama with 20–28 setae.
Thorax. Antepronotal setae 4; dorsocentrals 18; acrostichals 20–21; prescutellars 2; supraalars 1–2; prealars 8–10; scutellars 9–12.
Legs. Spur on fore tibia 35–43 µm long with 5 lateral teeth. Spurs on mid tibia 45–48 and 53–58 µm long with 6 and 8 lateral teeth. Spurs on hind tibia 45–48 and 50–65 µm long with 6 lateral teeth. Tibial comb on hind leg with 5 setae. Lengths (µm) and proportions of legs as in Table 6 View TABLE 6 .
Hypopygium ( Fig. 26 View FIGURES 23 – 26 ). Tergite IX with irregular row of 14–16 setae. Gonocoxite 168–188 µm long. Gonostylus 155–175µm long. Median volsella trianglular 23–23 µm long, 20–35 µm wide. HR 1.07–1.08. HV 2.16–2.26.
Diagnosis
This new species differs from other known species of the genus Hayesomyia in having a triangular median volsella, which is unique for the genus. All other known species have the median volsella bifurcate, or at least apically concave.
TABLE 6. Lengths (µm) and proportions of legs of H. triangula sp. n.
| fe | ti | ta1 | ta2 | ta3 | ta4 | ta5 | LR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1 | 800–975 | 980–1100 | 830–1000 | 420–500 | 310–310 | 210–250 | 120–140 | 0.85–0.91 |
| p2 | 850–975 | 860–1025 | 530–670 | 240–300 | 190–240 | 160–180 | 90 | 0.62–0.65 |
| p3 | 740–925 | 1075–1250 | 870–1000 | 460–510 | 350–370 | 220–250 | 130 | 0.80–0.81 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Tanypodinae |
|
Genus |