Rhabdomiris koreanus Kim et Jung, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4688.3.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:CCB54C2C-6812-47FF-B6E6-D5C33BFE15A1 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E187EC-1E51-2F36-489A-FF51FC7AFAFD |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Rhabdomiris koreanus Kim et Jung |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Rhabdomiris koreanus Kim et Jung sp. nov.
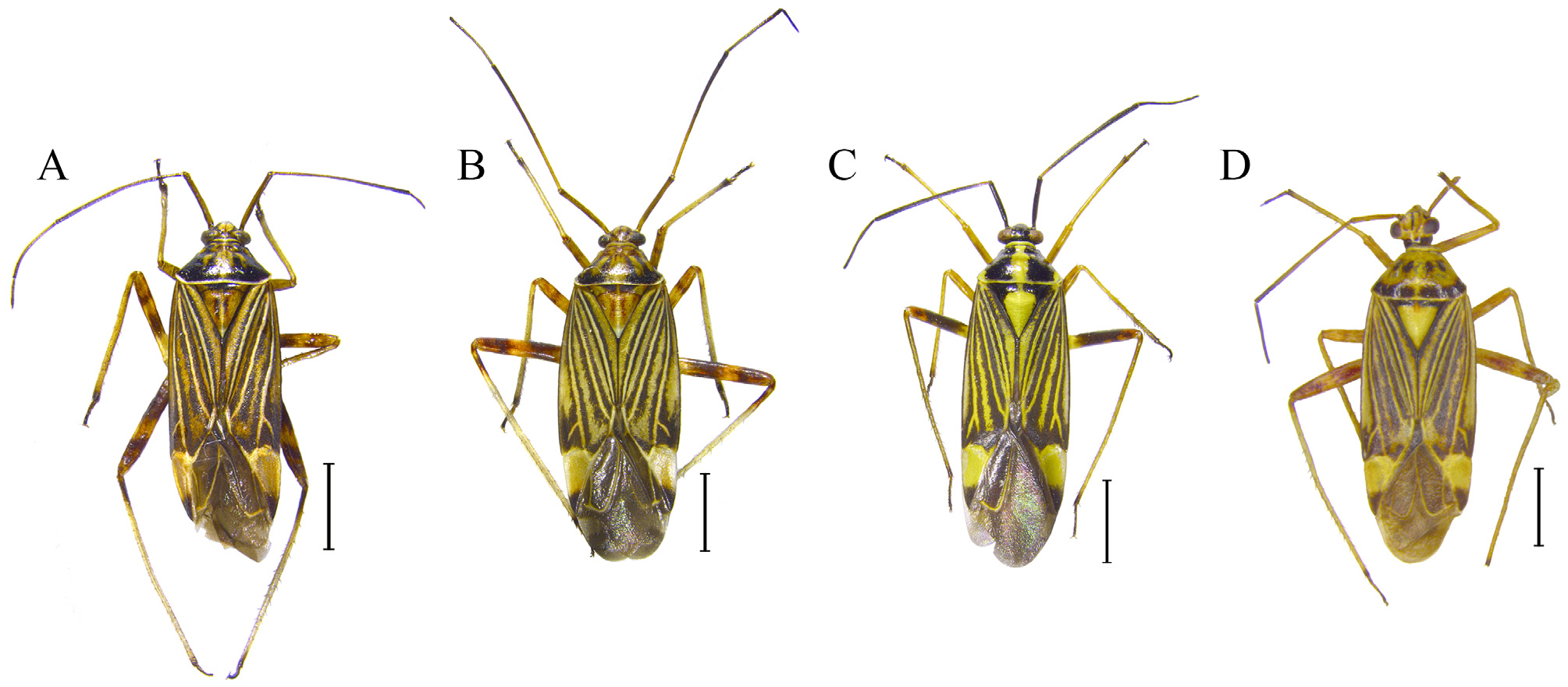
( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 A–B, 2A–H)
Rhabdomiris striatellus Oh et al., 2018: 481 View in CoL (misidentification for Korean record).
Diagnosis: Distinguished by body brownish and somewhat larger than the other species of this genus; basal part of third antennal segment pale brown; frons pale brown with narrow longitudinal dark stripe; pronotum yellowish brown with dark stripes, connecting to posterior dark part; scutellum brown with dark stripe medially; mesoscutum brown, median dark brown ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 A–B); left paramere relatively thick, angled dorsally, process of sensory lobe relatively short and straight, lateral tooth small or indistinctly developed ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 A–B); right paramere thick, hypophysis weakly coiled apically ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ); endosomal spicule much longer than membranous lobe, slightly broader subapically, thin and sharp apically; lateral sclerite I thick and its apex blunt; lateral sclerite II broad with tiny spinules in upper part; medial sclerite shorter than spicule and as long as membranous lobe ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 D–F); sclerotized ring elongated in shape; sclerotized perimeter of combined common oviduct and dorsal wall of genital chamber broadly developed ( Fig. 2G View FIGURE 2 ); dorsal structure developed, anterior part with distinct small spinules ( Fig. 2H View FIGURE 2 ).
Description: Male: Body elongated-oval, lateral margin of hemelytra subparallel, length 8.30–8.48. COLOR- ATION: brown with dark/pale brown stripes. Head: brown; frons pale brown; clypeus pale brown with dark longitudinal stripe; antennae dark brown, basal part of third antennal segment pale brown except for base and apical part; labium yellowish brown, first labial segment pale brown with two longitudinal dark stripes, 1/2 apical part of fourth labial segment dark brown. Thorax: pronotum dark brown, with one large brown macule and two smaller macule medially, posterior margin of pronotum pale brown; collar pale brown; callus brown with dark spot; scutellum brown with a pair of dark stripes medially, mesoscutum brown with dark brown spot medially; ostiole peritreme pale brown; hemelytra brown with dark brown stripes; clavus brown with 2 dark brown stripes along with claval vein and claval suture, commissure dark brown; corium brown with 4 dark brown stripes along with radial and cubital veins; embolial margin dark brown; cuneus brown, apex of cuneus dark brown, paracuneus dark brown; membrane grayish dark brown, vein brown; legs brown; hindfemur dark brown with pale brown spots, 1/3 basal part of hindfemur pale brown; base and apex of tibia dark brown with dark spines, basal part of hindtibia dark brown; tarsus dark brown. Abdomen: dark brown with pale brown patches laterally. SURFACE AND VESTITURE: glossy, head covered with sparsely silvery short pubescence; antennae with erected short setae, apex of first antennal segment with dense erect setae; labium covered with short pubescence; pronotum glabrous without pubescence; scutellum covered with sparsely short pubescence; hemelytron covered with short pubescence. STRUCTURE: Head: vertex width shorter than first antennal segment; second antennal segment about twice as long as third antennal segment, first antennal segment thick, proportion of antennal segments 1.4:3.2:1.7:0.7; labium reaching hind coxae; proportion of first to fourth labial segments 0.5:0.6:0.6:0.9. Thorax: pronotum trapezoid, mesal pronotal length longer than width of anterior margin, callus swollen; scutellum equilateral; lateral margin of hemelytra subparallel and slightly rounded; cuneal fracture developed; legs slender. Abdomen: rounded, reaching corium. GENITALIA: Left paramere thick and angled dorsally with hook-shaped hypophysis, sensory lobe with noticeable process, process short and straight ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ), lateral tooth small or indistinctly developed in lateral view ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ); right paramere thick with long hypophysis, hypophysis distinctly coiled apically ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ); endosoma membranous, secondary gonopore slightly wider than maximal width of ductus seminis part, with one long spicule and three sclerites; sp much longer than membranous lobe, broader subapical part, thin and sharp apically; ls I thick and its apex blunt and slightly curved; ls II broad with tiny spinules in upper part; ms bifurcated, shorter than sp and as long as membranous lobe, length of each part different ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 D–F).
Female: Ovoid, length 8.21–8.62. COLORATION: as in male except for antennae brown, 1/2 apical part of second antennal segment dark brown and paler pronotum with narrower dark patterns. SURFACE AND VESTITURE: as in male. STRUCTURE: more rounded oval in overall shape than body of male; except for proportion of antennal segments 1.4: 3.3: 1.8: 0.7; proportion of labial segments 0.6: 0.6: 0.7: 0.9. GENITALIA: sr extremely elongated oval, remoted each other, spgc largely developed, concave medially ( Fig. 2G View FIGURE 2 ); irl not surpassing irs, irl broader than ds, with distinct small spinules, ds oval and broadly developed, small spinules in only anterior part ( Fig. 2H View FIGURE 2 ).
Measurements (in mm): Male (n = 3)/female (n = 3): Body length, clypeus–apex of membrane:8.30–8.48/8.21– 8.62; head length, excluding collar: 0.45–0.48/0.51–0.52; head width, including compound eyes: 1.19–1.22/1.19– 1.21; vertex width: 0.51–0.52/0.54–0.56; 1 st antennal segment length: 1.44–1.46/1.35–1.49; 2 nd antennal segment length: 3.21–3.27/3.29–3.42; 3 rd antennal segment length: 1.74–1.79/1.77–1.93; 4 th antennal segment length: 0.70– 0.72/missing–0.74; 1 st labial segment length: 0.50–0.53/0.64–0.74; 2 nd labial segment length: 0.59–0.62/0.64–0.69; 3 rd labial segment length: 0.61–0.63/0.68–0.74; 4 th labial segment length: 0.90–0.93/0.94–0.96; total labial length: 2.60–2.71/2.74–3.06; anterior pronotal margin width (straight): 0.87–0.88/0.80–0.84; mesal pronotal length: 0.95–1.00/0.87–0.96; posterior pronotal margin width (straight): 2.23–2.26/2.19–2.31; anterior margin of scutellum width (straight): 1.35–1.38/1.42–1.53; mesal length of scutellum: 1.45–1.51/1.60–1.70; outer embolial margin length (straight): 4.22–4.34/4.13–4.37; outer cuneal margin length (straight): 1.49–1.52/1.51–1.53; maximum width across hemelytra: 1.28–1.33/1.44–1.47; hindleg (femur: tibia: tarsus): 3.10–3.21: 4.81–4.89: 0.72–0.74/3.19–3.27: 4.68–4.91: 0.77–0.80.
Specimen Examined: Holotype: [ CNU] 1♂, Myeonggae-ri , Nae-myeon , Hongcheon-gun, Gangwon-do, South Korea, by Light trap, 13.vi.2015, W.G. Kim leg. ; Paratypes: [ CNU] 2♀♀, Myeonggae-ri , Nae-myeon , Hongcheongun, Gangwon-do, South Korea, by Light trap, 28.v.2015, J.Kim leg. ; Paratypes: [ CNU] 2♂♂ 3♀♀, Gimhwa-eup , Cheorwon-gun, Gangwon-do, South Korea, on Quercus acutissima , 14.v.2018, J.Kim leg.
Distribution: Korea.
Hosts: Quercus acutissima , Q. mongolica (Fagaceae) .
Etymology: Named after type locality, the Korean Peninsula.
Biology: The nymphs and adult of this species are found on its host plants Quercus acutissima , and Q. mongolica , especially flowers of this plant in May. This species is also sometimes attracted by light trap in late May to middle June.
Remarks: This new species is similar in general appearance to European species R. striatellus , but this new species can be distinguished by external and genital structures: pale frons with narrow dark longitudinal stripe; brownish scutellum with dark markings connecting to posterior dark band; dark middle part of mesoscutum; much longer endosomal spicule than membranous lobe; elongated sclerotized rings; largely developed dorsal structure with small spinules in only anterior part; and posterior wall without lobes.
| CNU |
Capital Normal University, College of Life Sciences |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Rhabdomiris koreanus Kim et Jung
| Kim, Junggon, Kim, Young Jin, Lim, Jongok & Jung, Sunghoon 2019 |
Rhabdomiris striatellus
| Oh M. & Yasunaga, T. & Duwal, R. K. & Lee, S. 2018: 481 |