Glyptothorax amnestus, Ng, Heok Hee & Kottelat, Maurice, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4188.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:AA85050E-7653-44BE-9330-AC617BFE6DF8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6063744 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E0BE0E-FF9D-541F-FF58-FCB6FAE550CE |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Glyptothorax amnestus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Glyptothorax amnestus new species
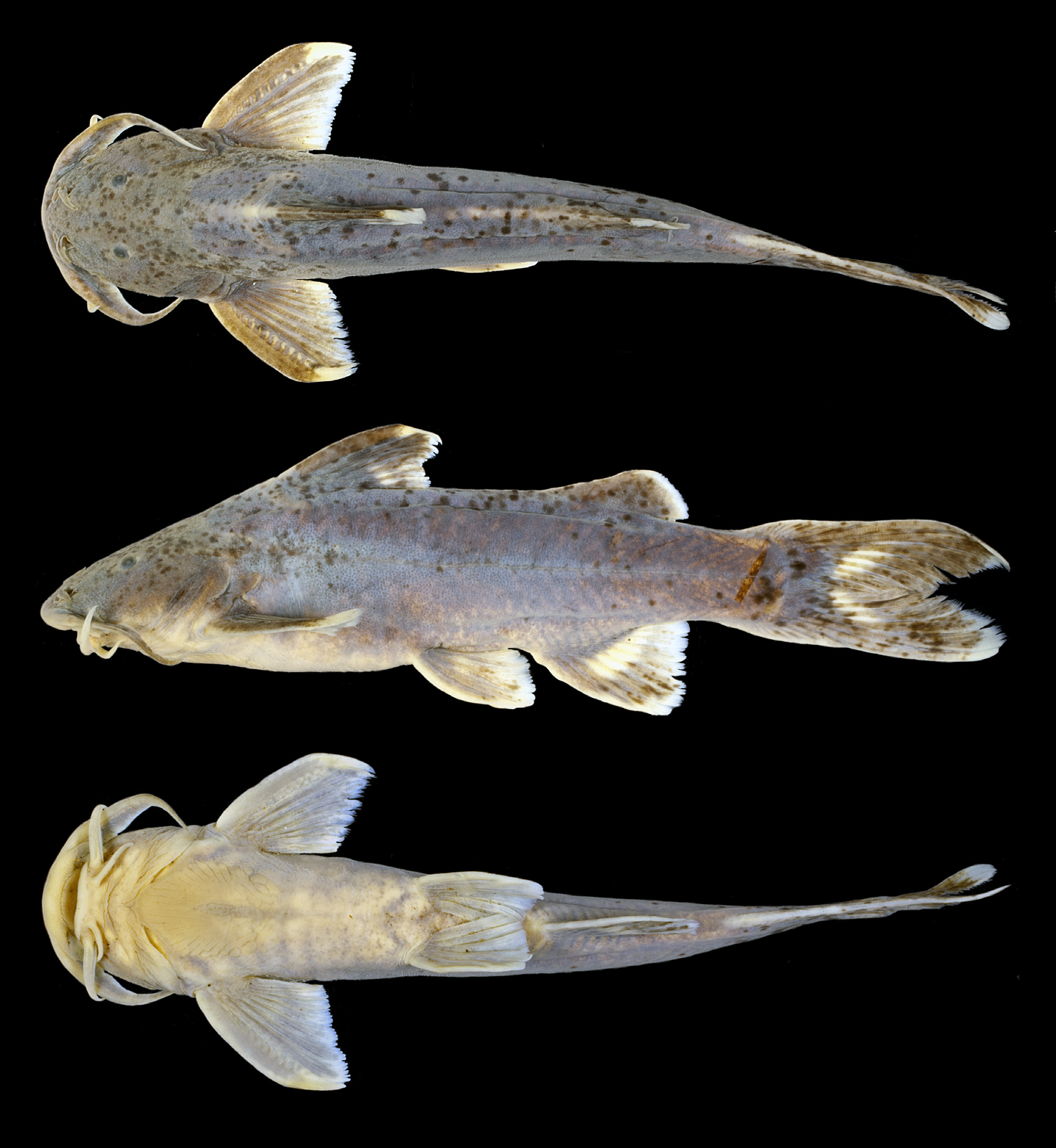
( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 )
Pimelodus cyanochloros (non Bleeker, 1846)— Bleeker, 1852a: 89; 1854: 65; 1858a: 25; 1858f: 1.
Pimelodus platypogon (non Valenciennes, 1840)— Bleeker, 1852b: 591.
Glyptosternon platypogon (non Valenciennes, 1840) Bleeker, 1858b: 225; 1858c: 217; 1858f: 1; 1860a: 47; 1860b: 1.
Glyptothorax platypogon View in CoL (non Valenciennes, 1840)—Bleeker, 1862: 63, Pl. 83 Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 (in part); Fowler, 1904: 500; 1915: 220; Kottelat et al., 1993: 76, pl. 37 (in part); Tan & Ng, 2000: 290.
Glyptosternum platypogon (non Valenciennes, 1840)— Günther, 1864: 187; Volz, 1907: 175; Weber & de Beaufort, 1913: 267 (in part); Tan & Kottelat, 2009: 21.
Glyptosternum majus (non Boulenger, 1894)— Regan, 1920: 308.
Glyptothorax schmidti View in CoL (non Volz, 1904)—Ng & Hadiaty, 2008: 146 (in part), Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 D, Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 C; Jiang et al., 2011: 280.
Glyptothorax aff. schmidti View in CoL — Tan & Kottelat, 2009: 21.
Type material. Holotype: MZB 17214, 88.1 m SL: Sumatera Barat: Padang Panjang, on road from Padang to Bukittinggi; N. K. Ng & J. C. - Y. Lai, 8 July 2003.
Paratypes: SUMATRA: UMMZ 155703 View Materials (2), 31.9–43.8 mm SL ; Sumatra; A. Thienemann, 15 March 1929. ZMA 119.982 View Materials (1), 77.4 mm SL ; Sumatera Utara: Medan. CMK 4537 (6), 36.4–56.7 mm SL ; Sumatera Utara: Sungai Seruai at Biru Biru; P. G. Bianco & M. Kottelat, 28 November 1984 . ZMA 115.522 View Materials (1), 55.7 mm SL; Sumatera Barat: Batang Harau at Harau Canyon ; E. Jacobson, 1932 . ANSP 27286 (8), 35.6–58.6 mm SL; CAS-SU 8022 View Materials (4), 45.4–51.6 mm SL; Sumatera Barat: Kabupaten Tanah Datar, Batusangkar ; A. C. Harrison & H. M. Hiller, 1901 . ZRC 54231 (5), 51.2–80.9 mm SL; Sumatera Barat: Danau Singkarak drainage, Hulu Sungai Paninggahan; D. Roesma, 2008. CMK 4633 (2), 25.5–27.8 mm SL ; Sumatera Barat: Sungai Sumpur, tributary of Danau Singkarak; P. G. Bianco & M. Kottelat, 4 December 1984 . CMK 4645 (4), 33.1–80.0 mm SL; Sumatera Barat: Sungai Dareh at Keju Aro, km 24 on road from Solok to Padang; P. G. Bianco & M. Kottelat, 5 December 1984. UMMZ 243372 View Materials (2), 26.5–56.3 mm SL ; Sumatera Barat: tributary of Batang Lasi at Muarakelaban, ca. 26 km towards Solok on Trans-Sumatra Highway in the direction of Padang , 0°42'48"S 100°47'13"E; H. H. Ng, 14 December 2003 GoogleMaps . UMMZ 243337 View Materials (5), 49.7–66.4 mm SL; Sumatera Barat: market at Sungaidareh , 0°58'S 101°30'E; H. H. Ng et al., 14 December 2003 GoogleMaps . ZMA 119.981 View Materials (1), 44.3 mm SL; Sumatera Barat: Batang Pangian; E. Jacobson, March 1914 . ZMA 115.521 View Materials (2), 47.4–54.4 mm SL; Jambi: Danau Kerinci; E. Jacobson, July 1915 . ZRC 38708 (6), 25.0–55.0 mm SL; Jambi: Kerinci, Sungai Seli , 2°27'36"S 101°33'57"E; H. H. Tan et al., 11 June 1996 GoogleMaps . UMMZ 155699 View Materials (2), 41.9–49.8 mm SL; Sumatera Selatan: Musi River at Air Simpang; A. Thienemann, 6 May 1929 . ZRC 53526 (6), 33.3–68.2 mm SL; CMK 20533 (7), 41.3–58.0 mm SL; Sumatera Selatan: market in Lahat, Lematang (Musi) drainage, 3°48'S 103°32'E; M. Kottelat & H.H. Ng, 9 May 2008 GoogleMaps . ZRC 49141 (2), 73.0– 87.9 mm SL; Bengkulu: southern region; T. Sim et al., September 2003 . ZRC 54230 (6), 51.4–59.9 mm SL; Bengkulu: Batu Layang; D. Roesma, 2008. USNM 87967 About USNM (2), 28.1–31.0 mm SL ; Bengkulu: rice fields near Kepahiang; H. C. Kellers, 14 January 1926 . ZMA 115.520 View Materials (4), 45.0– 91.2 mm SL; Sumatera Selatan: Pagaralam, P. A. Ouwens, 23 November 1918 .
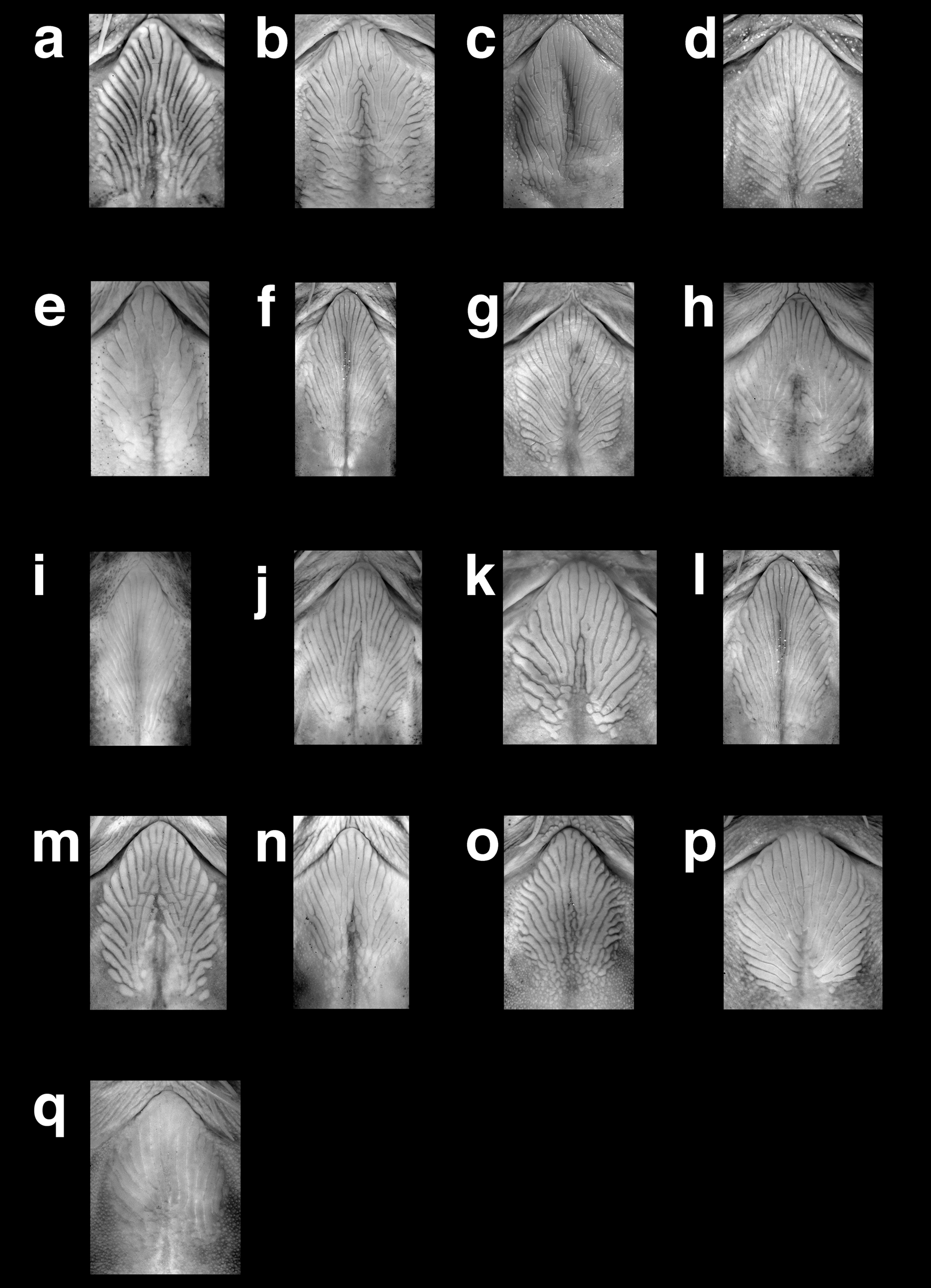
Diagnosis. Glyptothorax amnestus differs from congeners in Sundaland except for G. decussatus , G. major and G. plectilis in having (vs. lacking) anteromedial striae in the thoracic adhesive apparatus. It differs from G. decussatus in lacking (vs. having) a dark vertical bar at the base of the caudal fin in the shape of an irregular cross, from G. major in having the anterolateral edges of the thoracic adhesive apparatus almost straight (vs. markedly concave; compare Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 a and 3m) and a deeper caudal peduncle (9.8–11.2% SL vs. 7.7–10.1), and from G. plectilis in having an oblong thoracic adhesive apparatus with almost straight anterolateral edges (vs. ovate with gently convex anterolateral edges; Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ) and non-prominent tubercles of uniform size (vs. with prominent, enlarged tubercles) along the flanks. The following unique combination of characters further distinguishes G. amnestus from Sundaic congeners: approximately half of premaxillary toothband exposed when mouth is closed; eye diameter 6–10% HL; head width 19.9–23.0% SL; margin of dorsal fin concave; dorsal to adipose distance 17.9–23.4% SL; maximum height of adipose fin 2.2–2.6 times in its length, straight dorsoposterior margin of adipose fin; body depth at anus 15.3–20.6% SL; post-adipose distance 15.8–19.7% SL; caudal peduncle depth 1.4– 2.2 times in its length and 1.4–2.1 times in body depth at dorsal-fin origin; uniformly dark body without contrasting markings; and dark spots on dorsal and lateral surfaces of body.
Description. Morphometric data in Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Head depressed; body subcylindrical. Dorsal profile rising evenly from tip of snout to origin of dorsal fin, then sloping gently ventrally from origin of dorsal fin to end of caudal peduncle. Ventral profile straight to anal-fin base, then sloping gently dorsally from anal-fin base to end of caudal peduncle. Anus and urogenital openings located at vertical through middle of adpressed pelvic fin. Skin tuberculate, with tubercles of even size on sides of body. Lateral line complete and midlateral. Vertebrae 16+17=33* (3), 16+18=34 (2), 17+17=34 (3), 18+16=34 (1), 17+18=35 (4), 18+17=35 (4), 19+16=35 (2) or 18+18=36 (2).
Head depressed and broad, triangular when viewed laterally. Snout prominent. Anterior and posterior nares large and separated only by base of nasal barbel. Gill opening broad, extending from ventral margin of posttemporal to isthmus. First branchial arch with 2+6 (8), 2+7* (8) or 2+8 (4) rakers. Bony elements of dorsal surface of head covered with thick, tuberculate skin. Eye ovoid, horizontal axis longest; located entirely in dorsal half of head.
Barbels in four pairs. Maxillary barbel long and slender, extending to middle of pectoral-fin base. Nasal barbel slender, extending to midway between its base and anterior orbital margin. Inner mandibular-barbel extending to midway between its base and that of pectoral spine. Outer mandibular barbel extending to two-thirds of distance between its base and that of pectoral spine.
Mouth inferior, premaxillary tooth band partially (approximately half) exposed when mouth is closed. Oral teeth small and villiform, in irregular rows on all tooth-bearing surfaces. Premaxillary teeth appearing in single broad semilunate band. Dentary teeth in a single crescentic band, consisting of two separate halves tightly bound at midline.
Thoracic adhesive apparatus consisting of keratinized striae in an elongate oblong field extending from isthmus to almost posterior limit of pectoral-fin base ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 a); anterolateral edges of adhesive apparatus almost straight. Anteromedial striae present. Narrow, v-shaped medial pit on posterior half.
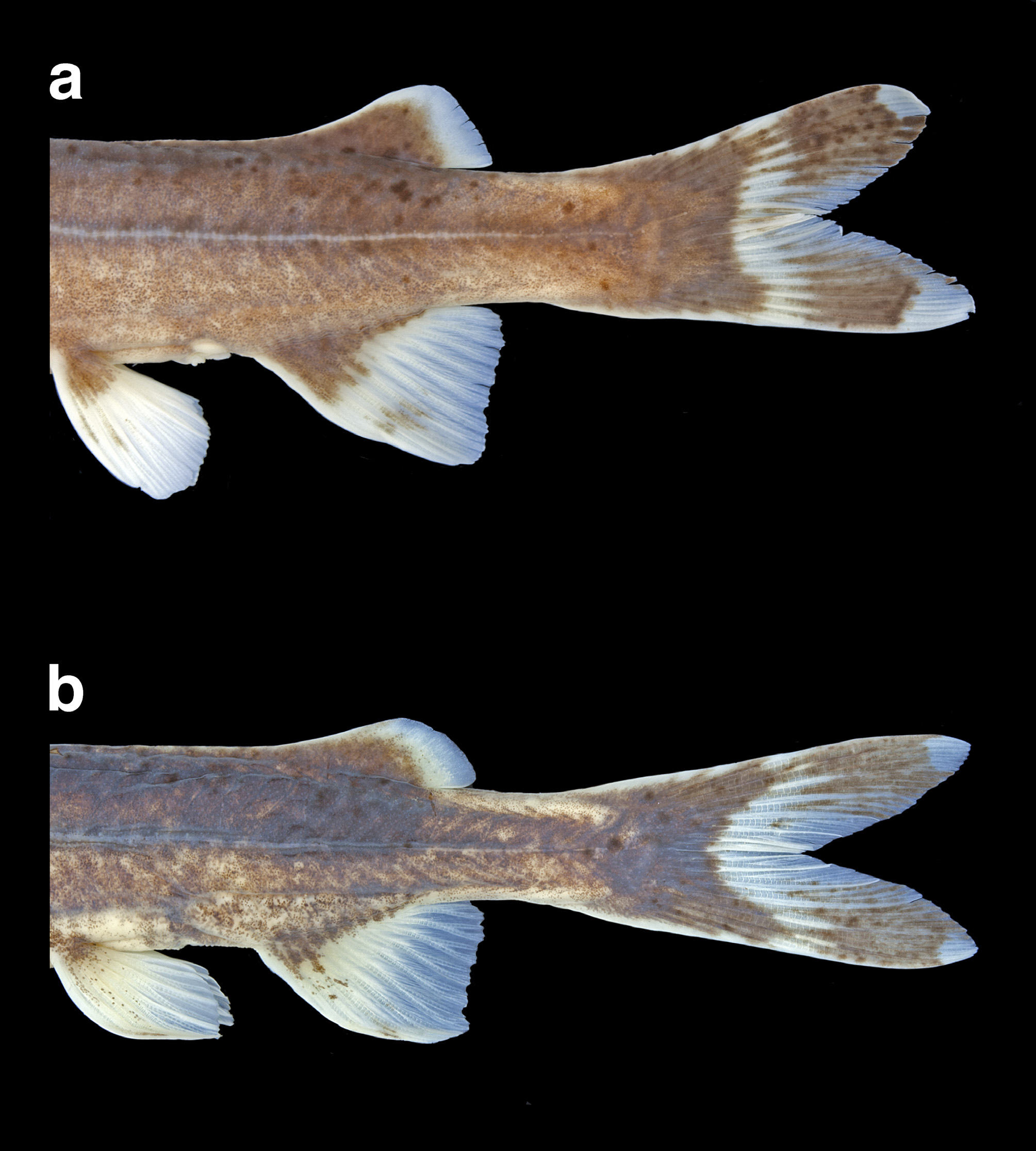
Dorsal fin located above anterior third of body, with I,6 (20) rays; fin margin concave; spine short and straight, smooth on anterior margin; posterior margin smooth in some individuals and with up to 6 low projections on others. Adipose fin with anterior margin straight or slightly concave and posterior margin straight. Caudal fin strongly forked, with lower lobe slightly longer than upper lobe and i,7,8,i (20) principal rays. Procurrent rays symmetrical and extending only slightly anterior to fin base. Anal-fin base vertically opposite adipose-fin base. Anal fin with straight anterior margin and straight or slightly concave posterior margin; with iv,8* (13), iv,8,i (2) or iv,9 (5) rays. Pelvic-fin origin at vertical through posterior limit of dorsal-fin base. Pelvic fin with slightly convex margin and i,5 (20) rays; tip of adpressed fin not reaching anal-fin origin. Pectoral fin with I,7,i (1), I,8* (18) or I,8,i (1) rays; posterior fin margin slightly concave; anterior spine margin smooth, posterior margin with 4–12 ( holotype =12) serrations.
Coloration. In 70% ethanol: dorsal and lateral surfaces of head and body gray to grayish brown, fading to light gray or beige on ventral surfaces. Dorsal and lateral surfaces of head and body with small irregular darker spots. A thin, light brown mid-dorsal stripe extending from base of last dorsal-fin ray to origin of adipose fin; stripe absent in some individuals. Laterosensory pores rimmed in beige, imparting appearance of a diffuse light brown or light gray midlateral line in some individuals. Dorsal and ventral surfaces of caudal peduncle slightly paler in some individuals. All fins with rays proximally gray to grayish brown, becoming hyaline more distally, and diffuse melanophores on fin membranes. Pectoral and pelvic fins with gray or grayish brown on bases of rays and hyaline posterior margin. Anal fin with gray or grayish brown base; gray or grayish brown spot on anterior third of fin present in some individuals. Adipose fin gray or grayish brown with hyaline distal margin. Base of caudal fin with dark crescent in most individuals. Each caudal-fin lobe with irregular, elongate gray or grayish brown blotch on about half of outer fin; most of inner rays of lobes hyaline. Maxillary and nasal barbels gray or grayish brown dorsally, light brown or light gray ventrally. Mandibular barbels beige or light gray.
Habitat. Glyptothorax amnestus is typically found in upland rivers and streams with a moderately fast current and a substrate composed predominantly of rocks and gravel ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ).
Distribution. Glyptothorax amnestus is known from middle and upper portions of river drainages throughout Sumatra except for its northern tip, from the Deli River drainage southwards to the Musi River drainage ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ). It has also been recorded by Bleeker (1852a) from Belitung Island, but this awaits verification.
Etymology. The specific epithet is Latinized from the Greek adjective ἀµνηστος, meaning forgotten. This is used in allusion to the fact that this species has been misidentified for more than 170 years.
Comparisons. Glyptothorax amnestus superficially resembles G. platypogon , but can be diagnosed from it by the morphology of the thoracic adhesive apparatus as outlined in the diagnosis. It further differs from G. platypogon in having dark spots on the dorsal and lateral surfaces of the body (vs. absent) and in having a taller adipose fin (maximum height 2.2–2.6 times in its length vs. 3.4). Besides G. plectilis , whose differences with G. amnestus are already outlined in the diagnosis, there are six other congeners known from Sumatra: G. famelicus , G. f u s c u s, G. keluk , G. ketambe , G. platypogonides and G. schmidti . Glyptothorax amnestus can be further distinguished from G. famelicus , G. ketambe , and G. schmidti in lacking (vs. having) a prominent pale midlateral stripe on the body, and in having a deeper body (depth at anus 15.3–20.6% SL vs. 11.4–15.7) and a deeper caudal peduncle (9.8–11.2% SL vs. 5.8–8.9), and from G. schmidti in having a shorter dorsal to adipose distance (17.9–23.4% SL vs. 23.9–28.1). It further differs from G. f u s c u s in having a concave (vs. straight) margin of the dorsal fin and a less tapering body, as manifested by the smaller ratio between the body and caudal peduncle depths (caudal peduncle depth 1.4–2.1 times in body depth at dorsal-fin origin vs. 2.3–2.8), from G. keluk in having a broader snout when viewed dorsally ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 ), a deeper caudal peduncle (9.8–11.2% SL vs. 7.7–8.8) and a straight (vs. convex) dorsoposterior margin of the adipose fin ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ), and from G. platypogonides in having a smaller eye (diameter 6–10% HL vs. 11–14), a deeper body (depth at anus 15.3–20.6% SL vs. 12.1–14.8), and a deeper caudal peduncle (9.8–11.2% SL vs. 6.5–7.9). Compared to the remaining Sundaland congeners, G. amnestus is further distinguished from G. exodon in having approximately half of the premaxillary toothband (vs. almost entire toothband) exposed when the mouth is closed, a smaller eye (diameter 6–10% HL vs. 10–13), a wider head (19.9–23.0% SL vs. 16.0–18.1), a deeper body (depth at anus 15.3–20.6% SL vs. 13.8–15.8), a deeper caudal peduncle (9.8–11.2% SL vs. 6.8–7.3) and a shorter postadipose distance (15.8–19.7% SL vs. 21.5–24.0), from G. nieuwenhuisi in having a deeper caudal peduncle (9.8– 11.2% SL vs. 7.0–8.4), and from G. pictus in having a uniformly dark body without contrasting markings (vs. paler body with dark vertical bars at adipose-fin base and base of caudal fin). It further differs from G. platypogon in having a straight (vs. convex) dorsoposterior margin of the adipose fin, and from G. prashadi in having a shorter and deeper caudal peduncle (caudal peduncle depth 1.4–2.2 times in its length vs. 2.1–2.6). Glyptothorax amnestus is further distinguished from both G. robustus and G. stibaros in having a deeper caudal peduncle (9.8–11.2% SL vs. 6.6–8.3), from G. robustus in having (vs. lacking) a medial pit in the thoracic adhesive apparatus, and from G. stibaros in having low projections (vs. distinct serrae) on the posterior margin of the dorsal-fin spine.
TABLE 1. Morphometric data for Glyptothorax amnestus (n = 20).
| Holotype MZB 17214 | Range | Mean±SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard length (mm) %SL | 88.1 | 49.7–88.1 | |
| Predorsal length Preanal length Prepelvic length | 35.4 63.7 48.0 | 35.4–38.6 63.5–69.7 46.9–52.8 | 37.1±1.18 66.3±2.19 49.8±1.68 |
| Prepectoral length Length of dorsal-fin base Dorsal-fin spine length | 23.2 14.6 17.6 | 19.9–24.5 11.0–15.1 13.7–18.9 | 22.2±1.64 13.4±1.32 16.4±1.72 |
| Length of anal-fin base Pelvic-fin length Pectoral-fin length | 15.3 16.8 22.4 | 13.9–18.2 14.1–17.1 22.1–25.6 | 16.2±1.17 15.5±0.86 23.5±1.17 |
| Pectoral-fin spine length Caudal-fin length Length of adipose-fin base | 16.9 32.2 15.3 | 16.0–20.9 25.8–32.2 12.1–17.4 | 18.3±1.37 27.9±1.85 15.6±1.57 |
| Dorsal to adipose distance Post-adipose distance Length of caudal peduncle | 22.1 17.5 18.5 | 17.9–23.4 15.8–19.7 15.9–21.2 | 21.3±1.53 17.9±1.08 18.8±1.64 |
| Depth of caudal peduncle Body depth at anus Body depth at dorsal-fin origin | 11.1 19.6 24.8 | 9.8–11.2 15.3–20.6 19.4–24.8 | 10.5±0.52 17.8±1.47 20.9±1.46 |
| Head length Head width Head depth | 26.9 20.7 16.8 | 23.8–29.0 19.9–23.0 14.9–18.5 | 27.2±1.35 20.9±0.87 16.3±1.12 |
| %HL Snout length Interorbital distance | 50 28 | 45–52 27–32 | 48±2.5 29±1.8 |
| Eye diameter Nasal barbel length Maxillary barbel length | 6 17 92 | 6–10 17–31 72–116 | 8±1.3 22±4.6 93±10.7 |
| Inner mandibular barbel length Outer mandibular barbel length | 27 47 | 27–41 46–59 | 32±3.7 53±4.8 |
| MZB |
Museum Zoologicum Bogoriense |
| UMMZ |
University of Michigan, Museum of Zoology |
| ZMA |
Universiteit van Amsterdam, Zoologisch Museum |
| CAS-SU |
California Academy of Sciences, Stanford University Collection |
| ZRC |
Zoological Reference Collection, National University of Singapore |
| USNM |
Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Glyptothorax amnestus
| Ng, Heok Hee & Kottelat, Maurice 2016 |
Glyptothorax aff. schmidti
| Tan 2009: 21 |
Glyptothorax schmidti
| Jiang 2011: 280 |
| Hadiaty 2008: 146 |
Glyptosternum majus
| Regan 1920: 308 |
Glyptothorax platypogon
| Tan 2000: 290 |
| Kottelat 1993: 76 |
| Fowler 1904: 500 |
Glyptosternum platypogon
| Tan 2009: 21 |
| Beaufort 1913: 267 |
| Volz 1907: 175 |
| Gunther 1864: 187 |
Glyptosternon platypogon
| Bleeker 1858: 225 |
Pimelodus cyanochloros
| Bleeker 1852: 89 |
Pimelodus platypogon
| Bleeker 1852: 591 |