Glyptothorax famelicus, Ng, Heok Hee & Kottelat, Maurice, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4188.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:AA85050E-7653-44BE-9330-AC617BFE6DF8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6063750 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E0BE0E-FF8D-5404-FF58-FF65FE53501B |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Glyptothorax famelicus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Glyptothorax famelicus new species
( Fig. 11 View FIGURE 11 )
Type material. Holotype: USNM 193015, 73.3 mm SL; Sumatra : Sumatera Utara, Danau Toba at Parapat; D. Silan, 1937.
Paratypes. USNM 410773 About USNM (6), 25.5–74.3 mm SL; data as for holotype.
Diagnosis. Glyptothorax famelicus differs from Sundaic congeners except for G. ketambe and G. schmidti in having a uniformly dark body with prominent pale mid-dorsal and midlateral stripes (vs. with either uniform body with or without dark spots or a mottled body, all without prominent pale mid-dorsal and midlateral stripes). It can be distinguished from G. ketambe in having a shorter head (22.6–23.6% SL vs. 24.0–25.5), a more slender caudal peduncle (depth 5.8–7.3% SL vs. 7.6–8.9) and more preanal vertebrae (19–20 vs. 16–17), and from G. schmidti in having a longer thoracic adhesive apparatus (reaching to or just beyond vs. not reaching the level of the last pectoral-fin-ray bases; 63.4–71.0% HL vs. 55.1–60.0). The following unique combination of the characters further distinguishes G. famelicu s from its Sundaic congeners: eye diameter 7–8% HL; interorbital distance 28–31% HL; anteromedial striae in thoracic adhesive apparatus absent; predorsal length 32.1–35.2% SL; dorsal-fin spine length 8.9–14.0% SL; margin of dorsal fin concave, smooth posterior margin of dorsal-fin spine; pectoral-fin spine length 14.0–15.6% SL; adipose-fin base length 11.4–12.8% SL; straight dorsoposterior margin of adipose fin; body depth at anus 11.4–14.3% SL; post-adipose distance 19.1–22.0% SL; and caudal peduncle length 19.4–21.2% SL.
Description. Morphometric data in Table 4 View TABLE 4 . Head depressed; body very slender, subcylindrical. Dorsal profile rising evenly from tip of snout to origin of dorsal fin, then sloping gently ventrally from origin of dorsal fin to end of caudal peduncle. Ventral profile straight to anal-fin base, then sloping gently dorsally from anal-fin base to end of caudal peduncle. Anus and urogenital openings located at vertical through middle of adpressed pelvic fin. Skin tuberculate, with tubercles of even size on sides of body. Lateral line complete and midlateral. Vertebrae 19+18=37 (1), 19+19=38* (4) or 20+18=38 (2).
Head depressed and moderately broad, triangular when viewed laterally. Snout prominent. Anterior and posterior nares large and separated only by base of nasal barbel. Gill opening broad, extending from ventral margin of post-temporal to isthmus. First branchial arch with 2+7 (3) or 2+8* (4) rakers. Bony elements of dorsal surface of head covered with thick, tuberculate skin. Eye ovoid, horizontal axis longest; located entirely in dorsal half of head.
Barbels in four pairs. Maxillary barbel long and slender, extending to middle of pectoral-fin base. Nasal barbel slender, extending to midway between its base and anterior orbital margin. Inner mandibular-barbel extending to midway between its base and that of pectoral spine. Outer mandibular barbel extending to two-thirds of distance between its base and that of pectoral spine.
Mouth inferior, premaxillary tooth band partially (approximately half) exposed when mouth is closed. Oral teeth small and villiform, in irregular rows on all tooth-bearing surfaces. Premaxillary teeth appearing in single broad semilunate band. Dentary teeth in a single crescentic band, consisting of two separate halves tightly bound at midline.
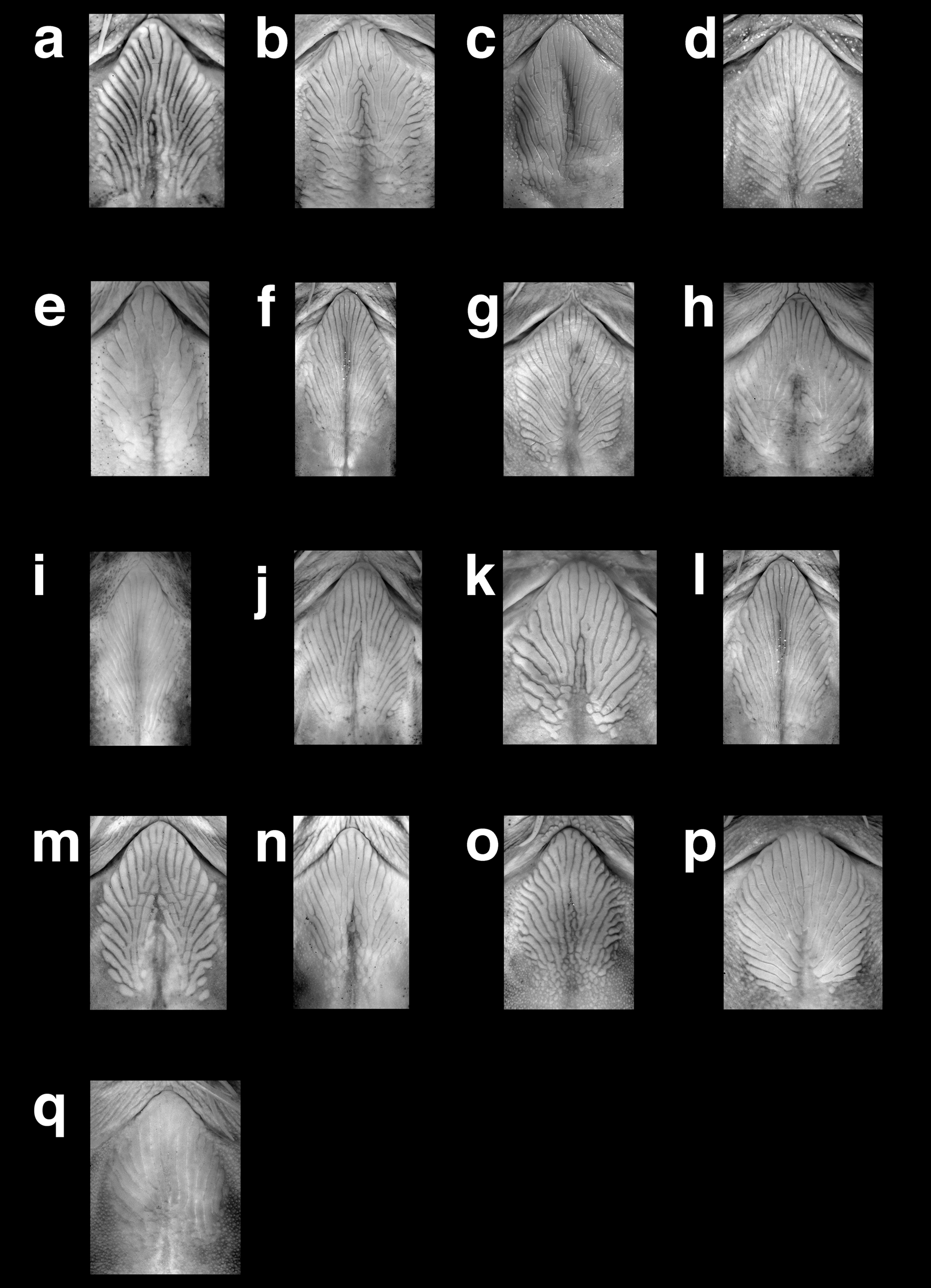
Thoracic adhesive apparatus consisting of keratinized striae in an ovate field extending from isthmus to or just beyond posterior limit of pectoral-fin base ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 d). Anteromedial striae absent. Chevron-shaped medial pit on posterior third.
Dorsal fin located above anterior third of body, with I,6 (7) rays; fin margin concave; spine short and straight, smooth on anterior and posterior margins. Adipose fin with anterior margin straight or slightly concave and posterior margin straight. Caudal fin strongly forked, with lower lobe slightly longer than upper lobe and i,7,8,i (7) principal rays. Procurrent rays symmetrical and extending only slightly anterior to fin base. Anal-fin base vertically opposite adipose-fin base. Anal fin with straight anterior margin and straight or slightly concave posterior margin; with iv,8* (6) or iv,9 (2) rays. Pelvic-fin origin at vertical through posterior limit of dorsal-fin base. Pelvic fin with slightly convex margin and i,5 (7) rays; tip of adpressed fin not reaching anal-fin origin. Pectoral fin with I,7,i* (4), I,8 (1) or I,8,i (2) rays; posterior fin margin slightly concave; anterior spine margin smooth, posterior margin with 10 serrations.
Coloration. In 70% ethanol: Dorsal and lateral surfaces of head, and body brown, fading to beige on ventral surfaces. A faint thin, lighter brown mid-dorsal stripe extending from base of last dorsal-fin ray to origin of adipose fin. Laterosensory pores along lateral line rimmed in beige, imparting appearance of a diffuse lighter brown midlateral line. All fins with brown rays, and diffuse melanophores on membranes. Pectoral and pelvic fins with brown on base of fin rays and hyaline posterior margin. Anal fin with brown base and hyaline posteroventral corner. Adipose fin brown, with hyaline distal margin. Caudal fin brown, with tip of lobes hyaline. Maxillary and nasal barbels brown dorsally, beige ventrally. Mandibular barbels beige.
Distribution. Glyptothorax famelicus is only known from the type series collected in the Danau (Lake) Toba drainage in northern Sumatra ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ).
Comparisons. Glyptothorax famelicus further differs from all Sundaic congeners except for G. exodon , G. keluk , G. ketambe , G. platypogonides and G. schmidti in having a more slender body (depth at anus 11.4–14.3% SL vs. 14.5–23.1) and from all Sundaic congeners except G. exodon , G. nieuwenhuisi , G. platypogonides , G. ro b u s t u s, G. schmidti and G. s t i b a ro s in having a more slender caudal peduncle (depth 5.8–7.3% SL vs. 7.4–11.4); it is further distinguished from G. exodon and G. platypogonides in having a smaller eye (diameter 7–8% HL vs. 10–14), a shorter dorsal-fin spine (8.9–14.0% SL vs. 15.0–20.0) and a shorter pectoral-fin spine (14.0–15.6% SL vs. 16.2– 22.7), and from G. platypogonides in having a smaller predorsal length (32.1–35.2% SL vs. 36.5–39.1). Besides G. ketambe , G. s c h m i d t i (whose differences with G. famelicus are already outlined in the diagnosis) and G. platypogonides (compared previously), there are five other congeners known from Sumatra: G. amnestus , G. fuscus , G. ke l u k, and G. plectilis . Glyptothorax famelicus further differs from all of these five species in having a smaller predorsal length (32.1–35.2% SL vs. 35.3–42.7), from G. amnestus in lacking (vs. having) anteromedial striae in the thoracic adhesive apparatus, and from G. f u s cu s in having a concave (vs. straight) margin of the dorsal fin, a shorter dorsal-fin spine (8.9–14.0% SL vs. 14.6–20.1), a shorter pectoral-fin spine (14.0–15.6% SL vs. 17.0– 22.7), a shorter adipose-fin base (11.4–12.8% SL vs. 13.1–21.0) and a shorter caudal fin (25.8–28.2% SL vs. 28.7– 33.9). It is further distinguished from G. keluk in having a shorter dorsal-fin spine (8.9–14.0% SL vs. 13.0–15.0), a shorter pectoral-fin spine (14.0–15.6% SL vs. 19.4–22.9), a shorter adipose-fin base (11.4–12.8% SL vs. 13.6– 17.2), a longer post-adipose distance (19.1–22.0% SL vs. 15.2–16.7) and a straight (vs. convex) dorsoposterior margin of the adipose fin, and from G. plectilis in lacking (vs. having) anteromedial striae in the thoracic adhesive apparatus, having a shorter adipose-fin base (11.4–12.8% SL vs. 12.9–17.2) and a longer post-adipose distance (19.1–22.0% SL vs. 14.0–17.6).
Among other Sundaic congeners, G. famelicus further differs from G. decussatus in lacking (vs. having) anteromedial striae in the thoracic adhesive apparatus, having a smaller predorsal length (32.1–35.2% SL vs. 35.8– 40.4), a shorter dorsal-fin spine (8.9–14.0% SL vs. 16.0–17.3), and a longer post-adipose distance (19.1–22.0% SL vs. 16.2–17.5% SL), from G. major in lacking (vs. having) anteromedial striae in the thoracic adhesive apparatus, having a smaller predorsal length (32.1–35.2% SL vs. 36.7–41.6), a shorter dorsal-fin spine (8.9–14.0% SL vs. 14.3–20.8) and a longer post-adipose distance (19.1–22.0% SL vs. 13.6–18.6), and from G. nieuwenhuisi in having a smaller predorsal length (32.1–35.2% SL vs. 36.5–41.6), a shorter dorsal-fin spine (8.9–14.0% SL vs. 14.0–18.5) and a longer caudal peduncle (19.4–21.2% SL vs. 16.8–19.5). It is further distinguished from G. pictus in having a smaller eye (diameter 7–8% HL vs. 8–13), a smaller predorsal length (32.1–35.2% SL vs. 35.1–40.4) and a shorter dorsal-fin spine (8.9–14.0% SL vs. 15.4–20.9), from G. platypogon in having a straight (vs. convex) dorsoposterior margin of the adipose fin and a longer post-adipose distance (19.1–22.0% SL vs. 14.6–17.6), and from G. prashadi in having a narrower head (16.7–20.0% SL vs. 20.2–22.8), a smaller predorsal length (32.1–35.2% SL vs. 37.7– 39.3) and a a concave (vs. straight) margin of the dorsal fin. Glyptothorax famelicus further differs from G. robustus in having (vs. lacking) a medial pit in the thoracic adhesive apparatus, a smaller predorsal length (32.1–35.2% SL vs. 36.7–40.0) and a shorter pectoral-fin spine (14.0–15.6% SL vs. 16.8–19.8), and from G. s t i b a ro s in having a smaller predorsal length (32.1–35.2% SL vs. 39.1–42.8), a shorter dorsal-fin spine (8.9–14.0% SL vs. 15.9–20.4), a shorter pectoral-fin spine (14.0–15.6% SL vs. 18.1–22.2), a shorter adipose-fin base (11.4–12.8% SL vs. 14.6– 17.8), a smooth (vs. serrated) posterior margin of the dorsal-fin spine and a longer post-adipose distance (19.1– 22.0% SL vs. 15.7–18.3).
TABLE 4. Morphometric data for Glyptothorax famelicus (n = 7).
| Holotype USNM 193015 | Range | Mean±SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard length (mm) %SL | 73.3 | 25.5–74.3 | |
| Predorsal length Preanal length Prepelvic length | 35.2 65.6 47.2 | 32.1–35.2 64.4–66.2 45.2–49.8 | 34.1±1.38 65.1±0.76 46.7±1.87 |
| Prepectoral length Length of dorsal-fin base Dorsal-fin spine length | 19.0 12.6 12.0 | 18.9–21.8 10.9–13.2 8.9–14.0 | 20.1±1.24 12.3±0.91 12.0±2.07 |
| Length of anal-fin base Pelvic-fin length Pectoral-fin length | 14.6 16.6 20.3 | 14.6–16.9 15.1–17.6 20.3–22.1 | 15.5±1.12 16.4±0.89 21.1±0.65 |
| Pectoral-fin spine length Caudal-fin length Length of adipose-fin base | 14.2 25.8 12.8 | 14.0–15.6 25.8–28.2 11.4–12.8 | 15.0±0.79 26.9±0.97 12.1±0.63 |
| Dorsal to adipose distance Post-adipose distance Length of caudal peduncle | 25.0 19.9 20.1 | 20.0–27.3 19.1–22.0 19.4–21.2 | 24.2±2.64 20.5±1.09 20.2±0.67 |
| Depth of caudal peduncle Body depth at anus Body depth at dorsal-fin origin | 6.5 11.9 14.0 | 5.8–7.3 11.4–14.3 14.0–17.8 | 6.5±0.53 12.9±1.27 15.7±1.39 |
| Head length Head width Head depth | 23.1 18.4 13.2 | 22.6–23.6 16.7–20.0 12.5–14.0 | 23.1±0.48 18.8±1.30 13.3±0.54 |
| %HL Snout length Interorbital distance | 49 28 | 45–52 28–31 | 49±2.5 29±1.0 |
| Eye diameter Nasal barbel length Maxillary barbel length | 8 23 102 | 7–8 19–24 88–102 | 8±0.5 22±2.1 95±6.0 |
| Inner mandibular barbel length Outer mandibular barbel length | 33 54 | 31–36 44–57 | 33±1.4 51±5.3 |
| USNM |
Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |