Hemicycliophora undefined-4
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1111/zoj.12145 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E087ED-FFB8-FFD3-FE9E-FD96FEFFF9B7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Marcus |
|
scientific name |
Hemicycliophora undefined-4 |
| status |
|
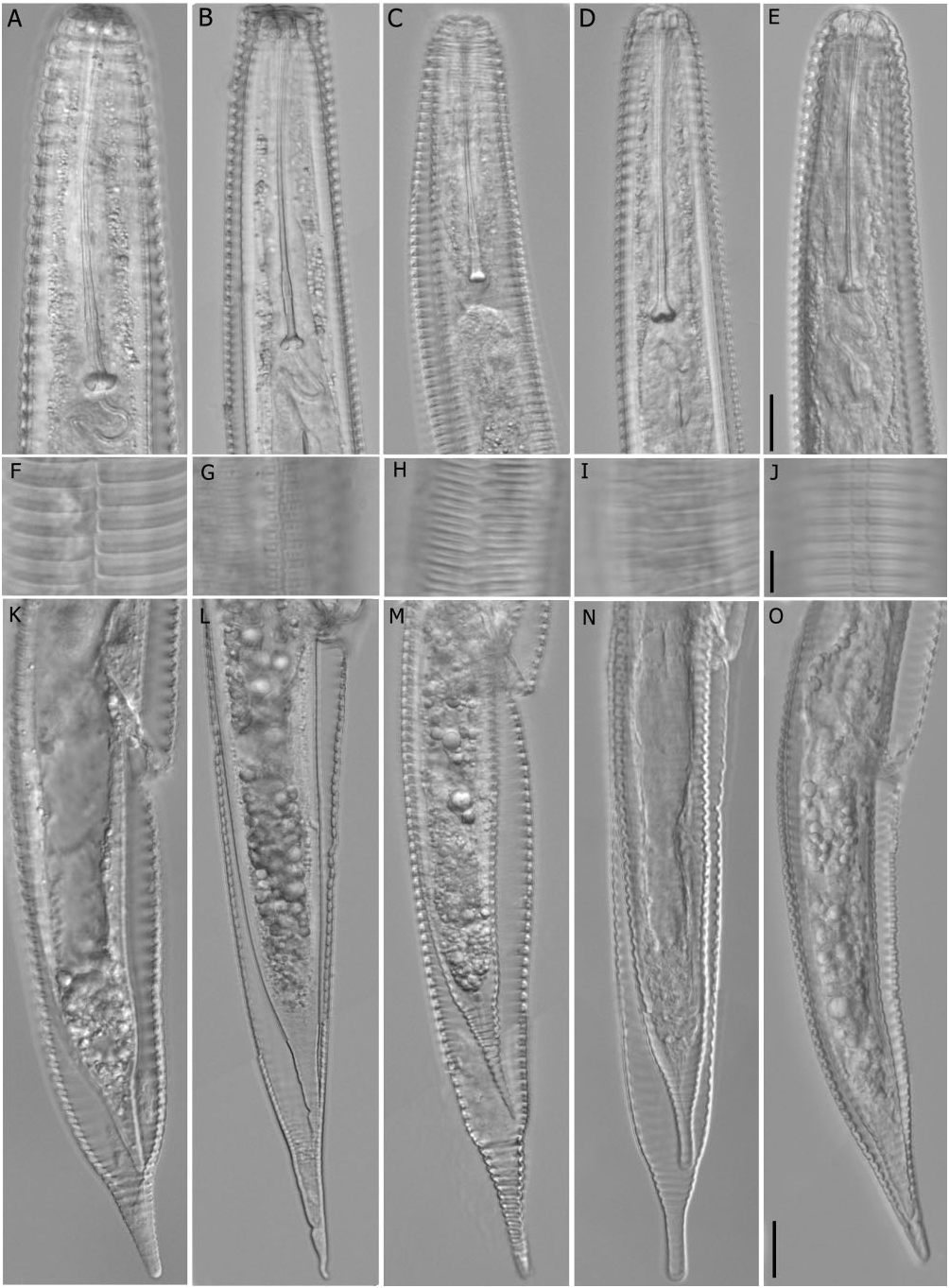
( FIGS 2D, I, N, S View Figure 2 15; TABLES 1, S7)
This species is characterized by a straight or slightly ventrally arcuate body, cuticular sheath loosely fitting body, lateral fields marked by breaks and anastomoses throughout body, sometimes with a central longitudinal line, annuli outside lateral field coarse or smooth, several anastomoses observed in anterior body region, lip region rectangular to truncate, or with slightly rounded anterior edges, and with three annuli, labial disc not protruded or slightly elevated, vulval lips modified, about one annulus long, vulval sleeve about one annulus long, tail cylindrical then abruptly curved dorsally in posterior third with less to no curvature ventrally, continuing to an attenuated narrow conical, almost cylindrical posterior portion with rounded terminus. No males were found. This species has a wide distribution in the USA where it was detected at one site in California, North Carolina , and Texas and in three localities in Florida.
The species is similar to Hemicycliophora epicharoides but differs from it mainly by a more narrowly conical to cylindrical terminal portion of the tail, and larger values than those reported for R (241–254 vs. 144– 209), Rst (24–28 vs. 15–21), Roes (number of annuli between anterior end of body and pharynx base) (41– 46 vs. 33–42), Rex (46–49 vs. 32–41), RV (50–64 vs. 31–46), RVan (16–25 vs. 9–17), and Ran (number of annuli between posterior end of body and anus) (29– 39 vs. 20–33). This species is clearly different from H. epicharoides in the ITS and D2-D3 of 28S rRNA gene sequences.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.