Acanthagrion truncatum Selys, 1876
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4881.2.12 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:85B391E6-98A3-4FC8-8C6D-8A4B5FECDBFC |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4323939 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DDC05F-9D29-014F-FF19-A3F6FB069ACA |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Acanthagrion truncatum Selys, 1876 |
| status |
|
Acanthagrion truncatum Selys, 1876 View in CoL
Figs. 1–4 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4
Material examined. 15 F-0 exuviae (4 ƋƋ, 11 ♀♀ all emerged in laboratory), seven F-0 larvae (1 Ƌ, 6 ♀♀ died before emergence). BRAZIL, Minas Gerais, Uberlândia, Universidade Federal de Uberlândia—Campus Glória (18.9572S, 48.2091W, 860 m asl), Collected and emerged between Feb-May 2020, H. Venâncio leg, LEBIO GoogleMaps .
Description. Exuviae pale to light-brown ( Fig. 1a View FIGURE 1 ), F-0 larvae overall coloration light to dark-brown ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ); slender; femora with light-brown bands; caudal lamellae long, 50–59% of total body length ( Figs. 1a View FIGURE 1 , 2 View FIGURE 2 ).
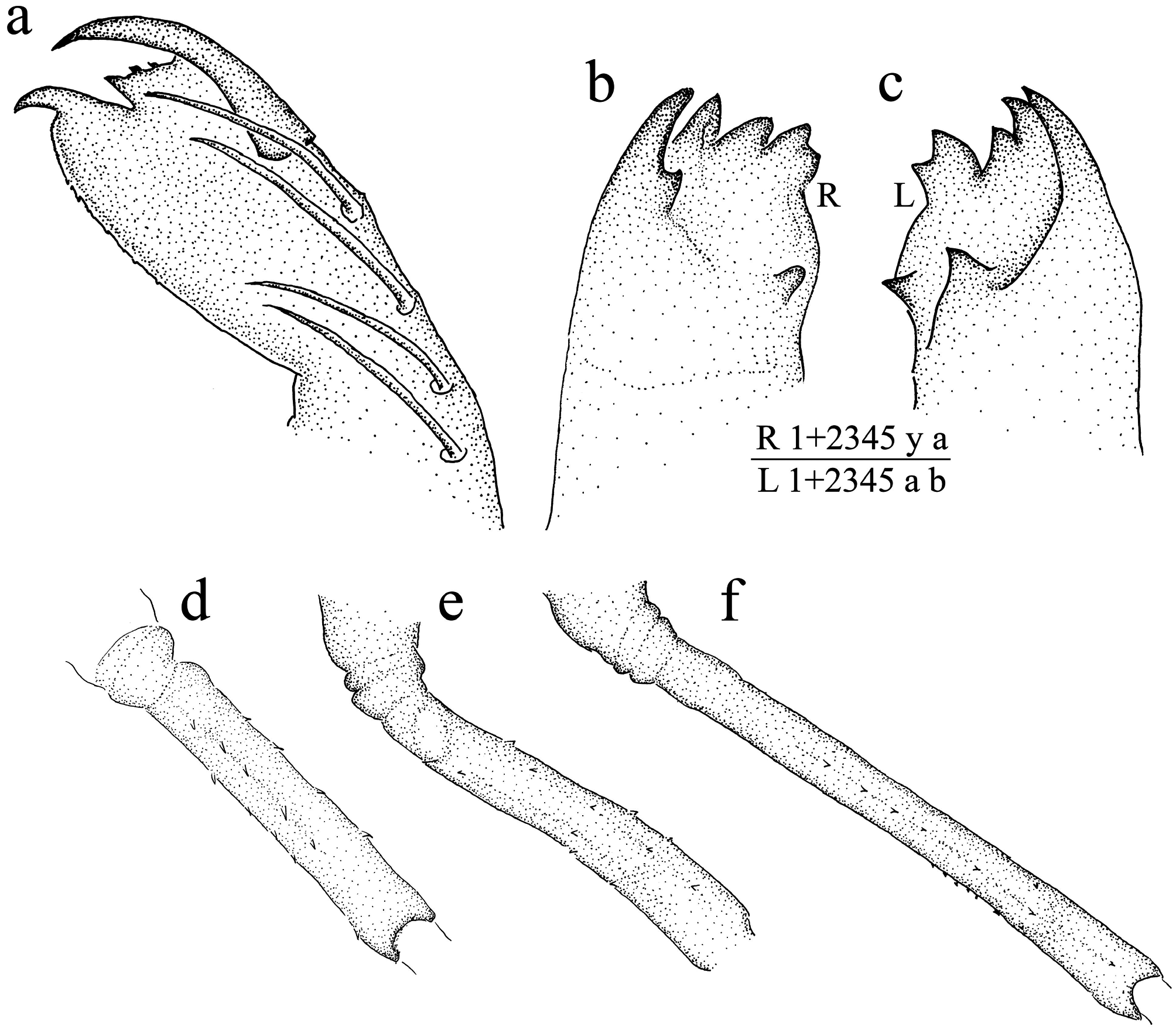
Head. Subpentagonal (similar to other Acanthagrion ), 0.55–0.60 as wide as long, wider than thorax and abdomen ( Figs. 1a View FIGURE 1 , 2 View FIGURE 2 ). In ventral view, overall shape of labrum concave anteriorly, with minute setae on anterior margin and a fine crenulation on surface; clypeus, frons and vertex smoothly rounded, glabrous with minute setae. Occipital margin widely concave, nearly straight at middle; cephalic lobes rounded, bulging at the postocular portion, with several short spines ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 a–b, 2). Antenna ( Fig. 1c View FIGURE 1 ) moderately long and filiform, 7-segmented, all segments uniformly colored light-brown to brown, scape and pedicel light-brown, cylindrical, 3rd antennomere the longest, proportional lengths of antennomeres: 0.62, 0.86, 1.0, 0.69, 0.50, 0.35, 0.14. Compound eyes rounded, medium sized, slightly wider than long, laterally prominent ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 a–c). Mandibles formula R 1+2345 y a / L 1+2345 a b, where b>a ( Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 b–c). Maxilla: galeolacinia with six teeth, three of them in the dorsal portion slightly incurved, medial one slightly longer, with a basal row of 6–8 minute setae; three ventral teeth of different size and robustness being the medial the longest and the basal one roughly vestigial: apical tooth 0.50, median one 1.0, basal tooth 0.1. Prementum-postmentum articulation slightly surpassing posterior margin of prothoracic coxae; prementum ( Fig. 1d View FIGURE 1 ) longer than wide, roughly pentagonal, lateral margins slightly concave, divergent apically, laterodorsally with a row of seven (or eight) spiniform setae and a group of three minute spines on the base of each palp; ligula tip prominent, rounded, finely crenulated; two long premental setae to each side of midline, plus a minute one on 80% of specimens (54% on left side only, 26% on both sides); 20% of specimens with two long premental setae on each side, lacking the minute one. Dorsal view of labial palps ( Fig. 1d View FIGURE 1 ) with four long setae each, in anterior view ( Fig. 3a View FIGURE 3 ), apical lobe divided into a dorsal and a ventral branches: dorsal branch squarely truncate, composed of three small teeth, of more or less of same size and robustness; ventral branch with a well-developed end hook, with its anterior margin finely crenulate; ventral margin of palp finely crenulate; movable hook slightly less than half of labial palp length, with acute apex, lacking basal setae.
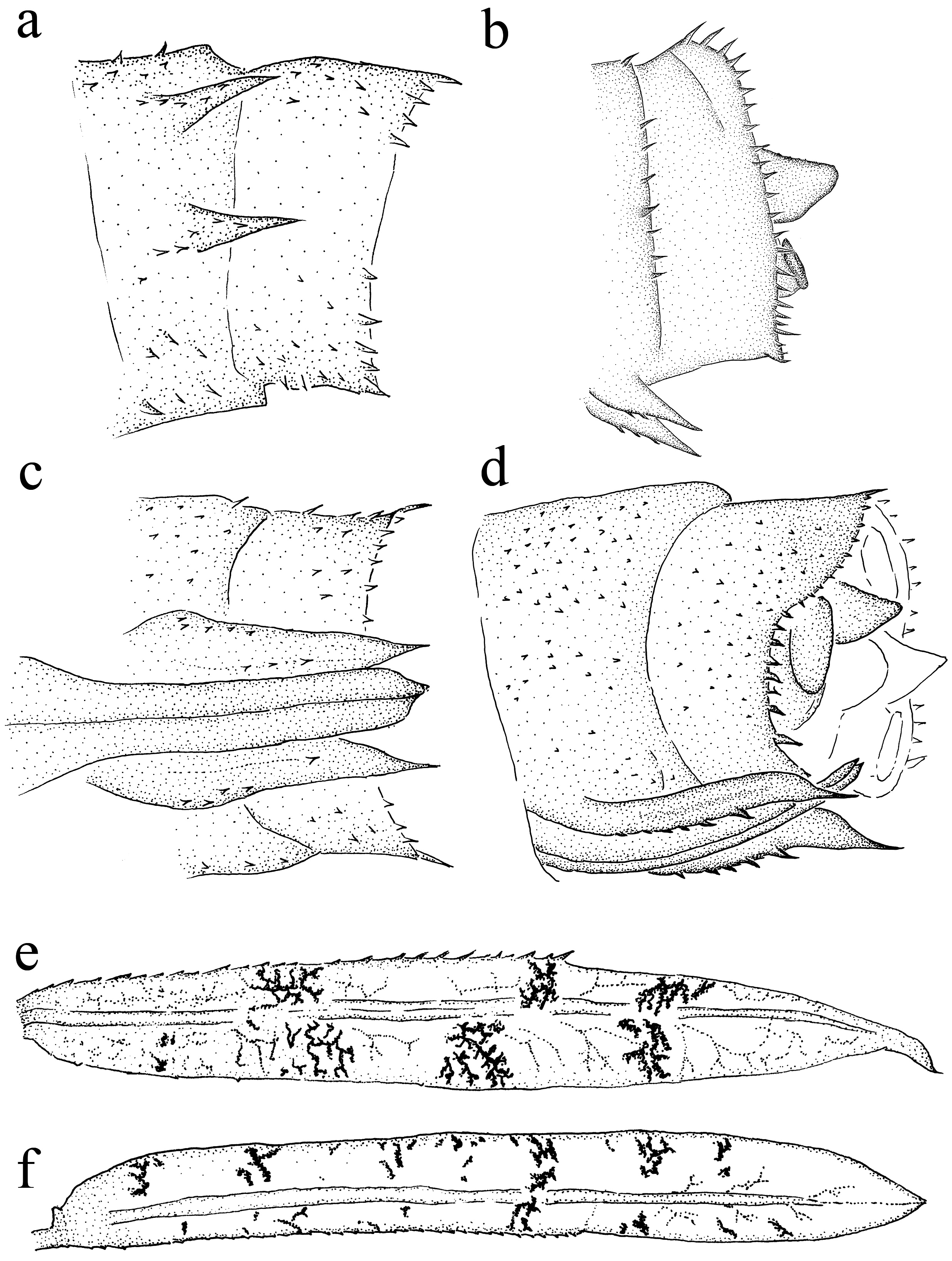
Thorax. Uniformly light-brown, mostly darker on the sutures, subtrapezoidal, glabrous on the medial portion; posterior margin smoothly concave with small setae on each lateral side; anterior and posterior wing sheaths reaching anterior margin and mid S4, respectively (not stretched individuals). Legs ( Figs. 1a View FIGURE 1 , 2 View FIGURE 2 a–c, 3d–f) long, tip of metathoracic tarsi almost reaching S10 when extended, slender, pale with apical and basal bands on all femora; dorsal and ventral borders of femora with a row of spiniform setae (6–7 pro-, 6–8 meso- and 11–12 on metafemur), an external row of 5–8 spiniform setae on prothoracic femora. Tibiae sparsely spined on internal surface, bearing several setae which increase in density towards the apex with>10 tridentate setae. Tarsi about 0.50 of tibiae, with two ventral rows of setae, claws with acute apex.
Abdomen. Covered with minute spines on dorsal and ventral surfaces of S2–10 and S9–10 apical margins; S1–8 with disrupted parallel stripes on middorsal line (as in Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 b–c), in some specimens only dark dots on apical mediodorsal segments; S3–7 with a prominent lateral carina. In ventral view ( Fig. 4a View FIGURE 4 ), male gonapophyses, sharply pointed, reaching ca. basal 0.4 of sternum 10, bearing 5–6 spines each; in lateral view ( Fig. 4b View FIGURE 4 ), male gonapophyses obliquely directed. Female gonapophyses slightly surpassing S10 posterior margin, bearing two rows of minute spines on each valve ( Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 c–d). Caudal lamellae ( Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 e–f) 8.5–9 times longer than widest part, measuring 50–59% of total body length; nodus at 0.6–0.62 of lamella length; ventral margin of antenodal portion of lateral lamella with>30 spines, dorsal margin bearing 2–3 spines; dorsal margin of antenodal portion of median lamella with four minute spines, ventral margin bearing>20 spines, increasing in size towards the nodus. Male cerci conical, dorsal margin nearly straight, ventral margin rounded, blunt-tipped ( Fig. 4b View FIGURE 4 ); female cerci with apex less blunt but not acute ( Fig. 4d View FIGURE 4 ).
Measurements. AL: 4.7–5.6; Pfl: 1.3–1.5; MsfL: 1.8–2; MtfL: 2.4–2.5; CeL: 0.11; MgL: 0.28–0.3; FgL: 1–1.1 (ovipositor), 0.7–0.8 (valves); MWh: 2.3–2.4; TL: 12–13.5. Higher values always for males.
Diagnosis. The larva of Acanthagrion truncatum fits better on the Group II, by presenting rounded cephalic lobes, 7-segmented antennae, acute apex of caudal lamellae, and 2 or 2+ 1 premental setae on each side of midline. It occurs in sympatry with other three Group II species in the collecting site (due to the presence of larvae and/or adults): A. aepiolum Tennessen, 2004 , A. gracile (Rambur, 1842) and A. lancea Selys, 1876 . According to data available on literature and examined material (we did not examined larvae material from A. aepiolum and A. lancea species), A. truncatum larvae can be distinguished by lacking 3 premental setae in any of the midline sides, which occurs in A. lancea and A. gracile ( Anjos-Santos et al. 2011) . Larvae of A. aepiolum also lacks 3 premental setae, however some specimens presented six antennomeres ( Lozano et al. 2007), which we did not observed in the examined specimens of A. truncatum (see Table 1 View TABLE 1 ). Other traits such as mandibular formula, total body length shape of apical caudal lamellae, and number of palpal setae are very similar between these four species and also other Acanthagrion larvae, thus not being reliable diagnostic characters ( Román-Heracleo et al. 2019).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |