Medleria caudata, Świerczewski & Malenovský & Stroiński, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5852/ejt.2018.422 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5987609 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D5831C-FFF8-FFE7-F914-FBACBD2AE655 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Medleria caudata |
| status |
gen. et sp. nov. |
Medleria caudata View in CoL gen. et sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:BF1F8ADE- 2703-41 DE-B80F-FDE9F50F452C
Figs 1–10 View Fig. 1 View Fig. 2 View Fig. 3 View Fig. 4 View Fig.5 View Fig.6 View Fig. 7 View Fig. 8 View Fig.9 View Fig. 10
Diagnosis
The only species in the genus; see diagnosis for the genus.
Etymology
From the Latin adjective ‘ caudatus ’ (= tailed, caudate). The specific epithet refers to the prolonged apical part of the tegmen.
Type material examined
Holotype YEMEN: ♂, [ YEMEN, SOCOTRA Island / Dixam Plateau , 850-920m / N 12°31′24″, E 53°58′29″ / 5.ii.2010 / L. Purchart & J. Vybiral leg.], [COLLECTIO / Moravské museum / Brno], dry-mounted, abdomen detached, dissected and stored in glycerol in a glass microvial ( MMBC) GoogleMaps .
Paratypes YEMEN: 3 ♂♂, 4 ♀♀, all specimens with the same collecting data as for the holotype, all dry-mounted, abdomens of some specimens detached, dissected and stored in glycerol in a glass microvial ( MMBC: 2 ♂♂, 3 ♀♀ GoogleMaps ; NMPC: 1 ♂, 1 ♀) GoogleMaps .
Description
SIZE. Total length 4.02–4.07 mm.
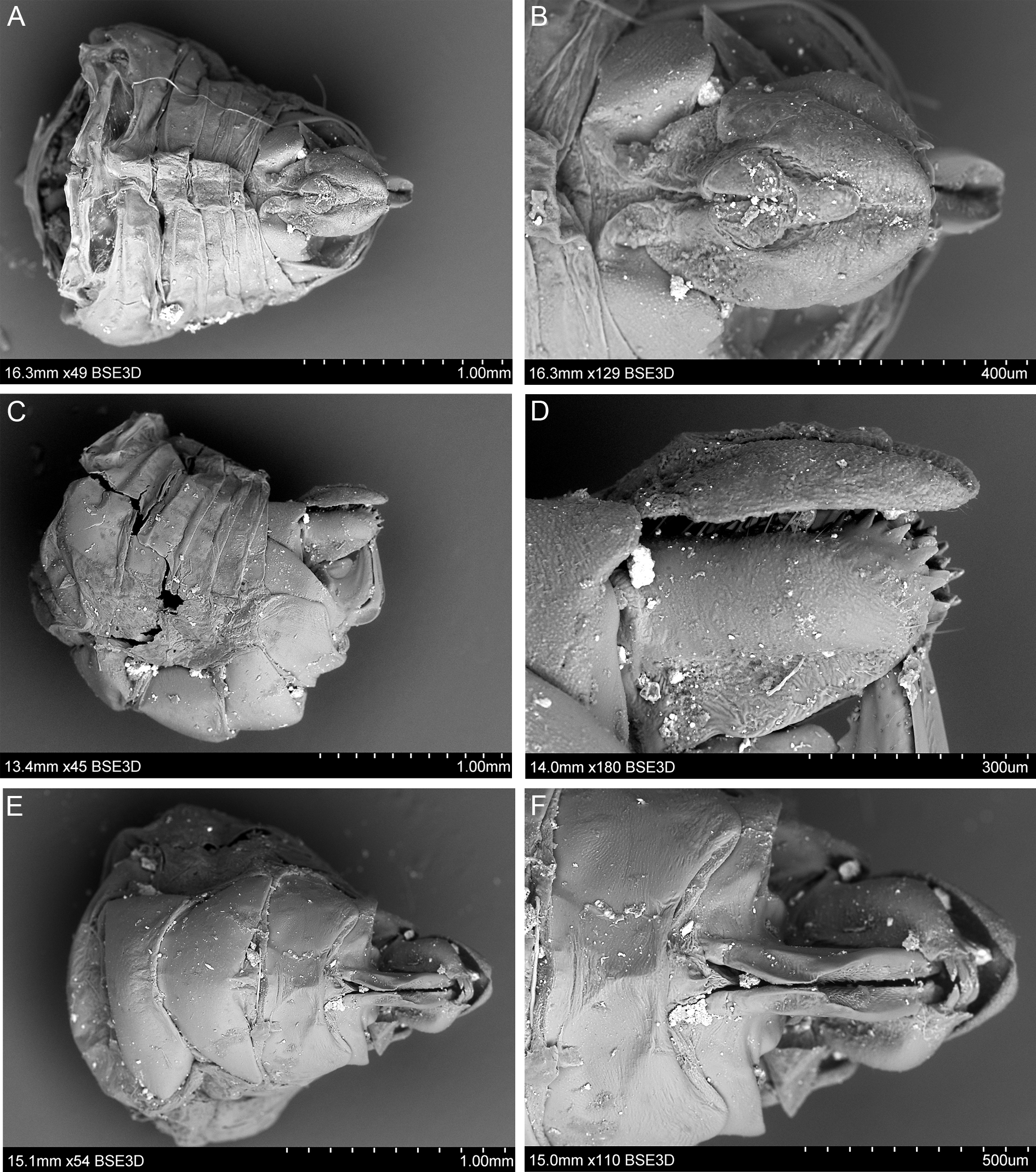
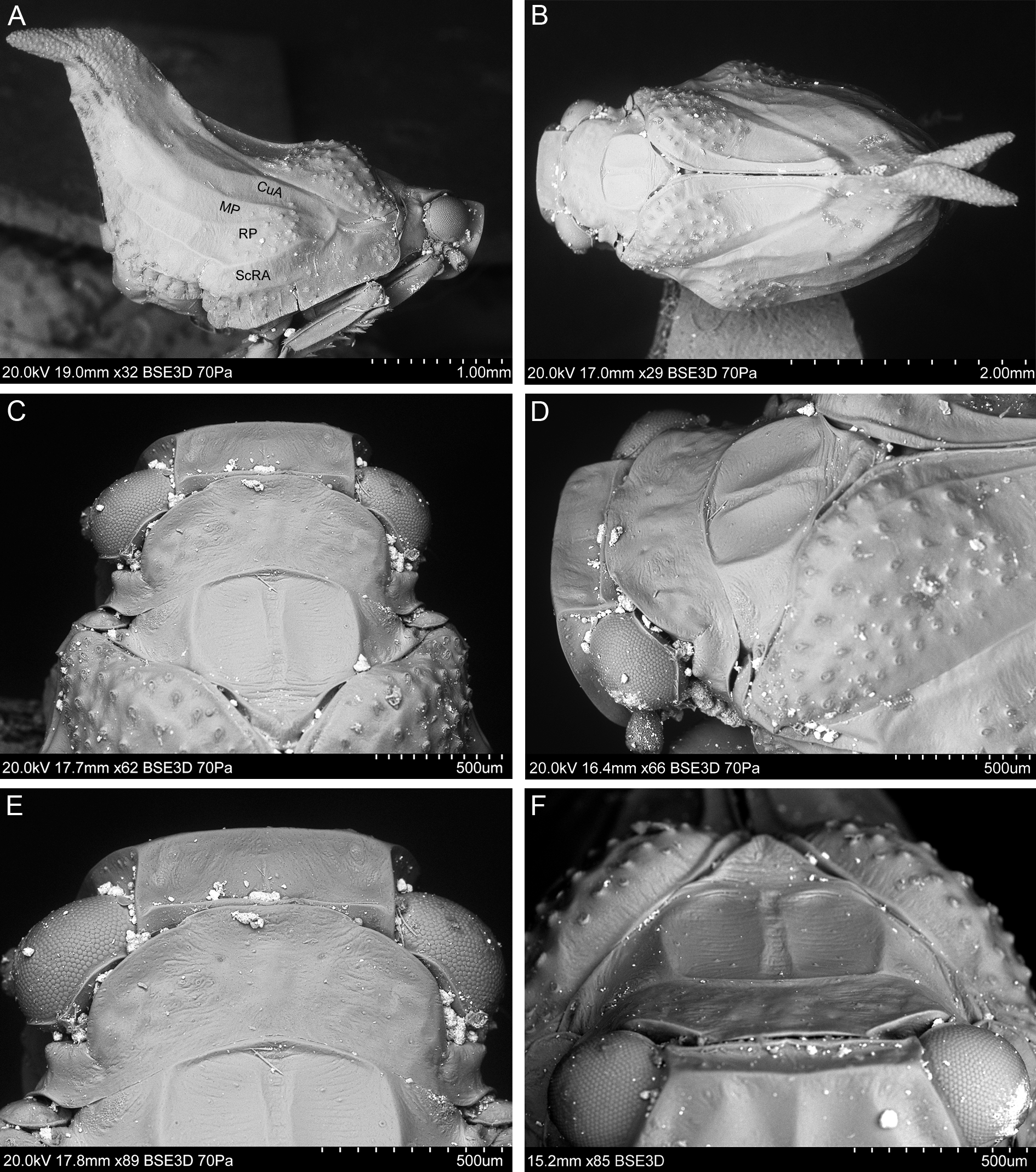
COLORATION. Ochreous, mottled with small dark brown to black markings on upper part of frons, lateral parts of mesonotum and scutellum, median portion of tegmen, tubercles on clavus and bulla, apical part of tegmen largely dark; abdominal sternites dark brown with yellow margins, legs brownish ( Fig. 1A–E View Fig. 1 ).
HEAD. Vertex: A / B = 3.00–4.29; anterior margin delicately arcuate; lateral margins almost straight and parallel, posterior margin sharp and elevated, almost straight; disc of vertex weakly depressed ( Figs 1E View Fig. 1 , 2D–F View Fig. 2 ). Frons: C / E = 0.83–1.00; D / E = 1.17–1.41; median carina reaching frons middle, lateral carinae distinctly longer than median one; area between bases of median and lateral carinae as well as area between lateral carinae and lateral margins depressed ( Figs 1D View Fig. 1 , 3C–D View Fig. 3 ). Disc of clypeus flattened.
THORAx. Pronotum: F / B = 1.50–2.14; anterior margin medially produced and flattened, posterior margin widely concave ( Fig. 2C–E View Fig. 2 ). Mesonotum: G / F = 2.00–2.31; G / B+F = 1.25–1.61; G / H = 0.70–0.75; area between median and lateral carinae depressed ( Fig. 2C–F View Fig. 2 ). Tegmen: I / J = 1.59–2.08. Metatibia with apical row of seven well-developed spines, external spines longer than ventral ones; basitarsomere with 7 apical spines; second tarsomere with two lateral spines.
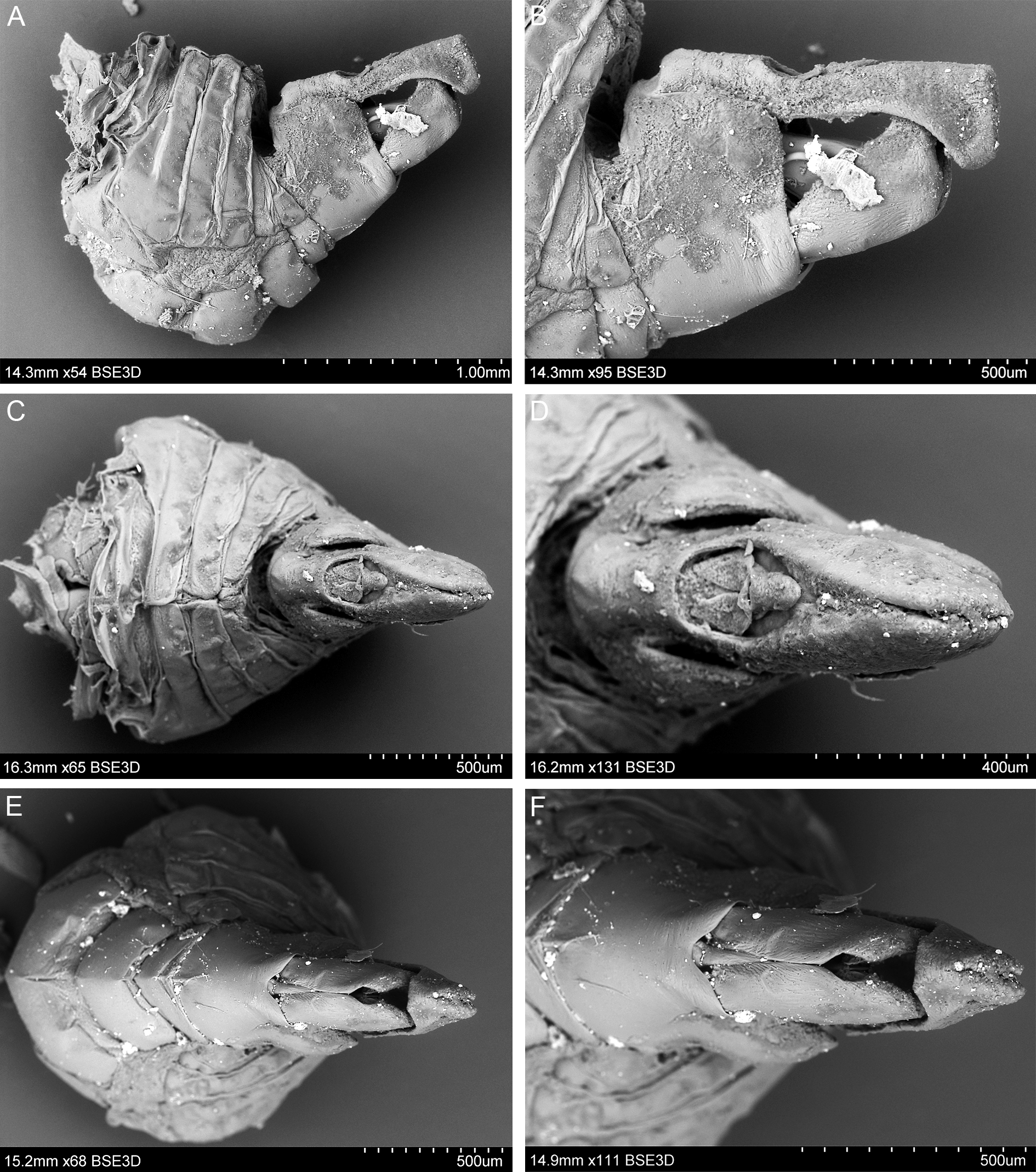
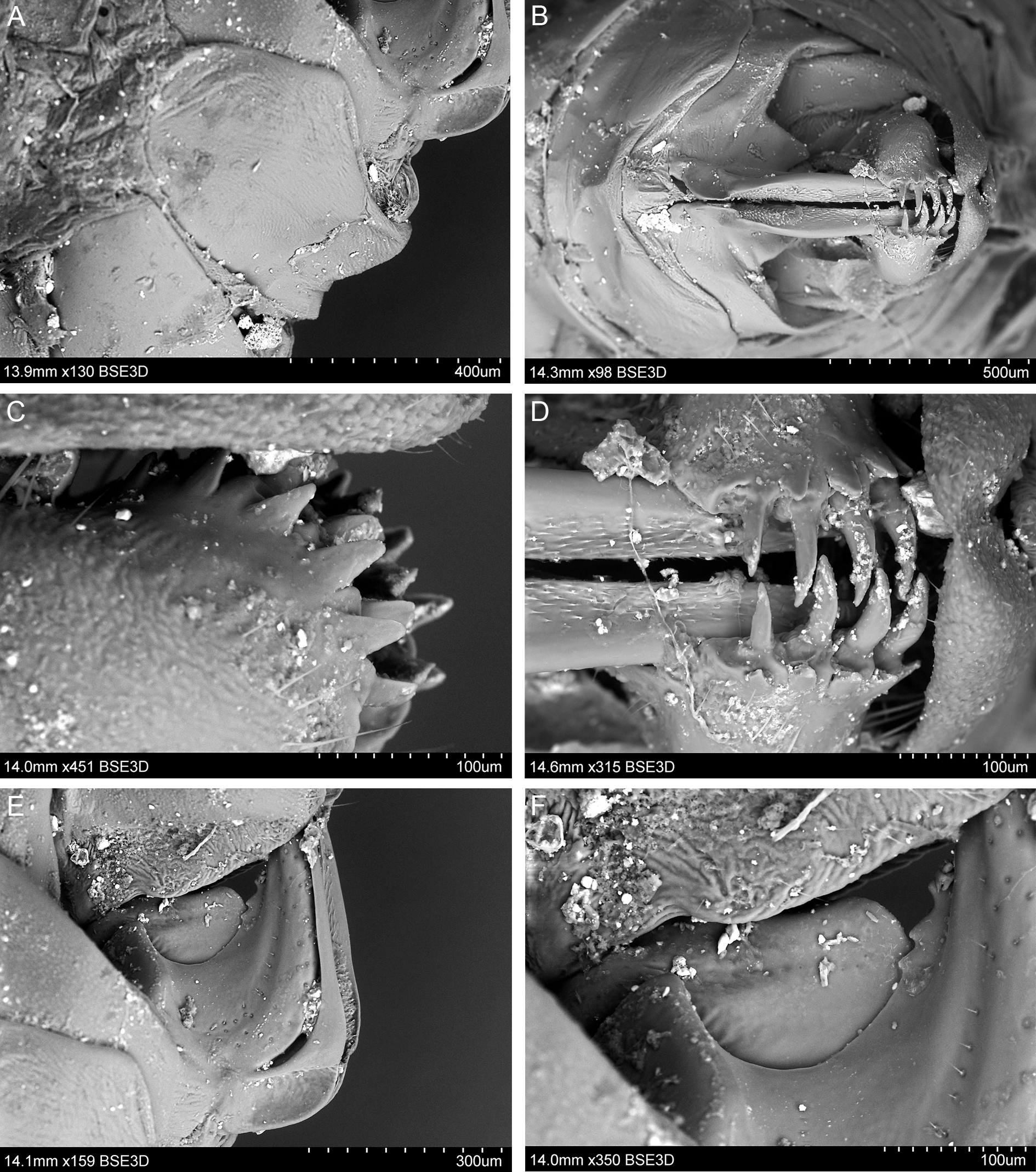
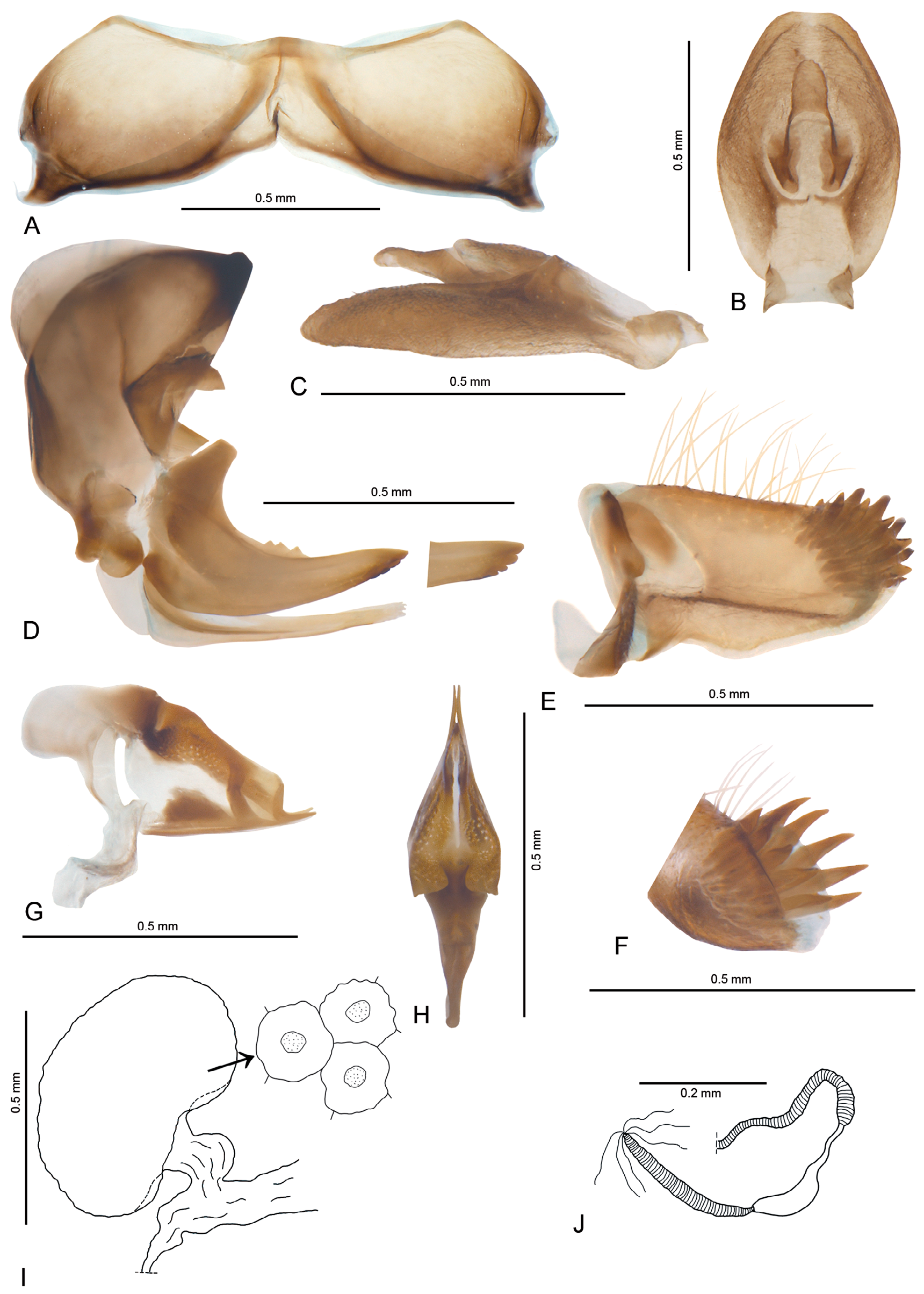
MALE TERMINALIA. Anal tube, in lateral view, with ventral margin weakly convex and dorsal margin weakly concave in median portion, postero-dorsal angle right ( Fig. 5A–B View Fig.5 ). Genital style with posterior margin straight, ventral and dorsal margins almost straight, subparallel, postero-ventral angle bluntly rounded, not extending the posterior margin ( Fig. 6A–C View Fig.6 ). Appendage of dorsal periandrium with well-sclerotized small teeth in its median curved part ( Fig. 6E View Fig.6 ). Dorsal part of aedeagus membranous ( Fig. 6G View Fig.6 ).
FEMALE TERMINALIA. Pregenital sternite with posterior margin convex medially, anterior margin concave ( Fig. 9A View Fig.9 ). Anal tube, in lateral view, tapering apicad, with bluntly rounded apex; anus placed anterior to midlength; ventral margin medially weakly arcuate ( Fig. 9C View Fig.9 ); in dorsal view, anal tube widest in its median portion, apically truncate, posterior margin almost straight ( Fig. 9B View Fig.9 ). Gonoplac with its dorsal part with membranous base, strongly sclerotized median portion and two rows of teeth placed posteriorly–external teeth small and flat, internal teeth huge and hook-like; ventral part weakly sclerotized ( Figs 8D View Fig. 8 , 9E View Fig.9 ). Gonapophysis VIII with dorsal margin bearing three teeth, ventral margin subapically slightly up-folded with four teeth; basal part of gonocoxal process with strongly sclerotized strip ( Fig. 9D View Fig.9 ). Spermatheca with ductus receptaculi not divided into two parts, ribbed, widened apically; diverticulum ductus smooth, with narrow basal part and elongate apical bulba ( Fig. 9J View Fig.9 ). Two large eggs (1.2 mm) in ventro-dorsal position were discovered during dissection of the female abdomen.
Host plant and habitat
The type series was collected by beating shrubs on a warm and sunny day, in a sparse semi-arid shrubland on a coarse, stony substrate of a montane limestone plateau ( Fig. 10A–B View Fig. 10 ). The vegetation was almost uniformly composed of Croton cf. socotranus Balf. f. ( Euphorbiaceae ). This plant species is thus a probable host of M. caudata gen. et sp. nov. ( Fig. 10C View Fig. 10 ).
Distribution
Yemen: Socotra Island; so far only known from the Dixam GoogleMaps montane plateau (12°31′24″ N, 53°58′29″ E) in the central part of the island.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.