Aguana spitzi, Mejdalani & Domahovski & Cavichioli, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4577.1.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:4D18F08C-F248-45A3-A3F1-1CA4FF0968D7 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5940914 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7E7C6E88-D7D2-4D03-B035-A8F557B680C6 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:7E7C6E88-D7D2-4D03-B035-A8F557B680C6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Aguana spitzi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Aguana spitzi View in CoL sp. nov.
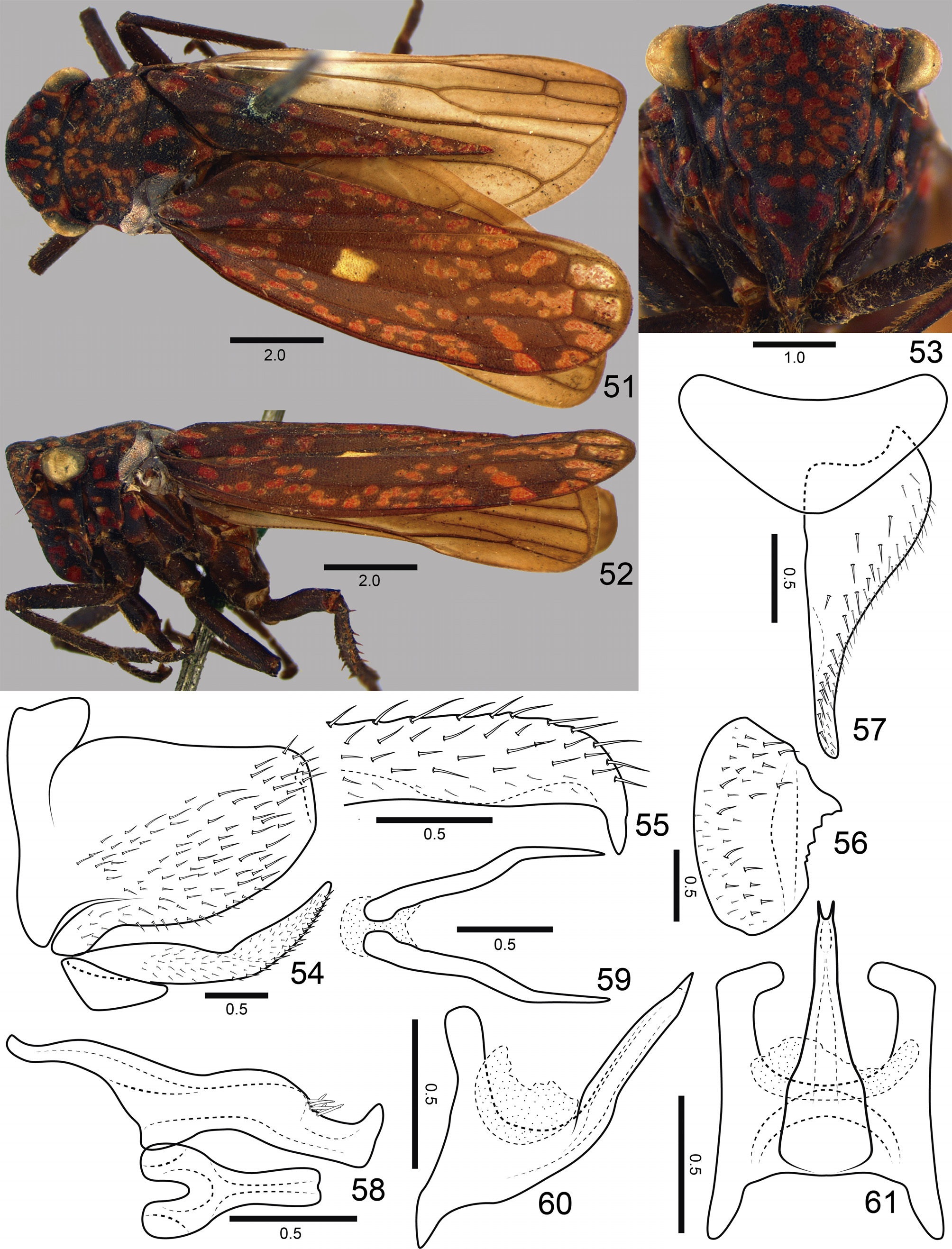
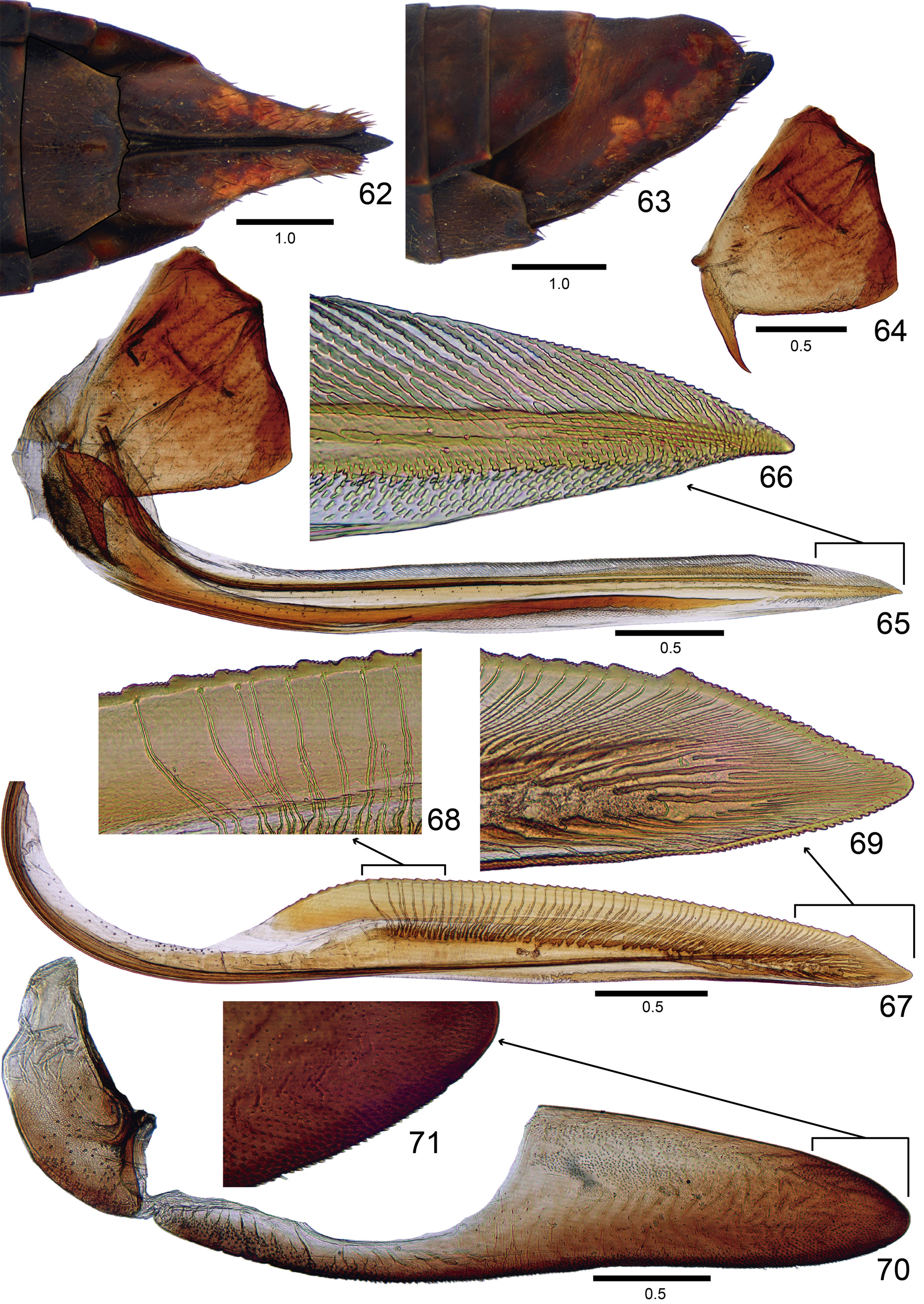
( Figs 51–71 View FIGURES 51–61 View FIGURES 62–71 )
Length. Male 13.6 mm (n = 1). Females 12.6–13.0 mm (n = 2).
Head and thorax ( Figs 51–53 View FIGURES 51–61 ) much as described by Young (1977: 37) for the genus and in the diagnosis given above. Color as in Figs 51–53 View FIGURES 51–61 ; apical half of crown dark brown to black at center; forewing spots and vermiculations pale red, their quantity distinctly smaller than in the previous two species.
Male terminalia. Pygofer ( Figs 54–56 View FIGURES 51–61 ), in lateral view, moderately produced posteriorly; posterior margin truncate, with projection turned inwards and forming serrated triangular process with acute apex; small macrosetae from ventrobasal portion to apex, surface of process without macrosetae. Subgenital plate ( Figs 54, 57 View FIGURES 51–61 ), in ventral view, subtriangular; broad at base and slender from basal third to apex; small macrosetae and microsetae distributed mostly along outer lateral margin; in lateral view, plate extending posteriorly as far as pygofer apex. Style ( Fig. 58 View FIGURES 51–61 ), in dorsal view, extending posteriorly beyond apex of connective; with outer preapical lobe; outer margin behind lobe with setae; apex expanded, foot-shaped. Connective ( Fig. 58 View FIGURES 51–61 ), in dorsal view, Y-shaped; arms short; stalk elongate, not expanded apically. Aedeagus ( Figs 60, 61 View FIGURES 51–61 ) symmetrical; in lateral view, with distinct basidorsal and basiventral apodemes; shaft slender, directed dorsally, with pair of small apical processes. Membranous area between anal tube and dorsal aedeagal surface damaged. Paraphyses ( Fig. 59 View FIGURES 51–61 ), in ventral view, with rami long, acute, and divergent from each other.
Female terminalia. Sternite VII ( Figs 62, 63 View FIGURES 62–71 ) not strongly produced posteriorly; in ventral view, with posterior margin transverse and with slight median projection; apex of this projection emarginate. Pygofer ( Figs 62, 63 View FIGURES 62–71 ), in lateral view, moderately produced posteriorly; distal margin broadly rounded; ventral margin slightly sinuous; macrosetae distributed mostly on posterior portion and extending anteriorly along ventral area. First valvifer ( Figs 64, 65 View FIGURES 62–71 ), in lateral view, subtrapezoidal, with conspicuous, basiventral spiniform process, anterior margin with small dentiform process, posterior margin slightly sinuous. First valvula ( Figs 65, 66 View FIGURES 62–71 ), in lateral view, with dorsal and ventral margins approximately parallel; apex acute; dorsal sculptured area strigate, extending from basal portion to apex of blade; ventral sculptured area scale-like, restricted to apical portion of blade; ventral interlocking device restricted to basiventral half of blade; in ventral view, base of valvula distinctly expanded outwards. Second valvula ( Figs 67–69 View FIGURES 62–71 ), in lateral view, distinctly expanded beyond basal curvature; apex subacute; preapical prominence indistinct; dorsal margin with about 50 mostly triangular continuous teeth; denticles distributed on teeth and on apical portion of blade, except on apex (dorsal dentate apical portion slightly longer than ventral portion); ducts extending towards teeth and apex of valvula (basalmost seven teeth or so do not receive ducts). Gonoplac ( Figs 70, 71 View FIGURES 62–71 ) of the usual Cicadellinae type: in lateral view, with basal half narrow and apical half distinctly expanded; apex obtuse; denticuli and setae distributed on apical portion and extending anteriorly along ventral margin.
Material examined. Holotype ♂: “ XI.1934.| SÃO PAULO \ Alto da S. [Serra] \ R. Spitz ” ( DZUP) . Paratypes: 1 ♀, same data as the holotype, except “ I.1927 ” and “ Alto da Serra ” ( DZUP) ; 1 ♀, same data as the holotype, except “ IX.26 ” and name of the collector illegible ( DZUP) .
Etymology. The name of the new species refers to the collector of the type series.
Remarks. Aguana spitzi sp. nov. can be recognized by the absence of a median spot on the apical half of the crown ( Fig. 51 View FIGURES 51–61 ), spots and vermiculations of the forewings pale red, their quantity distinctly smaller than in other species ( Figs 51, 52 View FIGURES 51–61 ), apical aedeagal processes extremely small ( Fig. 61 View FIGURES 51–61 ), and posterior margin of female sternite VII with slight median projection ( Fig. 62 View FIGURES 62–71 ). In one female paratype we observed four strepsipterans (two on each side) parasitizing the abdomen.
| DZUP |
Universidade Federal do Parana, Colecao de Entomologia Pe. Jesus Santiago Moure |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |