Benthocometes australiensis, Nielsen, Jørgen G., 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.197128 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5696848 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CD87FC-4D63-5776-8387-D0D4FB58851D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Benthocometes australiensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Benthocometes australiensis View in CoL n. sp.
Figs. 1–4 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4
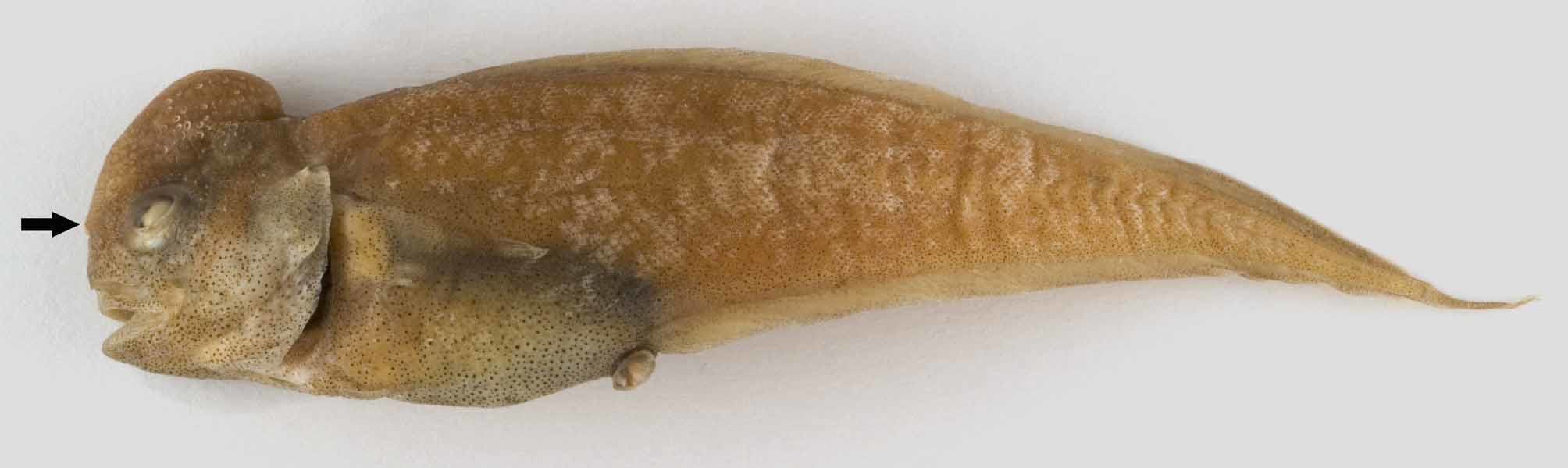
Material examined. Holotype: NMV A 29728 View Materials -016, female, 93 mm SL, off northwestern Australia, Kulumburu L29 transect, 13°15’54’’S, 123°22’27’’E to 13°16’21’’S, 123°21’24’’E, R/V Southern Surveyor, beam trawl, 390–394 m, 12 Apr. 2008.
Comparative material. See examined specimens of B. robustus (p. 6)
Diagnosis. Benthocometes australiensis differs from the only other species in the genus, B. robustus , by the low number of long gill rakers on anterior arch (3 vs 9–12); few predorsal pterygiophores (4 vs 7–10); form of palatine dentition (circular vs elongate); predorsal length (22.0 vs 26.5–31.0 % SL); upper jaw length (8.7 vs 11.0–13.0 % SL); dorsal fin origin above vertebra no. 3 (vs 6–7); anal fin origin below dorsal fin ray no. 24 (vs 17–20); few, fang-like teeth (vs many, small, granular teeth); distinct supraorbital pores (vs pores undeveloped).
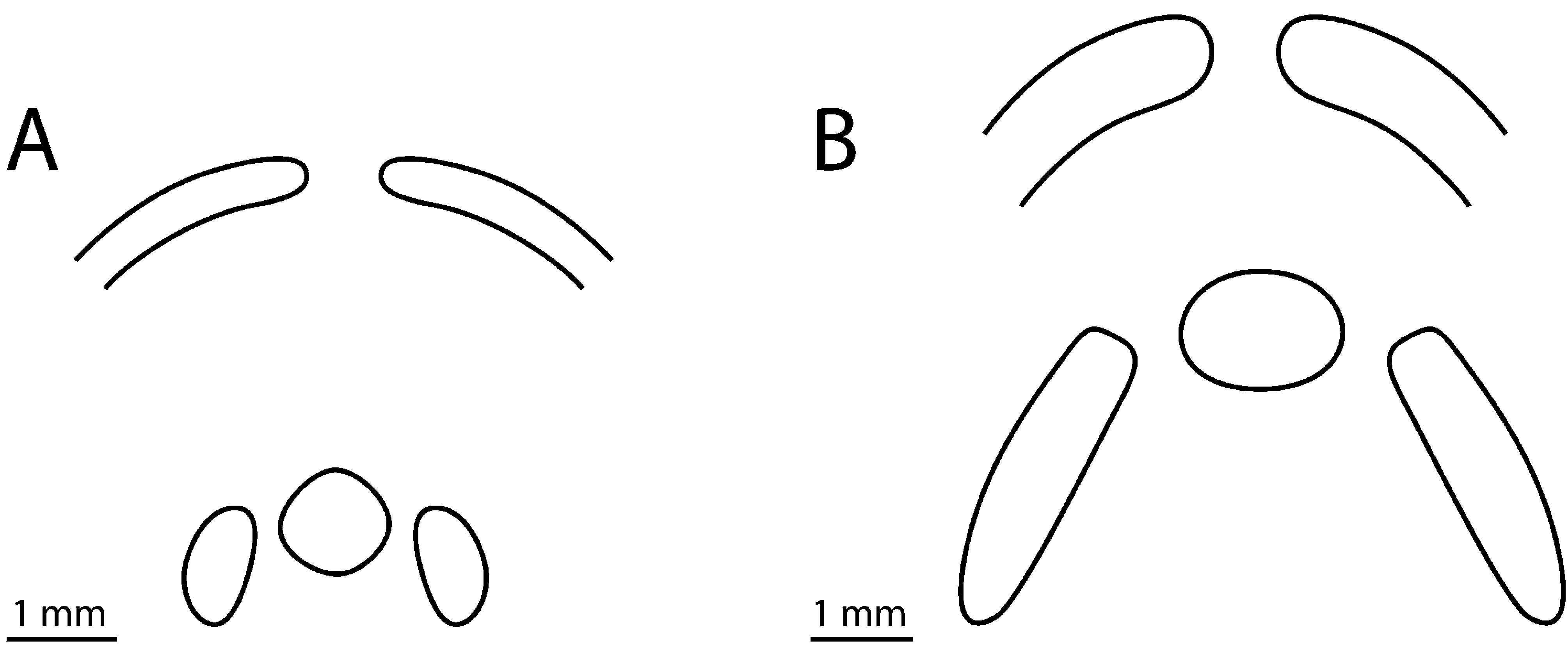
Description. The major meristic and morphometric characters are shown in Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Body short and robust and head small with blunt snout. Both head and body fully covered by small (1.3 mm under pectoral fin), oval, overlapping scales. Lateral line running midway between dorsal edge and midline of fish ending about one head-length from base of caudal fin. Vertical fins joined. Origin of dorsal fin far forward above base of pectoral fin, anal fin origin anterior to midpoint of fish, pectoral fin placed below midline of body almost reaching anus, pelvic fins reaching halfway to anal fin. Anterior nostril a low tube with a skin flap, posterior a mere hole. Tip of snout with about 10 small, black skin flaps. Diameter of eye larger than length of snout. Short upper jaw ending below anterior margin of eye. Opercle with two, sharp spines, upper pointing backwards and lower postero-ventrally; none of them reaching hind margin of opercle. Anterior gill arch ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A) with 2–3 small, spiny knobs on upper branch and lower branch with three long rakers and 6–7 small, spiny knobs. Longest of the ca. 50 gill filaments longer than rakers. Pseudobranchial filaments (6–8) very small.
.
* Cf. Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 ; ** Mean value in parentheses.
Head pore system: Number of pores in supraorbital row three, in infraorbital row five, in mandibular row three and in preopercular row two.
Dentition ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 A): All teeth small, but fang-like; anteriorly in each premaxillary a more distinct fang. Premaxillaries with ca. 15 teeth, uniserial posteriorly. Vomerine tooth patch round with ca. 15 teeth. Palatine dentition an oval patch with 10–12 teeth. Dentaries with 15–20 teeth, uniserial posterorly. One elongate, median basibranchial tooth patch.
Sagittal otolith ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 A–C): Otolith with blunt anterior and pointed posterior end, ventral rim even and dorsal rim with angle anteriorly; height 70 % of otolith-length; thickness 25 % of length; sulcus 65 % of otolith-length with caudal part almost as long as osteal part.
Axial skeleton (based on radiographs): Number of precaudal vertebrae 12. Anterior neural spine half length of second spine. Precaudal vertebrae 1–6 with pointed neural spines, 7–12 with blunt spines and all caudal neural spines with pointed tips. Anterior five haemal spines with blunt tips and the rest with pointed tips. Neural spines on precaudal vertebrae 5–12 with enlarged bases. Parapophyses on vertebrae 7–12 increasing in lengths posteriorad. Pleural ribs on vertebrae 3–12. Epipleural ribs not observed.
Coloration. Ground color of preserved specimen brownish with numerous small, black spots most dense on head and abdomen. Gill cover and peritoneum dark brown. Eye blue with white lens.
Distribution and biology. The holotype and only specimen was caught in a beam trawl at 390–394 m off Kimberley, Western Australia. In the same trawl-haul the following benthopelagic fish were taken (pers. comm. Martin Goman): Unidentified Congridae , Chlorophthalmus cf. acutifrons , Bregmaceros sp., Coelorinchus maculatus , Hymenocephalus longibarbis , Lucigadus ori , Chaunax sp., Phenacoscorpius sp., Plectrogenium sp., Malakichthys wakiyae , Bembrops sp., Kopua sp., Symphurus sp.
Etymology. The specific name refers to the regional locality of the type specimen.
TABLE 1. Meristic and morphometric characters of Benthocometes australiensis and robustus.
| B. austra- liensis holotype | West Atlantic 13 spms. | Benthocometes robustus “Bump- East Atlantic Total 29 heads* 12 spms. specimens** 4 spms. | No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL, mm | 93 | 57–110 | 59–95 20–123 20–123 | 29 |
| Meristic characters | ||||
| Dorsal fin rays | 98 | 93–111 | 96–107 94–107 93(100.8)111 | 29 |
| Predorsal pterygiophores | 4 | 7–10 | 8–10 7–9 7(8.6)10 | 23 |
| Caudal fin rays | 11 | 11 | 11 11 11 | 27 |
| Anal fin rays | 80 | 78–92 | 84–94 82–91 78(86.1)94 | 29 |
| Pectoral fin rays | 30 | 28–31 | 30–31 28–32 28(29.8)32 | 26 |
| Pelvic fin rays | 2 | 2 | 2 2 2 | 29 |
| Precaudal vertebrae | 12 | 11–12 | 11 11–12 11(11.2)12 | 29 |
| Total vertebrae | 50 | 48–50 | 48–50 47–50 47(49.0)50 | 29 |
| Dorsal fin origin above vertebra no. | 3 | 6 | 6–7 6 6(6.0)7 | 27 |
| Anal fin origin below dorsal fin ray no. | 24 | 17–20 | 17–18 17–20 17(18.4)20 | 27 |
| Anal fin origin below vertebra no. | 15 | 13–15 | 13–14 14–16 13(14.4)16 | 29 |
| Long gill rakers | 3 | 10–12 | 9–10 9–11 9(10.5)12 | 22 |
| Pseudobranchial filaments | 7–8 | 6–7 | 6–7 6–8 6(6.6)8 | 20 |
| Morphometric characters | ||||
| Head length | 23.0 | 20.0–23.5 | 22.0–25.0 21.5–22.5 20.0(21.9)25.0 | 19 |
| Depth at anal fin origin | 22.5 | 17.0–21.5 | 17.0–20.5 19.0–21.5 17.0(19.2)21.5 | 17 |
| Upper jaw length | 8.7 | 11.5–12.5 | 11.5–12.0 11.0–13.0 11.0(11.7)13.0 | 19 |
| Diameter of eye window | 5.7 | 5.4–6.9 | 5.8–6.4 5.5–6.7 5.4(6.1)6.9 | 19 |
| Interorbital width | 5.1 | 5.4–6.3 | 5.4–6.4 5.1–5.9 5.1(5.8)6.4 | 13 |
| Postorbital length | 13.0 | 10.5–12.5 | 11.0–12.0 11.0–13.0 10.5(11.7)13.0 | 17 |
| Preanal length | 46.0 | 40.5–47.0 | 41.0–45.0 41.0–46.0 40.5(43.7)47.0 | 19 |
| Predorsal length | 22.0 | 26.5–31.0 | 27.5–28.0 27.0–31.0 26.5(28.9)31.0 | 19 |
| From base of pelvic to anal fin origin | 25.0 | 22.0–27.5 | 24.5–25.5 24.0–26.5 22.0(24.7)27.5 | 17 |
| Pectoral fin length | 14.0 | 10.5–12.0 | 10.5–12.5 9.5–13.0 9.5(11.2)13.0 | 17 |
| Pelvic fin length | 14.0 | 9.1–12.5 | 11.0–11.5 9.8–11.5 9.1(10.7)12.5 | 15 |
| Snout to post. end of lateral line | 79 | 79–86 | 75–83 74–82 74(79.8)86 | 12 |
| NMV |
Museum Victoria |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |