Batrisodes grandiceps Zhang & Yin, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4938.2.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1BE3B4A4-8BA0-4267-A89C-2EAD3CCF13C9 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4563884 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C787F3-FFD3-E669-B6CF-09CF9C118204 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Batrisodes grandiceps Zhang & Yin |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Batrisodes grandiceps Zhang & Yin View in CoL , sp. nov.
( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 , 2 View FIGURE 2 )
Type material. HOLOTYPE: CHINA: ♂, ‘ China: Shaanxi, Ningshan County (ṪȐfl), Pingheliang Forest Park (ỸOiẌÑẎƙfin'ẘ), 33°28′14″N, 106°29′29″E, 13.vii.2012, 2050– 2150 m, mixed leaf litter, sifted, Y.-H. Pan leg.’ ( SNUC). GoogleMaps PARATYTYPES: CHINA: 4 ♂♂, 3 ♀♀, same label data as for holotype ( SNUC); GoogleMaps 1 ♂, 1 ♀, same label data as for holotype, except ‘ 12.vii.2012,’ ( SNUC); GoogleMaps 3 ♂♂, 2 ♀♀, ‘ China: Shaanxi, Ningshan County , Huoditang Forestry Centre (Ẋḿffifiá), 33°26′N, 108°27′E, 12.vii.2012, 1500–1700 m, mixed leaf litter, sifted, CHEN & LI leg.’ ( SNUC). GoogleMaps
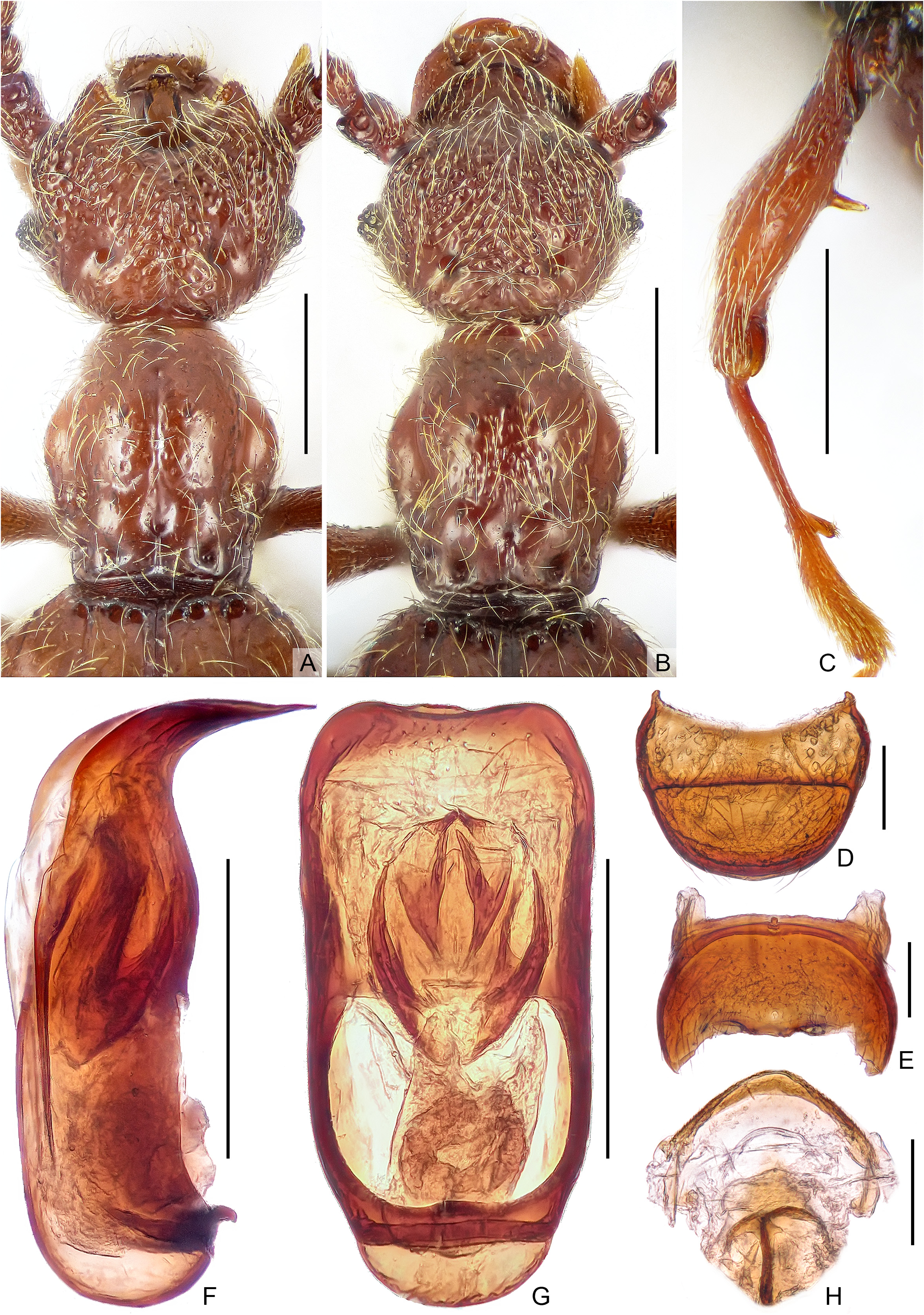
Diagnosis. Male. Body length 2.29–2.35 mm. Head base rounded, much wider than pronotum; frons with anterolateral margin greatly protruding anteriorly, deeply and roundly concave at middle; clypeus with large projection at middle, sides of projection more or less parallel in dorsal view; antennomere 3 larger than antennomere 2. Pronotum finely punctate, with four distinct discal teeth. Mesofemur with long ventral spine near middle, mesotibia expanded for apical 2/5 of tibial length, with blunt projection before middle. Aedeagus dorso-ventrally symmetric, with symmetric, strongly sclerotized endophallus. Female. Similar to male in external morphology, lacking modifications on head and legs, antennomere 3 same size of antennomere 2; may be identified only by geographical association with male.
Description. Male ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ). Body reddish brown, length from anterior margin of clypeus to apex of abdomen 2.29–2.35 mm. Head ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ) slight wider than long, length from anterior margin of clypeus to head base (excluding occipital constriction) 0.46–0.48 mm, width across eyes 0.53–0.55 mm; surface roughly punctate, with large, nude vertexal foveae; frons with anterolateral margin greatly protruding anteriorly, deeply and roundly concave at middle; clypeus with large projection at middle, sides of projection more or less parallel in dorsal view, clypeal anterior margin rounded; lateral vertexal carina faint, extending from occipital constriction to level of anterior margin of fovea, mediobasal carina as long as lateral ones. Eyes relatively small, each composed of approximately 35 facets. Antenna lacking distinct club, antennomere 1 (scape) thick, subcylindrical, antennomeres 2–10 moniliform, antennomere 3 distinctly larger than 2, antennomeres 4–8 of similar width, antennomere 9 much wider than 8, antennomeres 9 and 10 successively broader, each strongly transverse, antennomere 11 largest, subconical, lacking hook-like spine. Pronotum slightly longer than wide, length along midline 0.48–0.50 mm, maximum width 0.45 mm; sides rounded, widest near middle, disc slightly convex, finely punctate, with four distinct teeth; median and lateral longitudinal sulci distinct; with small nude median and setose lateral antebasal foveae; outer and inner pair of basolateral foveae distinct. Elytra wider than long, length along suture 0.60–0.62 mm, maximum width 0.72–0.75 mm; each elytron with three large, nude basal foveae, inner two close; discal striae shallow and short, extending posteriorly for 1/3 of elytral length. Mesofemur ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ) with long ventral spine near middle, mesotibia expanded for apical 1/3 of tibial length, with blunt ventral projection at apical 2/5, apex of projection rounded, with dense short setae. Abdomen widest at lateral margins of tergite 1 (IV), length of dorsally exposed part along midline 0.73–0.77 mm, maximum width 0.72 mm; tergite 1 (IV) with strongly oblique marginal carinae; discal carinae thick, tergite 5 (VIII) ( Fig. 2D View FIGURE 2 ) semicircular; sternite 6 (VIII) ( Fig. 2E View FIGURE 2 ) transverse. Aedeagus ( Fig. 2F, G View FIGURE 2 ) 0.41 mm long, median lobe dorso-ventrally symmetrical and flattened, broadest near apex, apical part narrowing toward apex and curved ventrally in lateral view; endophallus well-sclerotized, lateral lobes broad at base and evenly narrowing apically.
Female ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ). General morphology similar to male, lacking modifications on head ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ) and legs; antennomere 3 same size of antennomere 2; each eye composed of about 12 facets; genitalia ( Fig. 2H View FIGURE 2 ) symmetric, weakly sclerotized, 0.21 mm wide. Measurements of body parts (as for male): body length 2.25–2.31mm, length/ width of head 0.46–0.48 mm / 0.52–0.53 mm, pronotum 0.48–0.50 mm / 0.44–0.46 mm, elytra 0.58 mm / 0.74 mm, abdomen 0.73–0.75 mm / 0.74–0.75 mm.
Comparative notes. The new species is apparently most close to B. grossepunctatus sp. nov. described below by the males having a similar position and shape of the cephalic modifications and spination of the legs, as well as the presence of a well-sclerotized endophallus of the aedeagus. They can be clearly separated by the smaller body size (2.29–2.35 mm vs. 2.41–2.48 mm), somewhat parallel sides of the projection on the clypeus, the finely punctate pronotal disc, and the different shape of the lateral lobes of the aedeagal endophallus of the new species.
Distribution. China: Shaanxi.
Etymology. The new specific epithet refers to the large head of the new species.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |