Tor mekongensis, Hoàng, Ức, Ạm, Ạnh Ph, Durand, Jean-Dominique, Ần, Ngân Tr Ọng Tr & Phan, Phúc Đình, 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4006.3.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:CBDC7284-7EF2-49F4-A875-13E79B597E0A |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5631579 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C72546-7E28-7113-7EDE-02775DE2FDCD |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Tor mekongensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Tor mekongensis View in CoL sp. nov.
Holotype: UNS 00877, 337 mm SL; upper Ea Krong No drainage: upper Mekong basin in montane evergreen forest in Bidoup-Núi Bà National Park, Lâm Đồng Province, Vietnam (12°16’23.68” N 108°26’30.17” E, 672 m), 24 June 2014, Hoàng Đức Huy, Ph ạm Mạnh Hùng and Tr ần Tr ọng Ngân ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ).
Paratypes (all same locality as holotype): UNS 00878, 79.5 mm SL, 24 June 2014; UNS 00879, 76 mm SL, 24 June 2014.
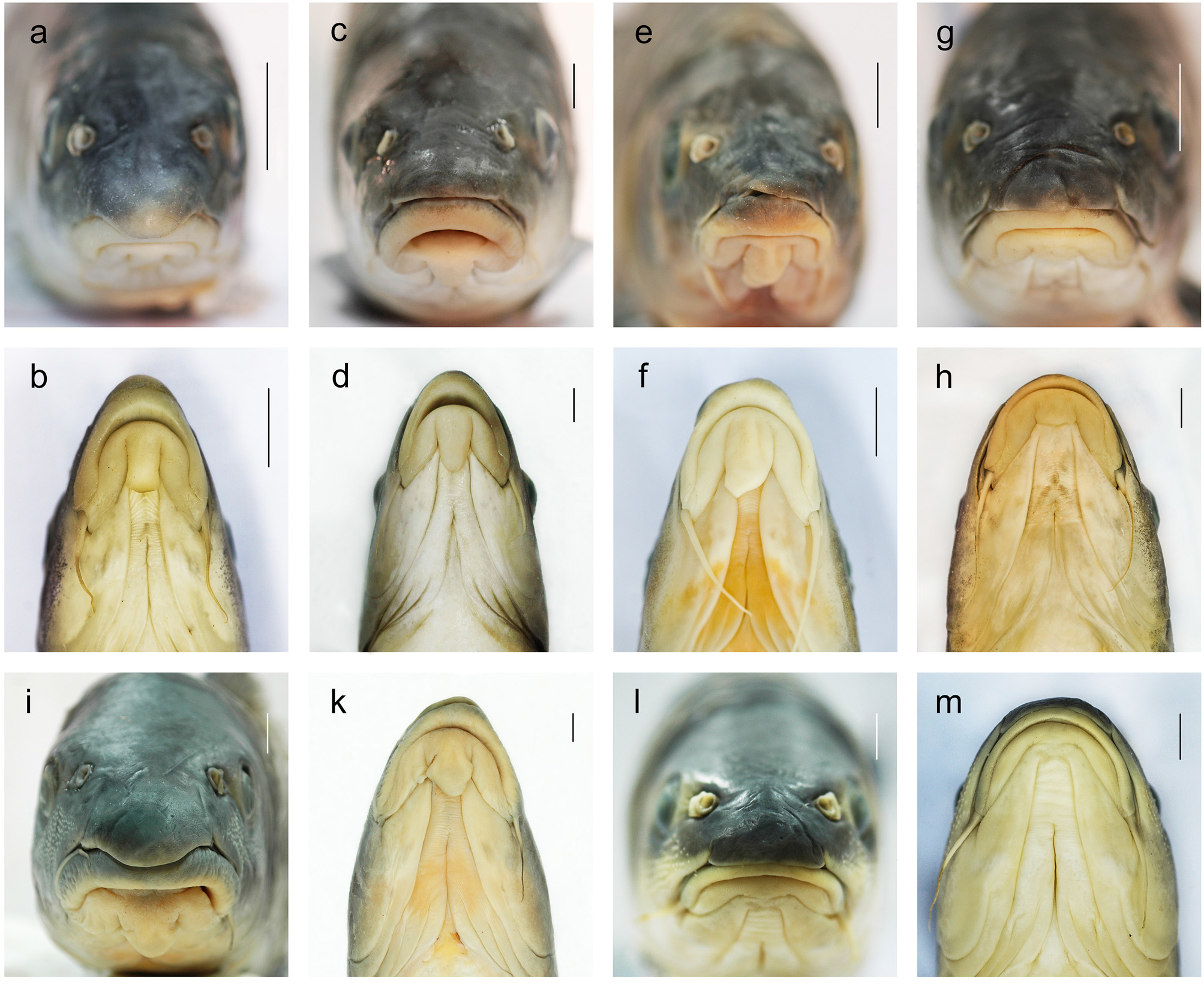
Diagnosis. Tor mekongensis is similar to T. tambra but differs genetically. Tor mekongensis differs from T. sinensis in having lateral scales 23 vs. 23–28, pelvic-fin rays 2/7 vs. 1/8–9, median lobe short vs. long, rostral hood rounded and blunt vs. prolonged into a lobe. Tor mekongensis differs from T. dongnaiensis in having predorsal scales 9 vs. 10, median lobe short vs. long, pelvic-fin rays 2/7 vs. 1/8, upper lip thin vs. thick, colour in life silver grey vs. yellowish, lobes of caudal fin nearly equal vs. unequal. Tor mekongensis differs from T. tambroides in having lateral scales 23 vs. 23–26, median lobe short vs. long, upper lip without median projection vs. median projection present. Tor mekongensis differs from T. ater in having lateral scales 23 vs. 30–31, scales in transverse row 3/1/2 vs. 5/1/2, predorsal scales 9 vs. 11–12, stripe on side of body absent vs. present.
Description. General appearance in Figure 5 View FIGURE 5 ; meristic and morphometric data of specimens given in Table 3 View TABLE 3 . Head longer than deep, its depth about 1.4–1.5 times in HL and its dorsal profile slightly convex. Snout blunt. Rostral hood rounded and blunt. Mouth subterminal and oblique, its posterior edge not extending to vertical line of orbit. Lips normal fleshy, median lobe of lower lip developed, but does not reach the line connecting the corners of the mouth ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 g, h). Upper lip not prolonged into a lobe. Rostral and maxillary barbels almost equal in length and both longer than eye diameter.
Body elongate, moderately compressed, body depth about 3.3–3.6 times in SL; caudal peduncle slender and long, about 1.5–2.0 times longer than deep. Lateral line complete, 23 scales; 9 predorsal scales; 3/1/2 scales in transverse row anterior to pelvic-fin insertion.
Dorsal with 4 simple and 9 branched rays, last simple ray smooth; dorsal-fin origin inserted slightly opposite to pelvic-fin origin; distal margin slightly concave. Pectoral fin pointed with 1 simple and 15 branched rays. Pelvic fin pointed, with 2 simple and 7 branched rays; axillary scale present. Anus immediately in front of anal fin. Anal fin pointed with 3 simple and 6 branched rays. Caudal fin deeply forked with 10+9 principal rays, 9+8 being branched.
Colour in life. Head dark on back, white on lower jaw. Body dark on back, grey on side, snowy white on belly. Scales silver grey. Dorsal and caudal fins grey on ray, yellow tinge distally. Pelvic fin and anal fin grey to dark grey, orange tinge distally. Pectoral fin pinkish on origin, grey on rays ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 a, b).
Colour in preservative. Similar to that of fresh condition except noted below. Body including head dark grey on back. Lower half of body greyish white. Dorsal fin, pectoral fin, pelvic fin and anal fin grey to blackish. Caudal fin grey on rays and pale on margin ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 c).
Etymology. Specific epithet is in reference to the type locality of Mekong drainage.
Suggested common names. Cá ngựa xám Mê Kông (Vietnamese), Mekong mahseer (English).
| UNS |
University of Science, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |