Bolboceras bopdevense Kalawate & Hillert, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4964.3.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9DCEC917-64BE-4955-B7CD-DF5E15FBDAF4 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4714769 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C4C91A-F103-FFB4-C3DA-F910FB06FDCF |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Bolboceras bopdevense Kalawate & Hillert |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Bolboceras bopdevense Kalawate & Hillert , new species
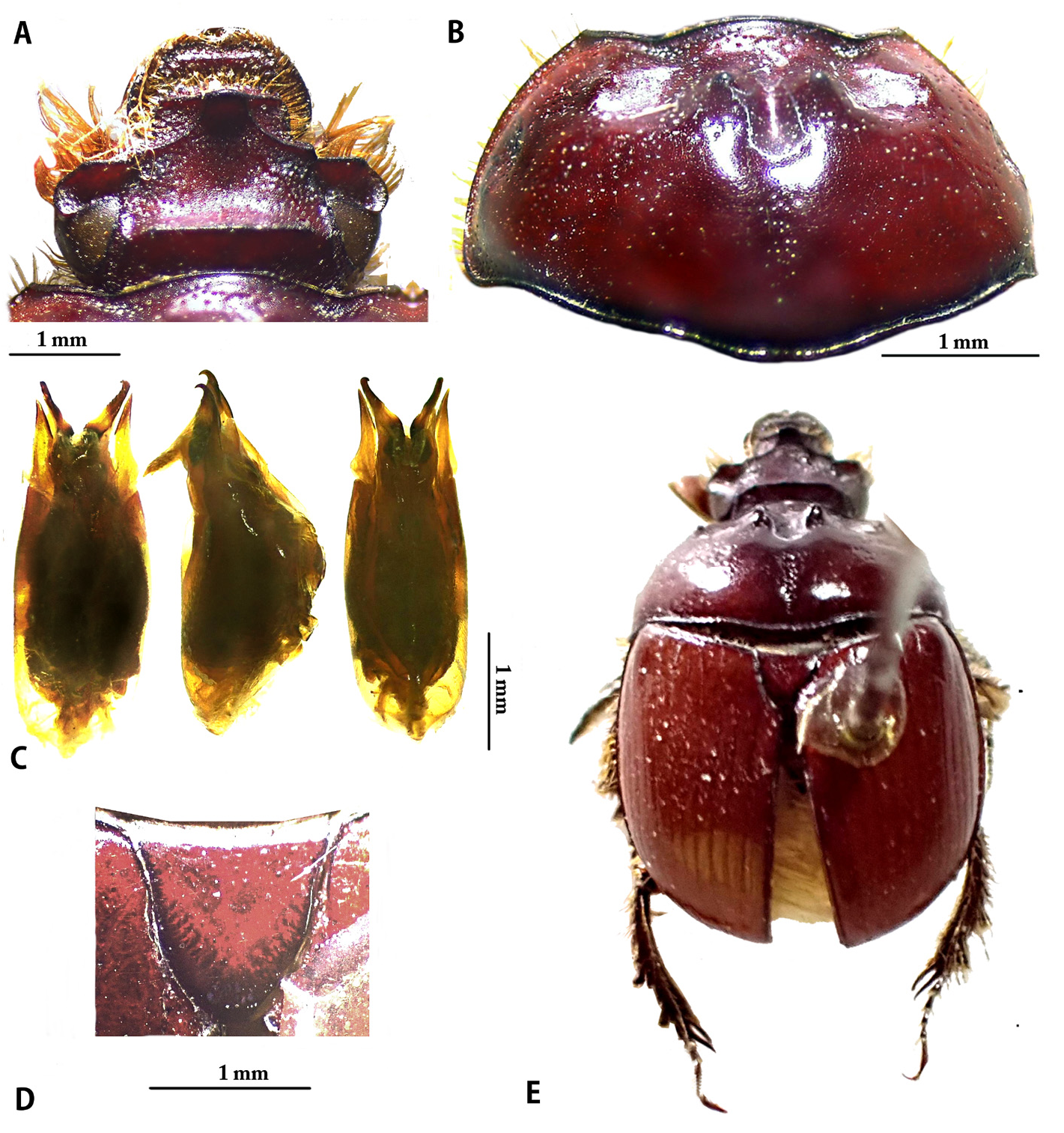
( Table 1 View TABLE 1 , Figs. 1A–E View FIGURE 1 , 4C View FIGURE 4 , 5 View FIGURE 5 )
Type locality. Kondhwa , Pune District, Maharashtra, India ( 18.477N, 73.894E, 700 m a.s.l.) GoogleMaps .
Type material. Holotype, male (collection of B.S. Lamba, ZSI-WRC, ENT-1/3534), “Bopdev Ghat, Kondhwa taluk, Pune district , Maharashtra, India, ( 18.477N, 73.894E, altitude 700 m), 29 September 1968 ”. GoogleMaps
Description of holotype, male ( Fig. 1E View FIGURE 1 ). Body distinctly convex, subglobular, dark brown and shiny.
Head ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 , 4C View FIGURE 4 ). Labrum with moderately concave anterior margin; transverse ridge distinct, fine; clypeus closely punctate; lateral perimarginal ridge of clypeus converging to single, anteromedian tubercle distinct, with very broad and blunt apex, oval in dorsal view. Perimarginal clypeal ridge distinct, k-shaped; frons smooth with few punctures; vertex distinctly, sparsely punctate; transversal interocular ridge strongly developed, almost straight, long, high, reaching to paraocular lines, lateral slope slight; Anterior edge of eye canthus straight, surface rugopunctate, distinctly upturned, forming distinctly elevated ridge with anterolateral blunt tubercle; paraocular line fine, almost straight virtually, reaching beyond level of interocular elevation, but not reaching base of head.
Pronotum ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ). Slightly depressed anteromedially in lateral view; conical discoparamedian protrusions present, apex blunt, anterior declivity slightly steep; discolateral protrusions slightly elevated; discomedian impression deeply impressed, almost U-shaped; discolateral impressions moderately shallow; very finely punctate midline impression at basomedian surface. Anterolateral angle of pronotum ca 90°, with acute anterolateral point. Surface of pronotum finely doubly punctate, primary punctation present laterally, anteriorly and along the margins, abundant, clusters of 15–20 punctures from edge of lateral (punctate) fovea on basomedian surface; second type of punctures are sparse and minute; base marginated.
Scutellum ( Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ). Almost smooth with minute and scattered punctures.
Elytra. With very shallowly impressed, finely punctate striae; intervals smooth.
Legs. Protibiae with 6 distinct exterior denticles, diminishing in size from apex to base, bordered in black; apex of terminal spur robust, tapering, acute, hooked. Mesotibiae and metatibiae with slightly elevated, transverse carinae.
Aedeagus ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ). Parameres acuminate, moderately curved at middle, tip acute. Lateral sclerotized aedeagal stalks robust, strongly sclerotized in basal and the upper portion, middle portion membranous, finely pointedhooked tip, recurved at apex, extending beyond the parameres.
Measurements. Body length: 11.46 mm, width: 7.14 mm. Head, length in dorsal view excluding labrum and mandibles: 1.80 mm, width: 3.42 mm; interocular ridge: 1.59 mm; ocular distance: 2.26 mm. Pronotum length: 4.17 mm, width: 6.80 mm. Scutellum length: 1.14 mm, width: 1.24 mm. Elytra, sutural length: 4.38 mm, maximum width combined: 6.99 mm. Genital capsule width 1.20 mm.
Differential diagnosis. The newly described species is closely related to B. sahyadriense Kalawate & Hillert, 2018 . Both species are characterized by clypeal tubercle situated at front edge of clypeus, perimarginal ridges of clypeus k-shaped and interocular ridge distinct, long and straight at the middle of the eye. The new species can be distinguished by a broadly elongate and well-developed clypeal tubercle in dorsal view. The anterior margin of genae is distinctly upturned, forming distinct elevated ridge, more or less weakly tuberculate at the middle of the front. The aedeagus is distinctly different, especially the lateral sclerotized aedeagal stalk ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ).
Other closely related species are B. nigricans and B. trimbakense Kalawate & Hillert , new species described below. The new species can be distinguished by the position and shape of the interocular ridge and the characteristics of the aedeagus. To separate this species from the other two, follow the key below and compare with Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ; Kalawate & Hillert (2018: 597, Figs. 2G–H View FIGURE 2 ) and Krikken (2013a: 51, Fig. 33).
Female. Unknown.
Etymology. The species is named after the type locality, Bopdev Ghat of the Pune district, Maharashtra.
Distribution. Known only from the type locality “Bopdev, Pune District, Maharashtra, India ”.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Bolboceratinae |
|
Genus |