Itara (Bornitara) tenompok Tan, Japir & Chung, 2024
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5424.1.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D3515496-31E1-48A4-B214-1AC668FB38D5 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10815097 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C15030-FFF1-FFC9-43C6-FA7EFE392449 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Itara (Bornitara) tenompok Tan, Japir & Chung |
| status |
sp. nov. |
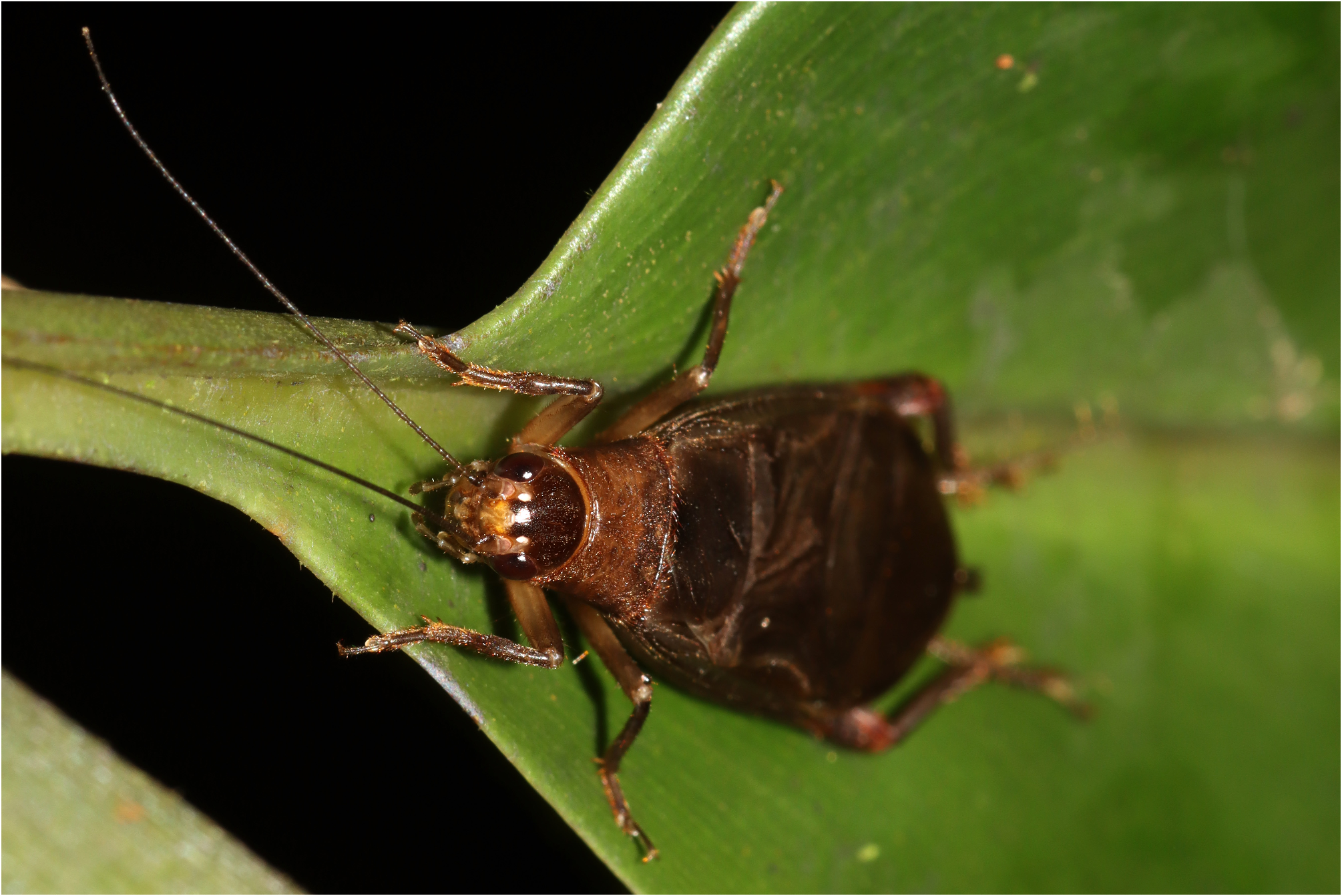
Itara (Bornitara) tenompok Tan, Japir & Chung , sp. nov.
( Figs 10–12 View FIGURE 10 View FIGURE 11 View FIGURE 12 )
Material examined. Holotype: EAST MALAYSIA: Sabah State • ♂; Tenompok Forest Reserve ; N6.01287, E116.50288, 1366.0± 13.5 m.a.s.l.; 6 November 2023, 20h15; on a ginger plant foliage; coll. M.K. Tan, R. Japir, M.A.B. Asidi & D.F.A. Damit; SBH.23.189 ( FRC) GoogleMaps
Diagnosis. This new species is most similar to Itara (Bornitara) borneoensis Gorochov, 1997 from Kalimantan and Itara (Bornitara) copiosa Gorochov, 2007 from Mount Trus Madi (Sabah) in the male genitalia; but differs by the pseudepiphallus having its apex narrower in dorsal view and not as strongly curved in lateral view, and by the pseudepiphallic parameres in ventral view having the distal part distinctly longer than the proximal part (instead of the proximal part longer) and a distinctly longer concavity along the inner margin ( Figs 13A, 13B View FIGURE 13 ). The new species also differs from Itara (Bornitara) copiosa by the pseudepiphallus longer and at apical half narrower; from Itara (Bornitara) borneoensis by the posterior-most harp vein forming a zig-zag line.
From the syntopic species Itara (Maxitara) kinabalu Gorochov, 2013 , this new species differs by the male genitalia ( Figs 13C–E View FIGURE 13 ) and by a smaller and slenderer habitus.
Etymology. The species is named after the type locality, Tenompok Forest Reserve.
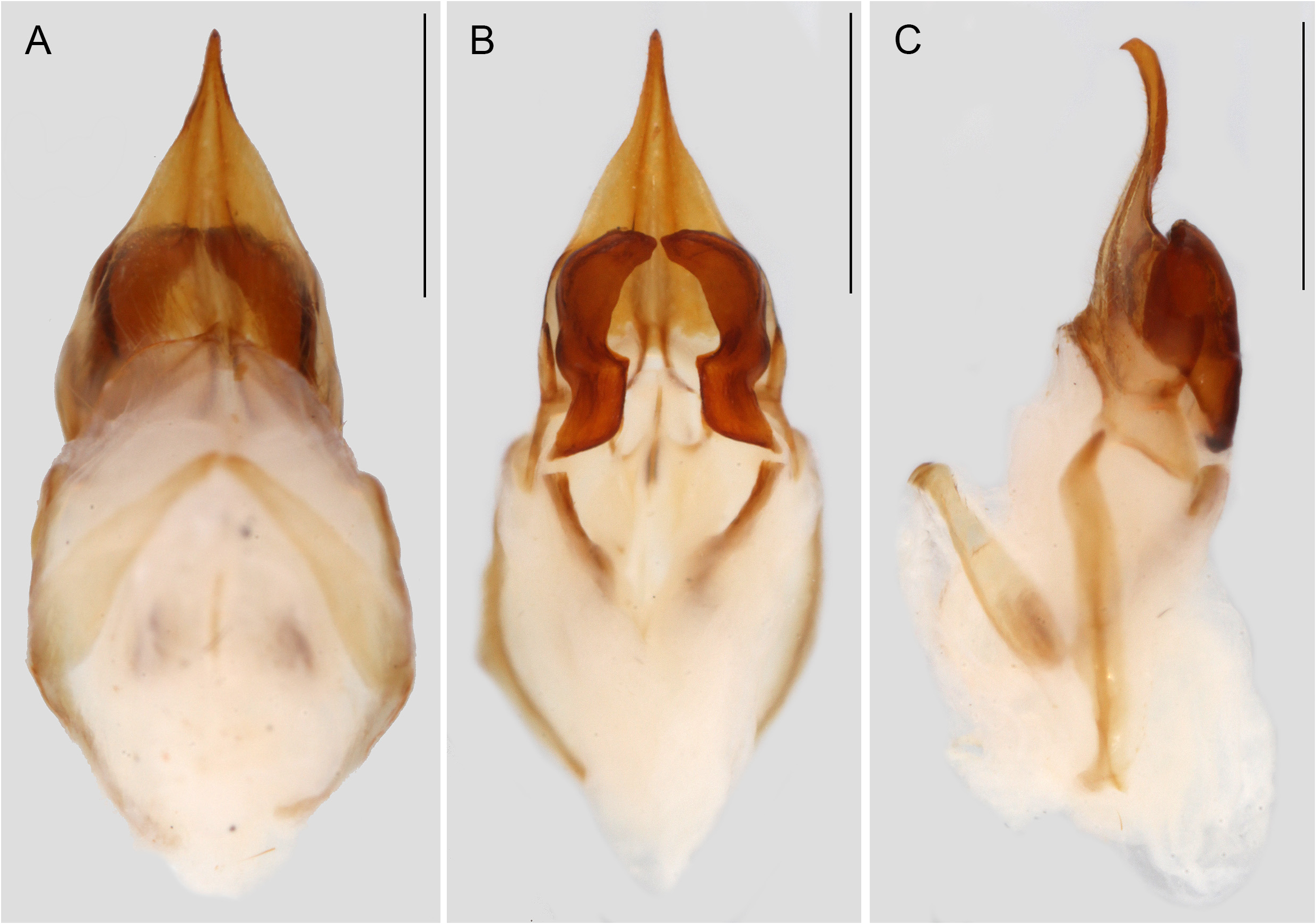
Description. Medium sized among congeners. Head dorsum shiny dark brown ( Fig. 11A View FIGURE 11 ). Fastigium darkened; 1.8 times wider than scapes ( Fig. 11A View FIGURE 11 ). Scapes brown with tint of dark brown ( Fig. 11A View FIGURE 11 ). Eyes in dorsal view faintly protruding anteriorly ( Fig. 11A View FIGURE 11 ) and in profile view taller than long ( Fig. 11B View FIGURE 11 ). Median ocellus hermispherical; lateral ocelli larger and broadly oval, located dorsal of scapes ( Fig. 11C View FIGURE 11 ). Maxillary palpi with fine short setae; with apical segment dark brown, longest and apical half strongly oblique; with subapical segment shorter than third segment; subapical segment at apex faintly expanding; third segment cylindrical ( Fig. 11D View FIGURE 11 ). Face in anterior view rounded, as tall as wide; area between scapes yellow brown; otherwise brown to grey brown ( Fig. 11C View FIGURE 11 ). Gena light brown; slightly dark brown posterior of eye ( Fig. 11B View FIGURE 11 ). Pronotal disk unicolourous dark brown; 1.6 times wider than long, widening posteriorly (posterior margin 1.5 times wider than anterior margin); very finely pubescent, with a row of setae along posterior and anterior margins; anterior margin broadly concave; posterior margin somewhat straightened at middle ( Fig. 11A View FIGURE 11 ). Pronotal lateral lobe same colouration as dorsal disk, ventral part with tint of fainter brown; ventral margin dark and nearly straight; ventro-posterior angle sloping ( Fig. 11B View FIGURE 11 ). TI without inner tympanum, outer tympanum with opening elongated oval ( Fig. 11E View FIGURE 11 ). TIII with 4 inner and 4 outer subapical spurs, 3 inner and 3 outer apical spurs; with 4 inner and 5 outer small spines before most proximal subapical spurs; without small spine between spurs. FIs and FIIs brown, with basal half paler. TIs generally brown. FIIIs pale brown; apical part including knee dark brown with tint of red brown. TIIIs generally yellow brown; spurs generally yellow brown with apices dark brown. Tergites and sternites yellow brown.
Male. FW 2.3 times longer than wide, surpassing abdominal apex, mostly yellow brown and hyalinous ( Fig. 11F View FIGURE 11 ). FW venation ( Fig. 11F View FIGURE 11 ): dorsal field in harp (ha) with four increasingly longer veins; posterior-most harp vein at base curved, at distal half forming zig-zag line. Mirror (mi) very large and transverse, 1.7 times as wide as long, very large and separated by one dividing vein; dividing vein broadly curved. Apical field relatively short, 1.2 times longer than length of mirror ( Fig. 11F View FIGURE 11 ). Lateral field with R and M generally parallel, with numerous very faint transverse veins; M and Sc mostly parallel and more closely spaced apart; Sc with numerous inter-laced projections, with ca. 10 tranverse projecting veins ( Fig. 11G View FIGURE 11 ). Hind wings only slightly surpassing apex of FW.
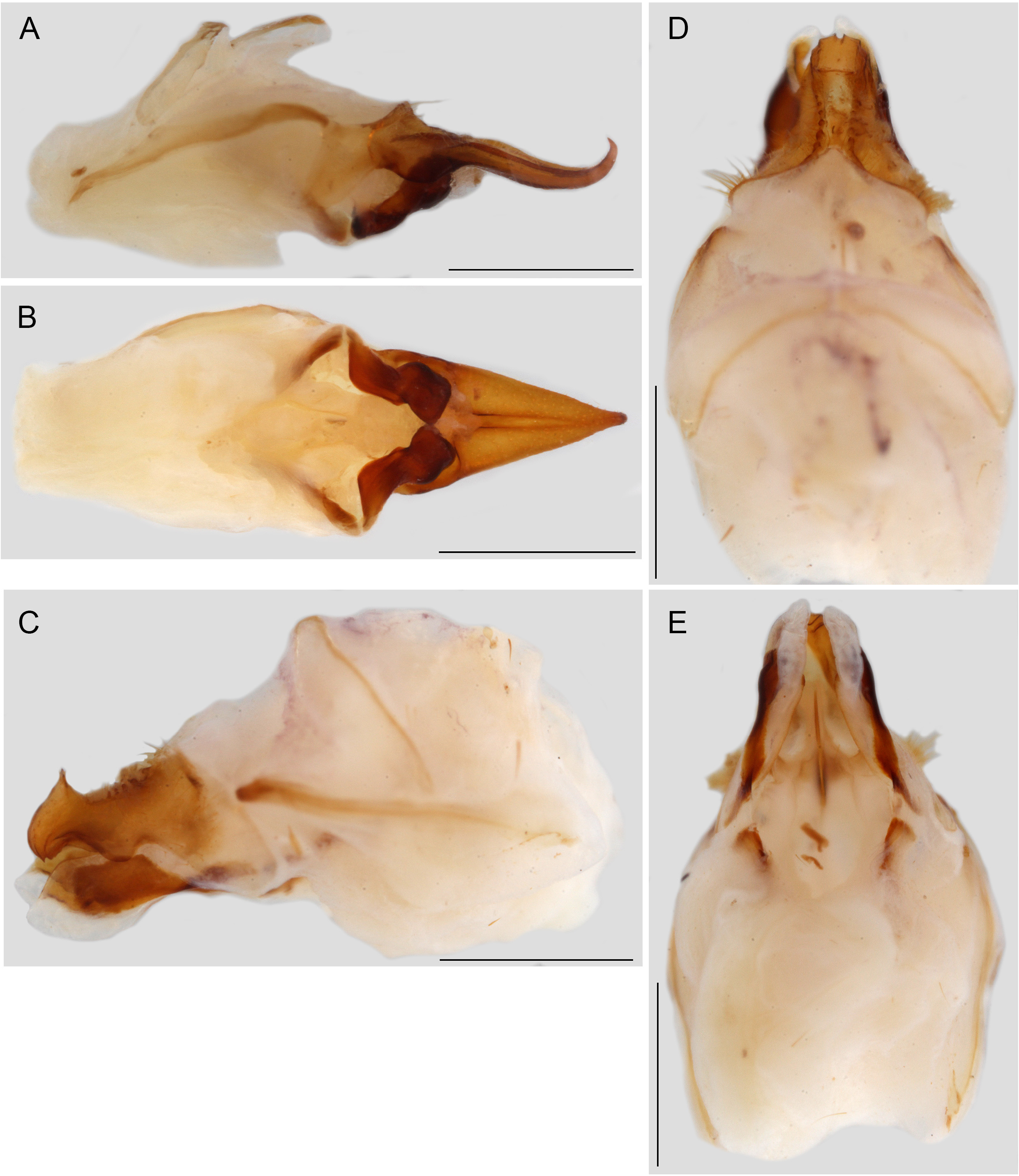
Male genitalia ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 ). Pseudepiphallus [epiphallus] typical of subgenus; in dorsal view triangular with apex acute; in lateral view flattened and at apex hooked. Pseudepiphallus in dorsal view: after middle strongly tapering, with lateral margin slightly concave. Pseudepiphallus in lateral view: with upper proximal edge slightly raised; dorsal margin at proximal half gently sloping, distal half slightly curved; at apex with a small tooth pointing dorsad; ventral margin lacking denticles on ventral surface, basally with tongue-shaped lobe pointing posteriorly, at middle slightly concave, distal half mostly straight. Pseudepiphallic parameres [ectoparameres] not surpassing apex of pseudepiphallus, sinuous. Pseudepiphallic parameres with proximal part reaching basal third with basal margin oblique and lateral margins straight and parallel; just before middle with inner margin forming 90° bent and outer margin broadly convex; thereafter with distal part having inner margin with deep and elongated concavity extending to near apex, outer margin broadly curved; at apex somewhat triangular and subobtuse. Ectophallic apodeme [endoparameral apodeme] in ventral view, straight to faintly curved. Ectophallic fold [rachis] needle-like, long and slender with posterior apex acute, tubular and strongly curved anteriorly into endophallic sclerite [formula]. Endophallic sclerite small, slender and Y-shaped, ventrad of ectophallic fold. Rami slightly curved, longer than pseudepiphallus length, at anterior ends not connected.
Female. Unknown.
Measurements (in mm). ♂ holotype: BL = 16.3; BWL = 24.1; HL = 2.1; PronL = 2.7; PronW = 4.3; FWL = 17.0; FWW = 7.5; HWT = 2.3; FIIIL = 10.5; TIIIL = 6.9; TaIIIL = 3.0.
Ecology. We found this species to co-occur in syntopy with Itara (Maxitara) kinabalu Gorochov, 2013 ( Fig. 14 View FIGURE 14 ), although it appears that this new species is lower in abundance (as more specimens of Itara (Maxitara) kinabalu were collected).
Type locality. EAST MALAYSIA: Sabah: Tenompok Forest Reserve
Distribution. Borneo (Sabah: Tenompok Forest Reserve)
Calling song. Unknown .
| FRC |
Fusarium Research Center |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Grylloidea |
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Itarinae |
|
Genus |