Utivarachna rimba Dhiya’ulhaq & Dupérré, 2024
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5418.5.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8681F446-C4A0-466F-A763-57F426B14523 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10794112 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C0D450-D175-953D-41AD-FF011D07D4AB |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Utivarachna rimba Dhiya’ulhaq & Dupérré |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Utivarachna rimba Dhiya’ulhaq & Dupérré , sp. nov.
Figures 10–13 View FIGURE 10 View FIGURE 11 View FIGURE 12 View FIGURE 13
Type material. Holotype: SUMATRA: Jambi Province: Bukit Duabelas National Park, Sarolangun ♂ (2013_ BF4.2_AraTrac001N_002), canopy fogging in rainforest, 01°56’30.8”S, 102°34’50.6”E, altitude 91 m, 4.X.2013, leg. J. Drescher ( MZB). GoogleMaps
Paratypes: SUMATRA: Jambi Province: 3♂ 2♀ (2013_BF4.2_AraTrac001N), same data as holotype ( MZB); Bukit Duabelas National Park , Sarolangun GoogleMaps : 2♂ (2013_BF1.1_AraTrac001N), canopy fogging in rainforest, 01°59’42.6”S, 102°45’08.0”E, altitude 69 m, 8.X.2013, leg. J. Drescher (SMF); 1♀ (2013_BF2.1_AraTrac001N), canopy fogging in rainforest, 01°58’55.2”S, 102°45’02.6”E, altitude 73 m, 7.X.2013, leg. J. Drescher (ZMHA0023866); Dusun Baru , Air Hitam, Sarolangun, 1♀ (2013_BJ4.1_AraTrac001N), canopy fogging in jungle rubber plantation, 02 ⁰00’56.8”S, 102 ⁰45’12.6”E, altitude 64 m, 14.VII.2013, leg. J. Drescher (ZMH-A0023867).
Etymology. The specific name is taken from Indonesian rimba meaning “jungle”, as most of the specimens were collected from research plots in lowland rainforest. Also in honor of the indigenous Orang Rimba people that inhabit the Bukit Duabelas National Park. Noun in apposition.
Diagnosis. This species belongs to the phyllicola -group based on the inflated tegulum and bursae located distantly from the spermatheca, close to the pedicel. Males of this species are most similar to those of U. gui and U. balonku sp. nov., but can be distinguished from U. gui by the narrower RTA with a longer, narrower, and more curved apical claw ( Figs 11B–11E View FIGURE 11 ); from U. balonku sp. nov. by the less inflated tegulum, the RTA and sperm duct being visible from ventral view (versus tegulum more inflated, ventrally covering the RTA and sperm duct in U. balonku sp. nov., Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ). Females of this species are most similar to those of U. gui and U. balonku sp. nov. by the slender copulatory ducts and U-shaped medial part of the connecting ducts, but can be distinguished from both by the almost tube-shaped spermathecae ( Figs 13B, C View FIGURE 13 ) (versus pear-shaped in both U. balonku sp. nov. ( Fig. 6B, C View FIGURE 6 ) and U. gui ( Jin et al. 2015: fig. 8F)) and additionally from U. gui by the shorter copulatory ducts, being roughly double the length of the spermathecae (versus three times the length of spermathecae in U. gui ( Jin et al. 2015: fig. 8F)).
Description. Male (Holotype). Total length 3.90. Carapace length 2.17; width 1.65. Carapace oval, darkbrown colored, strongly sclerotized, surface granulated, with each granule ending in long, white setae, lateral margin vaguely undulating; fovea indistinct; PER longer than AER, both slightly recurved ( Fig. 10A View FIGURE 10 ); clypeus short with slight projection between chelicerae. Eye diameters: AME 0.12; ALE 0.13; PLE 0.13; PME 0.13. Eye interdistances: AME–AME 0.07; AME–ALE 0.07; ALE–ALE 0.44; PME–PME 0.12; PME–PLE 0.14; ALE–PLE 0.14; AME–PME 0.09; PLE–PLE 0.69. MOA: length 0.36; anterior width 0.31; posterior width 0.40. Clypeus height 0.20. Sternum heart-shaped, slightly lighter than carapace, surface granulated ( Fig. 10B View FIGURE 10 ).
Abdomen length 1.73; width 1.55. Abdomen oval, most of dorsal surface covered with light-brown scutum ( Fig. 10A View FIGURE 10 ); ventral side of abdomen lightly sclerotized on area anterior to epigastric furrow, colored light brown; dark, wide band runs posteriorly from epigastric furrow, ending in circle surrounding spinnerets; rest of abdomen light gray ( Fig. 10B View FIGURE 10 ).
Legs uniformly light brown, covered with long white seta, especially on ventral surface. Leg I longer and much stouter than the other legs, ventrally filled with leg cuspules from tarsus to femur, except on patella ( Fig. 10C View FIGURE 10 ); metatarsi III and IV distally with a comb-like structure distally, followed by brush of setae. Leg measurements: leg I 5.65 (1.77, 0.66, 1.57, 1.02, 0.63); leg II 5.37 (1.65, 0.52, 1.35, 1.18, 0.67); leg III 3.62 (1.03, 0.36, 0.84, 0.92, 0.47); leg IV 4.91 (1.42, 0.40, 1.27, 1.27, 0.55).
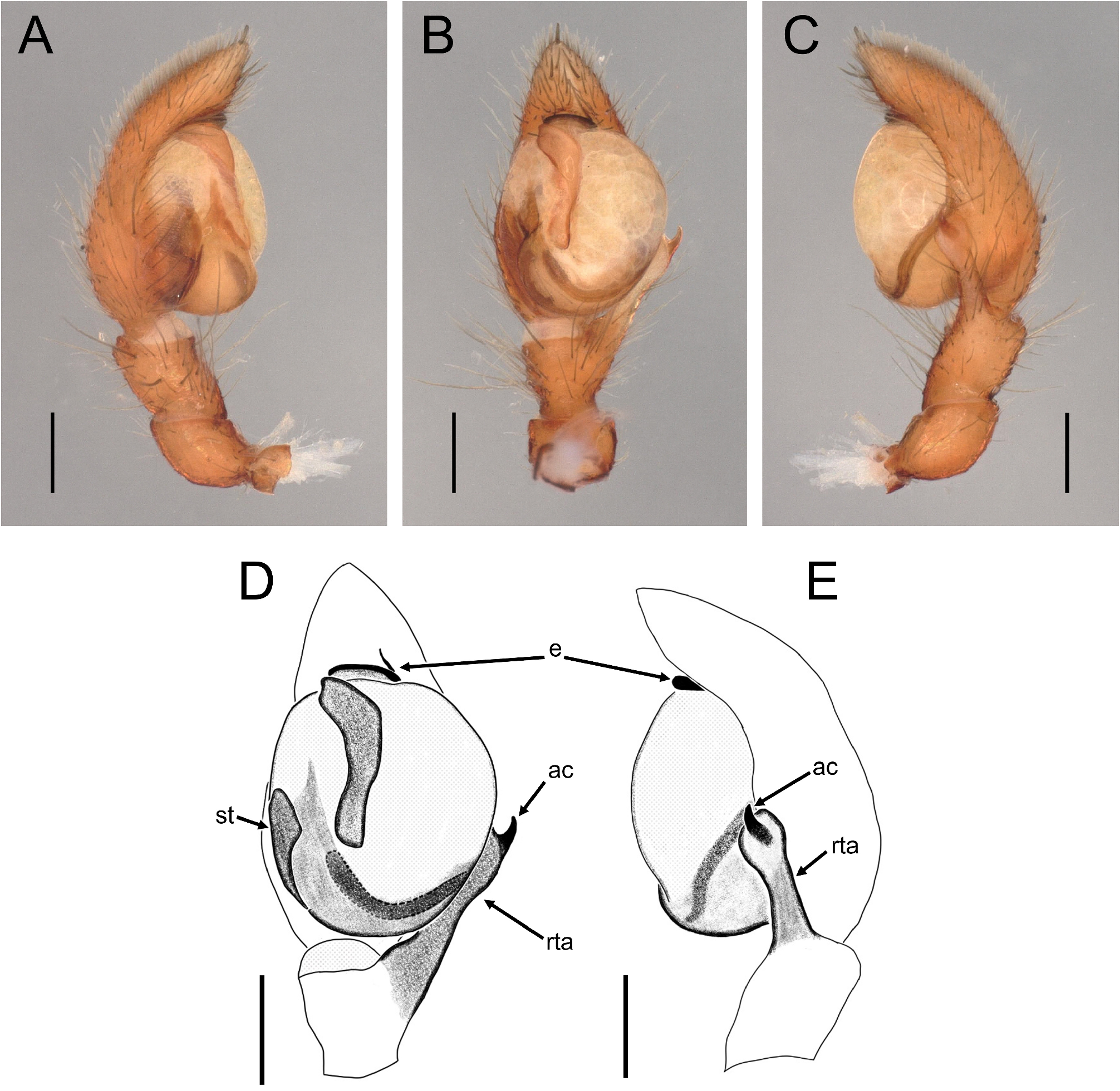
Male palp ( Fig. 11 View FIGURE 11 ): Cymbium oval. Bulb round. Tegulum inflated, but not covering RTA in ventral view. RTA long, distally spatulate, ending in sickle-shaped apical claw. Sperm duct visible in ventral view, widely Ushaped. Embolus arising from wide basal part originating from middle of bulb; distal part coiled horizontally, much narrower than bulb, looping once.
Female (Paratype). Total length 3.73. Carapace length 1.84; width 1.42. Eye diameters: AME 0.10; ALE 0.11; PLE 0.11; PME 0.12. Eye interdistances: AME–AME 0.06; AME–ALE 0.08; ALE–ALE 0.37; PME–PME 0.08; PME–PLE 0.10; ALE–PLE 0.11; AME–PME 0.08; PLE–PLE 0.57. MOA: length 0.30; anterior width 0.28; posterior width 0.34. Clypeus height 0.22. Abdomen length 1.89; width 1.38. General appearance as in male except dorsal scutum only covering half of abdomen ( Fig. 12A View FIGURE 12 ) and leg I cuspules sparser ( Fig. 12C View FIGURE 12 ). Leg measurements: leg I 4.80 (1.52, 0.54, 1.19, 0.91, 0.64); leg II 4.37 (1.35, 0.44, 1.08, 0.89, 0.61); leg III 3.13 (0.86, 0.27, 0.69, 0.83, 0.48); leg IV 4.35 (1.17, 0.34, 1.02, 1.25, 0.57).
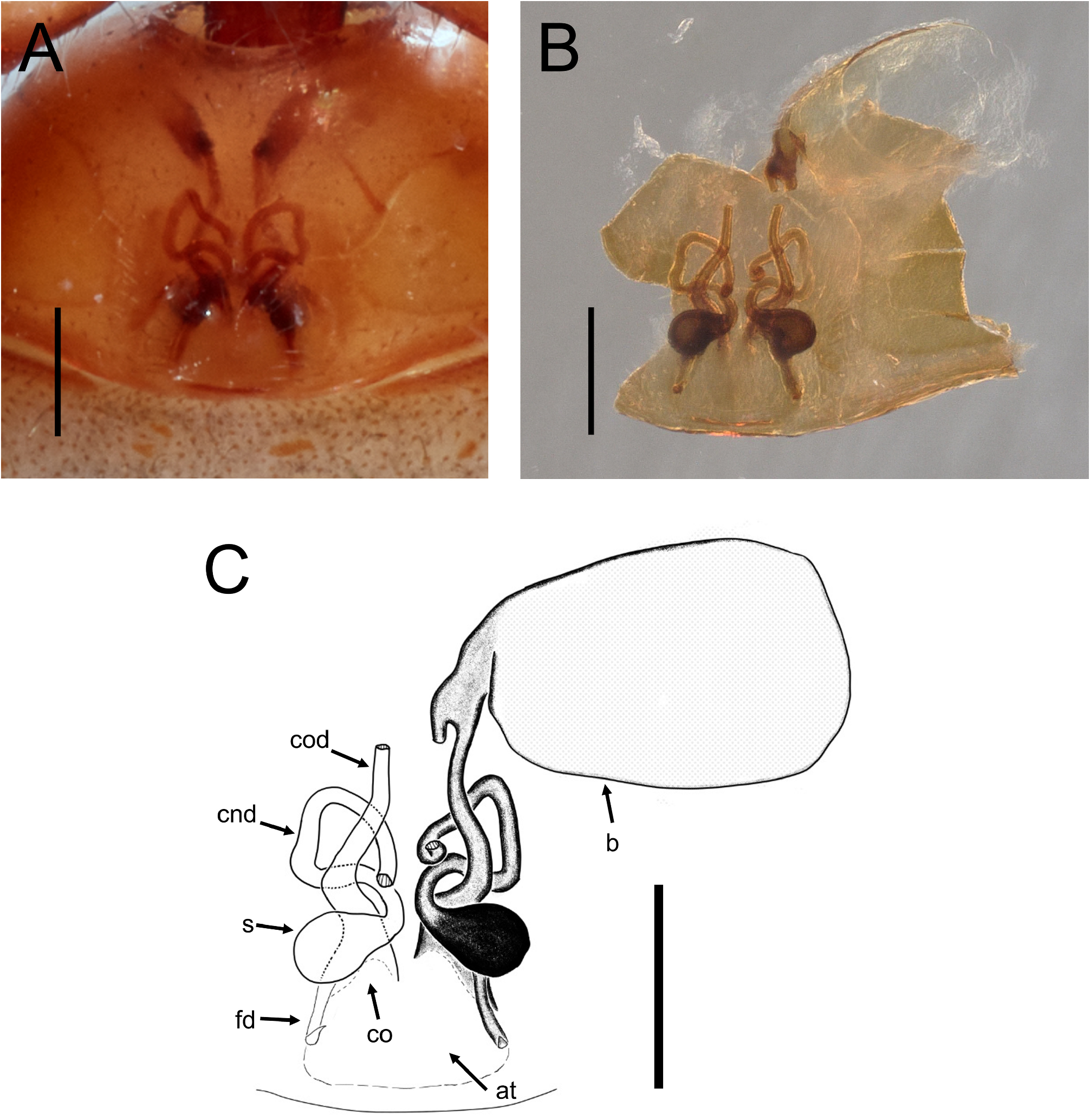
Copulatory organs ( Fig. 13 View FIGURE 13 ):Atrium wider than long. Copulatory openings located on anterior corners of atrium, close to epigastric furrow. Copulatory ducts narrow, slightly S-shaped, anteriorly with sharp turn. Bursae oval, very large and fragile, located close to pedicel. Connecting ducts narrow, prominently S-shaped, medial part U-shaped. Spermathecae almost rectangular-shaped, slightly bulbous posteriorly. Fertilization ducts straight, ⅔ the length of spermathecae.
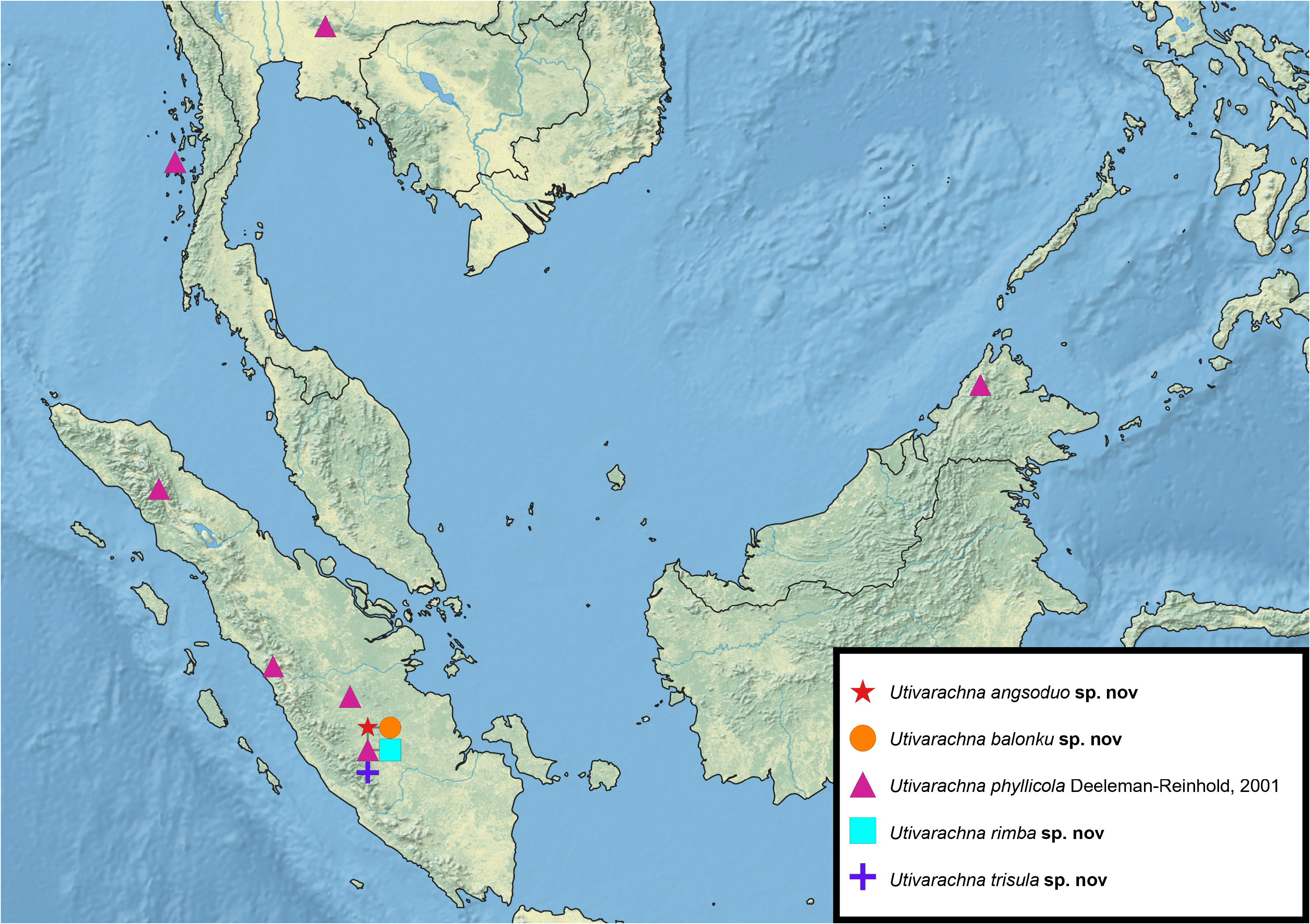
Distribution. Jambi Province, Sumatra ( Maps 1 View MAP 1 and 2 View MAP 2 )
Remarks. All specimens were collected by fogging in rainforests and jungle rubber plantations, and are considered arboreal.
| MZB |
MZB |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |