Glyptothorax forabilis, Ng, Heok Hee & Kottelat, Maurice, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4238.3.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3370E2CB-4EB2-4FE1-956C-06BDE2624948 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5624485 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03BF2E7F-FFBD-8536-FF37-FEACB3C94AE9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Glyptothorax forabilis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
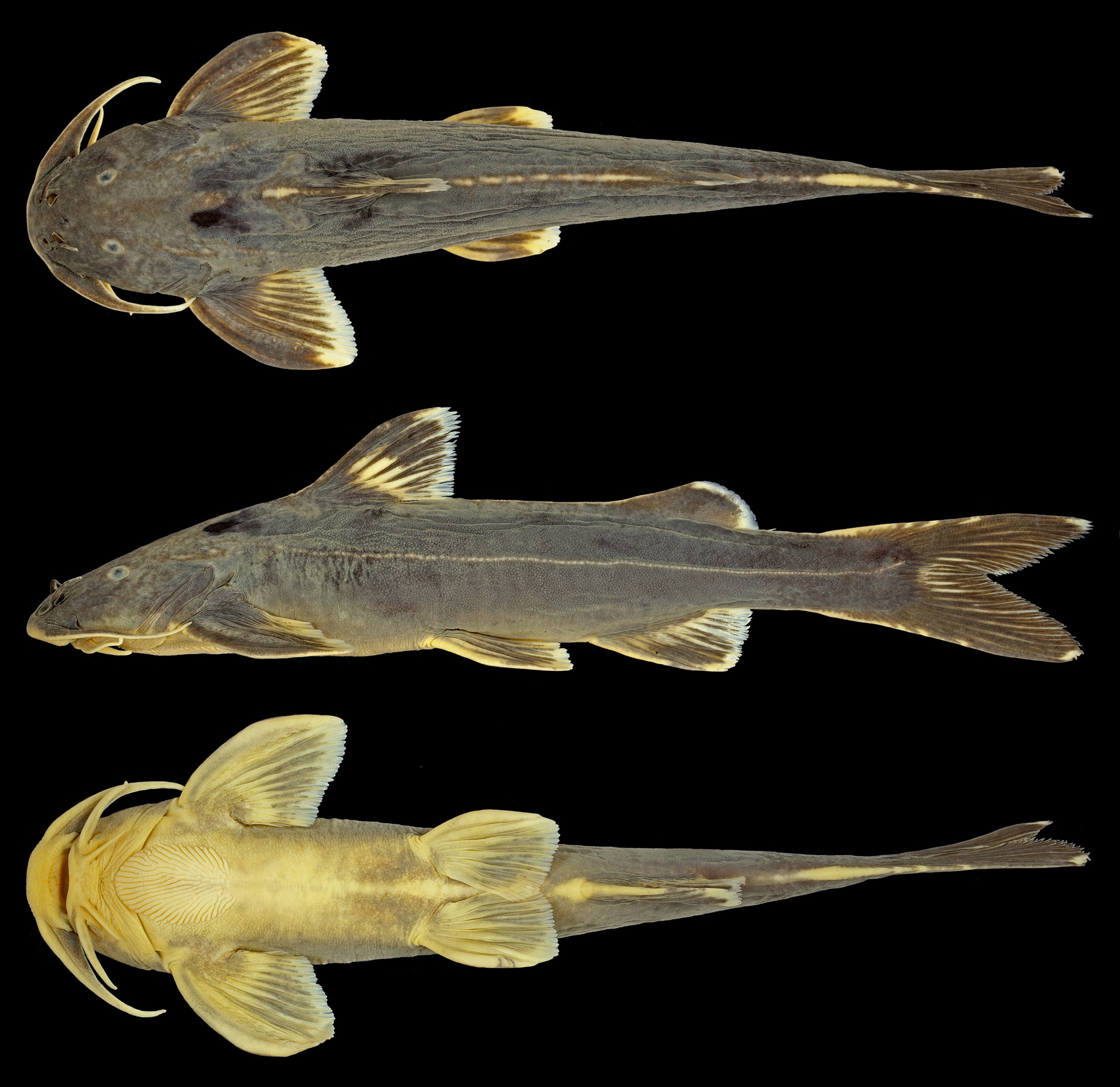
Glyptothorax forabilis new species
( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 )
Type material. Holotype: MHNG 2766.054, 76.7 mm SL; Laos: Champasak Province, Pakxong District, Bolaven Plateau, Xe Katam , about 2 km upstream of bridge on road from Pakxong to Attapeu, 15°07’05”N 106°37’01”E, 531 masl; M. Kottelat & T. Phommavong, 23 January 2013 GoogleMaps .
Paratypes: CMK 23452 (6), 52.3–89.6 mm SL; data as for holotype GoogleMaps . CMK 23444 (12), 39.8–75.7 mm SL; ZRC 55628 (3), 48.2–62.8 mm SL; Laos: Champasak Province, Pakxong District, Bolaven Plateau, Houay Makchan-Gnai (tributary of Xe Nam Noy) at bridge on road from Ban Ta-Od to Ban Nongphannouan , 15°04’15”N 106°32’34”E, 784 masl; M. Kottelat & T. Phommavong, 23 January 2013 GoogleMaps .
Additional material (non-type). CMK 23434 (1), 82.8 mm SL; Laos: Champasak Province, Pakxong District, Bolaven Plateau, Houay Makchan-Gnai in tea estate SE of Ban Chansavang , 15°9’41”N 106°25’20”E, 1107 masl; M. Kottelat & T. Phommavong, 23 January 2013. GoogleMaps
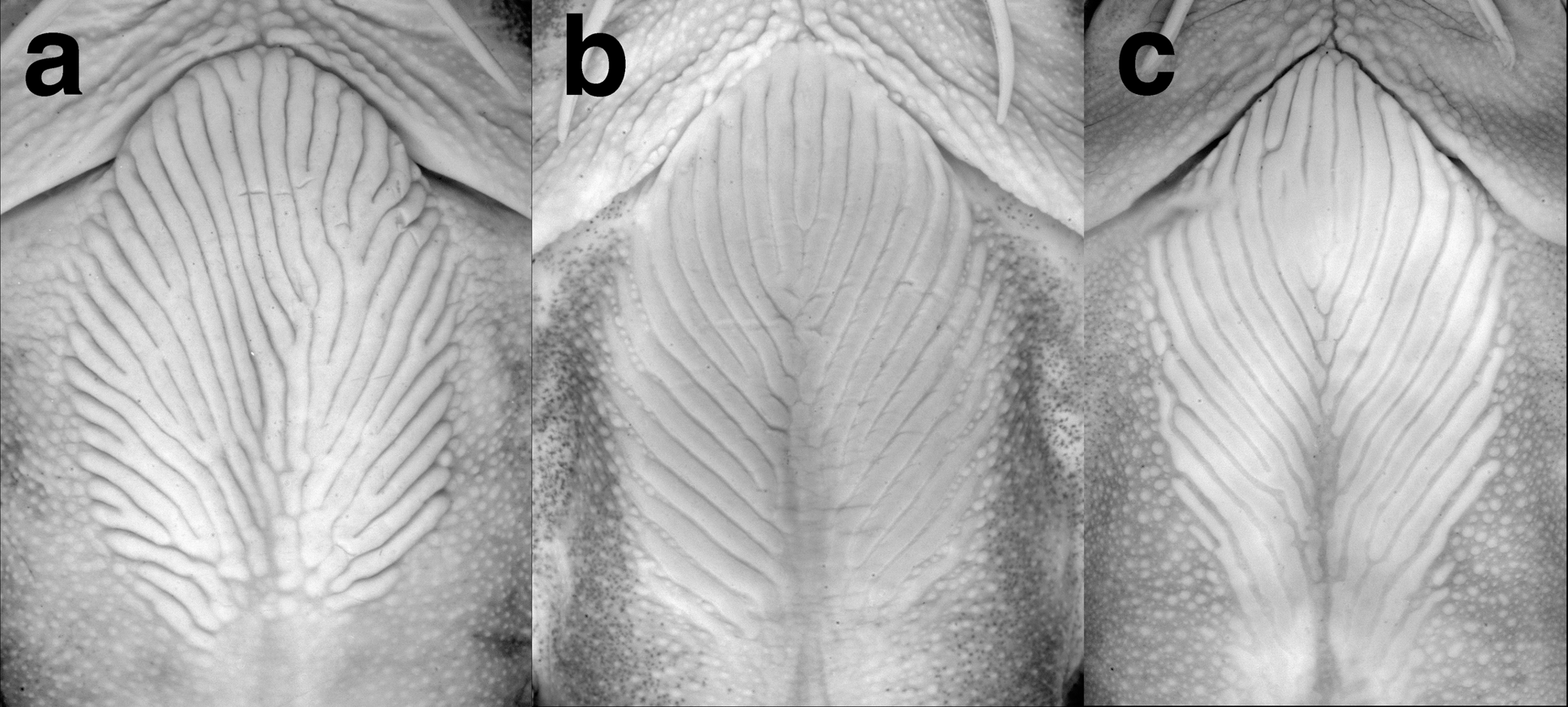
Diagnosis. Glyptothorax forabilis differs from Indochinese congeners except for G. coracinus , G. interspinalum , G. lanceatus , G. laosensis , G. longinema , G. strabonis , G. porrectus , G. trilineatus and G. zanaensis in having a uniformly dark gray body with pale midlateral and mid-dorsal stripes (vs. body with pale or dark bands, patches or spots). It is distinguished from G. coracinus , G. interspinalum , G. lanceatus , G. laosensis , G. longinema , G. strabonis , G. porrectus , G. trilineatus and G. zanaensis in lacking (vs. having) a medial pit on the thoracic adhesive apparatus ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). The following unique combination of characters further diagnoses G. forabilis from G. coracinus , G. interspinalum , G. laosensis , G. longicauda , G. longinema , G. strabonis , G. porrectus , G. trilineatus and G. zanaensis : eye diameter 8–11% HL; interorbital distance 25–31% HL; head width 17.0–19.2% SL; thoracic adhesive apparatus without anteromedial striae; very thin pale midlateral stripe only as wide as single tubercle; body depth at anus 12.4–15.0% SL; post-adipose distance 17.0–21.6% SL; caudal peduncle length 19.3–23.9% SL; caudal peduncle depth 7.4–9.0% SL (1.6–1.7 times in body depth at anus).
Description. Morphometric data in Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Head depressed; body subcylindrical. Dorsal profile rising evenly from tip of snout to origin of dorsal fin, then sloping gently ventrally from origin of dorsal fin to end of caudal peduncle. Ventral profile straight to anal-fin base, then sloping gently dorsally from anal-fin base to end of caudal peduncle. Anus and urogenital openings located at vertical through middle of adpressed pelvic fin. Depth of caudal peduncle 2.6–3.1 times in its length. Skin tuberculate, with tubercles of small and even size on sides of body. Lateral line complete and midlateral. Vertebrae 19+18=37 (2), 19+19=38* (4) or 20+19=39 (1). Tips of neural spines distally expanded, not visible as series of low bumps between dorsal and adipose fins.
Head depressed and broad, triangular when viewed laterally. Snout prominent. Anterior and posterior nares large and separated only by base of nasal barbel. Gill opening broad, extending from ventral margin of posttemporal to isthmus. First branchial arch with 2+8 (1) rakers. Bony elements of dorsal surface of head covered with thick, tuberculate skin. Eye ovoid, horizontal axis longest; located entirely in dorsal half of head.
Barbels in four pairs. Maxillary barbel long and slender, extending to base of second or third pectoral-fin ray. Nasal barbel slender, extending to midway between its base and anterior orbital margin. Inner mandibular-barbel extending to midway between its base and that of pectoral spine. Outer mandibular barbel extending to threequarters of distance between its base and that of pectoral spine.
Mouth inferior, premaxillary tooth band partially (approximately half) exposed when mouth is closed. Oral teeth small and villiform, in irregular rows on all tooth-bearing surfaces. Premaxillary teeth appearing in single broad semilunate band. Dentary teeth in a single crescentic band, consisting of two separate halves tightly bound at midline.
Thoracic adhesive apparatus consisting of keratinized striae in an ovate field ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 a) extending from isthmus to posterior limit of pectoral-fin base; anterolateral edges of adhesive apparatus gently convex. Striae extending throughout posterior half of apparatus; no medial pit devoid of striae.
Dorsal fin located above anterior third of body, with I,6 (12) rays; fin margin concave; spine short and straight, smooth on anterior and posterior margins. Adipose fin with anterior margin slightly concave and posterior margin gently convex. Caudal fin strongly forked, with lower lobe slightly longer than upper lobe and i,7,8,i (12) principal rays. Procurrent rays symmetrical and extending only slightly anterior to fin base. Anal-fin base vertically opposite adipose-fin base. Anal fin with straight anterior and posterior margins; with iii,9,i (1), iii,10 (1), iv,9 (1), iii,10,i (2), iv,9,i* (5), iv,10 (1) or iii,11 (1) rays. Pelvic-fin origin at vertical through posterior limit of dorsal-fin base. Pelvic fin with slightly convex margin and i,5 (12) rays; tip of adpressed fin not reaching anal-fin origin. Pectoral fin with I,9 (1), I,10* (10) or I,10,i (1) rays; posterior fin margin slightly concave; anterior spine margin smooth, posterior margin with 8–13 (holotype =12) serrations.
Coloration. In 70% ethanol: dorsal and lateral surfaces of head, and body dark gray, fading to beige on ventral surfaces. A faint thin, cream mid-dorsal stripe extending from base of last dorsal-fin ray to origin of adipose fin; stripe very faint in some individuals. Laterosensory pores and tubercles along lateral line rimmed in beige, imparting appearance of a thin pale midlateral line. All fins with dark gray fin rays, and diffuse melanophores on fin membranes. Pectoral and pelvic fins with dark gray on base of fin rays and hyaline posterior margin. Anal fin with dark gray base and hyaline posteroventral corner. Adipose fin dark gray, with hyaline distal margin. Caudal fin dark gray, with tip of lobes hyaline. Maxillary and nasal barbels dark gray dorsally, beige ventrally. Mandibular barbels beige. In life: body dark blackish brown.
Habitat. Glyptothorax forabilis was found in a stretch of the Xe Katam with high gradient and very fast water on boulders and rocks (type locality) and in the Houay Makchang-Gnai in a degraded stretch with relatively slow current over riffles and pools, and in a stretch with fast current on large stones, in a coffee plantation.
Distribution. Glyptothorax forabilis is known from the Xe Nam Noy drainage on the Bolaven Plateau, southern Laos ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ).
Etymology. The name forabilis (-is, -is, -e) is the Latin adjective meaning “that which may be pierced” or vulnerable. This is used to refer to the conservation status of this species (see Discussion).
TABLE 1. Morphometric data for Glyptothorax forabilis (n = 12).
| Holotype MHNG 2766.054 | Range | Mean±SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard length (mm) %SL | 76.7 | 39.8–89.6 | |
| Predorsal length Preanal length Prepelvic length | 34.7 66.2 48.4 | 31.1–36.1 62.9–67.2 45.4–48.4 | 34.2±1.51 65.2±1.51 46.6±1.04 |
| Prepectoral length Length of dorsal-fin base Dorsal-fin spine length | 19.6 12.4 13.8 | 16.7–19.6 11.2–14.5 12.3–16.1 | 18.1±1.08 12.7±1.06 14.2±1.15 |
| Length of anal-fin base Pelvic-fin length Pectoral-fin length | 16.6 17.5 25.4 | 14.5–16.9 14.8–17.8 20.0–25.4 | 16.0±0.80 16.8±0.93 22.9±1.57 |
| Pectoral-fin spine length Caudal-fin length Length of adipose-fin base | 18.0 23.9 16.0 | 13.5–18.0 23.9–28.4 12.6–17.3 | 15.8±1.35 27.0±1.51 15.4±1.52 |
| Dorsal to adipose distance Post-adipose distance Length of caudal peduncle | 24.8 21.6 23.2 | 22.0–26.3 17.0–21.6 19.3–23.9 | 24.9±1.45 19.7±1.80 21.8±1.76 |
| Depth of caudal peduncle Body depth at anus Head length | 9.0 15.0 25.8 | 7.4–9.0 12.4–15.0 23.0–25.8 | 8.0±0.59 13.6±1.06 24.0±1.01 |
| Head width Head depth %HL | 19.2 14.5 | 17.0–19.2 11.9–14.5 | 18.1±0.67 13.1±0.84 |
| Snout length Interorbital distance Eye diameter | 48 25 8 | 48–54 25–31 8–11 | 51±2.5 28±1.7 10±1.1 |
| Nasal barbel length Maxillary barbel length Inner mandibular barbel length | 22 79 30 | 20–28 75–99 26–40 | 25±3.3 86±7.2 34±5.0 |
| Outer mandibular barbel length | 40 | 40–54 | 48±4.5 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |