Toechorychus amapaeus Tedesco, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3633.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:60F0956C-A1F5-44CA-9D14-8C04343AD01F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5261753 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B987AE-FFB0-FFD1-0AE1-FC85FD62FEDF |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe (2021-08-25 00:06:26, last updated by Plazi 2023-11-04 17:58:49) |
|
scientific name |
Toechorychus amapaeus Tedesco |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Toechorychus amapaeus Tedesco , sp. nov.
( Figs 13 View FIGURES 12–15 , 50 View FIGURES 45–54. 45 , 66 View FIGURES 55–69 , 103 View FIGURES 97–104. 97–98 , 137 View FIGURES 133–138 , 168 View FIGURES 163–174 )
Description. Holotype FEMALE. Fore wing length 6.00 mm.
Head. Mandible 1.31 as long as basal width, moderately pilose; ventral margin slightly projected as crest; dorsal tooth distinctly longer than ventral tooth. Clypeus 1.71 as wide as high, subrectangular, minutely strigulate, apically smooth; apex 1.54 as long as base, truncate; apical margin sharp, medially slightly concave. Supraclypeal area medially strigate, laterally finely punctate, densely pilose, medially slightly prominent; between antennal foramens with U-shaped carina, medially widely interrupted; radicle foveolate. Antenna with 25 flagellomeres; white band starting at flagellomere 4, reaching flagellomere 11; flagellum slender; subapical flagellomeres slightly flattened. Supra-antennal area with stout, median, longitudinal carina or with stout, median, transversally arched carina, medially without longitudinal elevation, near antennal sockets not striate; dorsal half medially punctulate, or rugulose. Paraocular area finely punctulate. Vertex with very coarse punctures around ocelli, at anterior third with short, longitudinal sulcus, posterior two-thirds smooth; gena and vertex behind ocelli smooth, sparsely pilose; gena in lateral view at level of dorsal portion of occipital carina narrow, ventrally wide; occipital carina stout, dorsally absent, ventrally markedly projected as crest, reaching hypostomal carina far from mandible base; hypostomal carina projected as crest; malar space 1.06 as long as basal width of mandible.
Mesosoma . Mesosoma in dorsal view 2.02 as long as wide; in lateral view, mesosoma middle width 0.18 mm. Pronotum centrally smooth, latero-ventrally rugose behind collar, margin near mesopleuron ventrally markedly corrugated; pronotal swelling dorsally smooth, ventrally strigulate; collar dorso-laterally rounded, distinctly swollen, anteriorly smooth; epomia absent. Mesoscutum sparsely pilose, lobes dorsally punctulate, laterally markedly corrugated, central lobe with faint longitudinal carina; notauli deeply impressed, posteriorly abruptly curved, U-shaped. Scutoscutellar groove markedly corrugated; scutellum 0.87 as long as wide, smooth; scutellar carina incomplete, restricted approximately to anterior 0.6; postscutellum 0.30 as long as wide; hind margin of metanotum with two lateral teeth. Subalar ridge somewhat elongate; mesopleuron dorsally medially markedly strigate, ventrally strigulate; mesopleural groove corrugated; epicnemial carina stout, dorsally curving backwards; dorsal end of epicnemial carina reaching 0.2 of posterior margin of pronotum, behind epicnemial carina without rounded confused-rugulose area, but distinctly markedly strigate; sternaulus medially shallow, interrupted, reaching base of mid coxa, markedly sinuate, moderately impressed, faint from anterior 0.7 to 0.8, faintly corrugated; scrobe very shallow, forming sulcus. Mesothoracic venter punctate and strigulate; median portion of posterior transverse carina of mesothoracic venter short and straight, regularly shaped, without projections. Transverse furrow at base of propodeum laterally 0.10 as long as anterior portion of propodeum deep and narrow, very faintly corrugated, almost smooth; propodeum 1.12 as long as wide medially; anterior margin of propodeum with two lateral teeth; anterior portion of propodeum finely strigulate or with sparse coarse punctures, medially with two posteriorly convergent longitudinal carinae; lateral longitudinal carina of propodeum indistinct; posterior portion of propodeum entirely markedly strigate, medially without distinctly stout longitudinal carina; anterior transverse carina of propodeum complete, stout, straight; posterior transverse carina absent; propodeal spiracle 1.55 as long as wide; pleural carina of propodeum irregular and faint, obsolescent posteriorly, fused with sculpture of lower division of metapleuron and propodeum; lower division of metapleuron faintly strigulate, sparsely pilose, juxtacoxal carina represented by very short ridges.
Wings. Fore wing: vein 2+3Rs almost straight; ramellus absent; vein 1M+Rs entirely sinuous; vein 1cu-a straight, arising far from vein 1M+Rs base, angle with vein M+Cu distinctly obtuse; vein 2Cu 0.71 as long as vein 2cu-a; vein 4Rs 0.89 as long as vein 4M, uniformly slightly convex; cell 1+2Rs 0.71 as high as pterostigma, rectangular; vein 2M approximately as long as vein 3M; vein 3M distinct, 1.20 as long as vein 2M. Hind wing: vein 1Cu 1.39 as long as vein cu-a; vein 2-1A reaching 0.96 of distance to posterior margin.
Legs. Tibia with sparse short bristles; hind coxa globose.
Metasoma. T1 0.51 as long as hind femur, with basolateral tooth; anteriorly smooth, posteriorly coriarious; spiracle at anterior 0.54, slightly prominent; postpetiole dorso-anteriorly convex; T2–8 minutely coriarious; almost glabrous; T2 1.15 as long as wide at apex; apex of T2 1.78 as wide as base. Dorsal valve of ovipositor with nodus indistinct; apex of lower valve with series of teeth; notch absent.
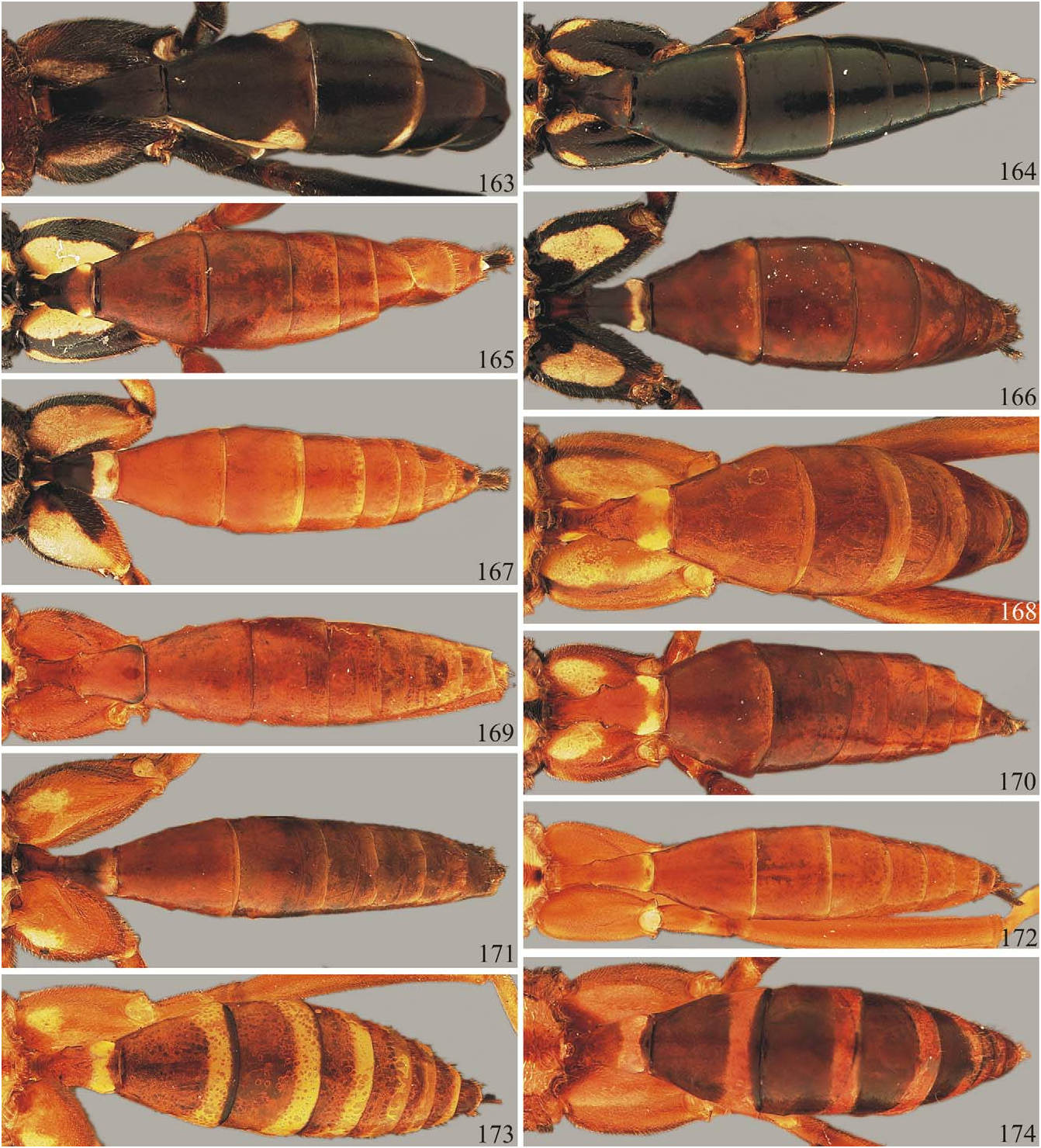
Color. Head yellow with black marks, mesosoma black and yellow and metasoma mostly orange (212,115,049). Head: yellow; mandible apex, clypeal apex, two lateral longitudinal stripes at supraclypeal area, supra-antennal area, interocellar area, vertex and gena, except complete large orbital band, and occiput, black; scape ventrally yellow, dorsally dark brown; flagellum ventrally entirely brown, dorsally whitish at f5–13. Mesosoma : mostly bright yellow (240,219,117); propleuron bright yellow, dorsally black; pronotum black except collar laterally and pronotal swelling, bright yellow; mesoscutum black, except longitudinal lanceolate mark at posterior 0.9 of central lobe; mesopleuron bright yellow with four black marks: anteriorly around hypoepimeron, entire mesopleural groove, rounded spot just behind epicnemial carina, and along posterior half of sternaulus; remainder of mesosoma black, except for the following bright yellow marks: axillary carina, scutellum, postscutellum, both upper and lower division of metapleuron, and two lateral longitudinal marks at posterior portion of propodeum. Legs: mostly orange; fore coxa, mid and hind coxae basally, bright yellow; fore coxa ventrally, mid and hind coxae dorsally with basal dark brown mark; hind coxa posteriorly with black spot; mid t5 dark brown. Metasoma: mostly orange; T1 laterally bright yellow, dorsally black with posterior 0.2 bright yellow; T2–8 orange; S2–8 bright yellow, laterally orange.
Variation. Scutoscutellar groove faintly corrugated. Rounded spot just behind epicnemial carina joining posterior black mark at sternaulus. Anterior portion of propodeum brownish around spiracle. Longitudinal stripes at posterior portion of propodeum brownish towards apex. Posterior black spot at hind coxa absent. Mid coxa dorsally entirely yellowish. T1 dorsally orange.
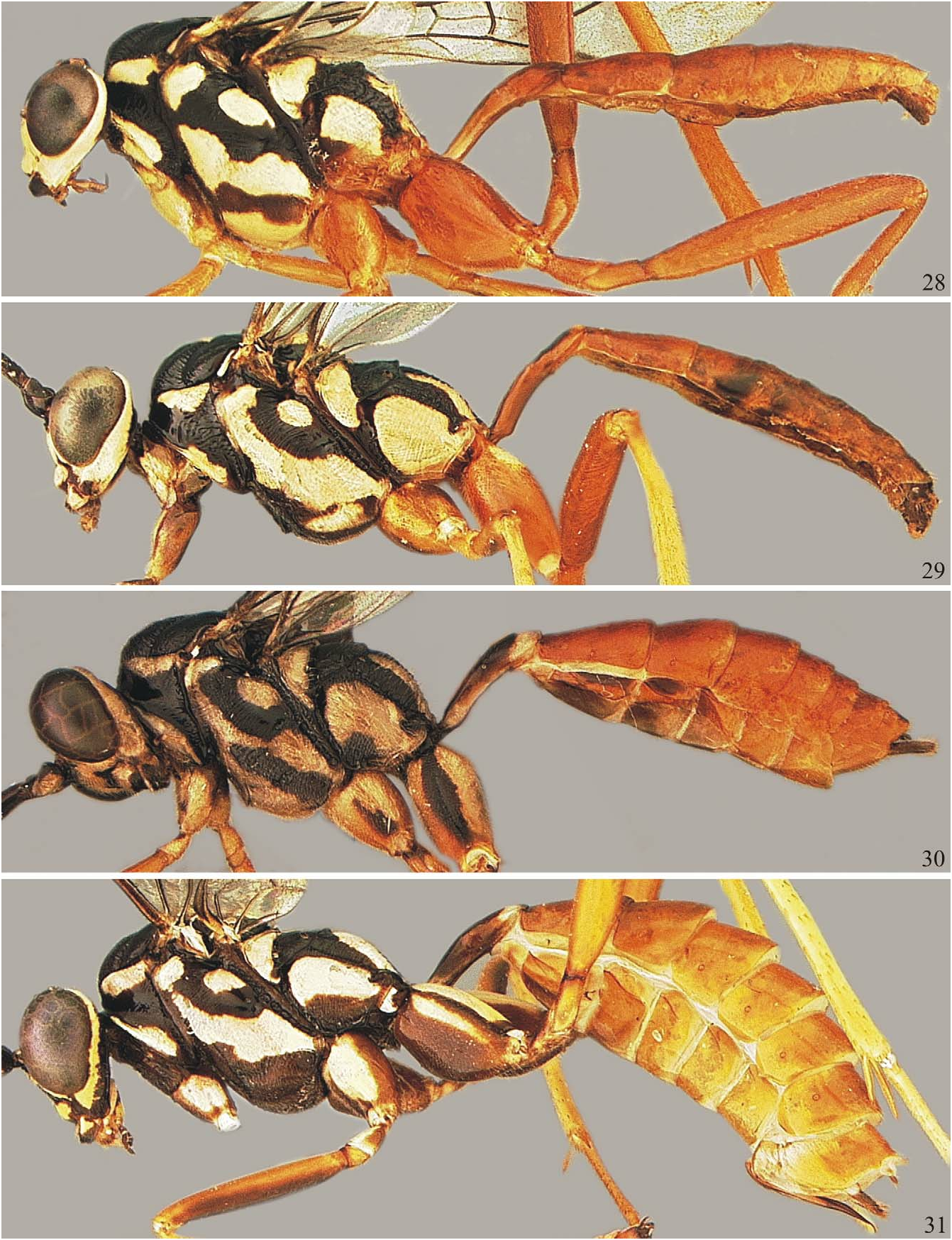
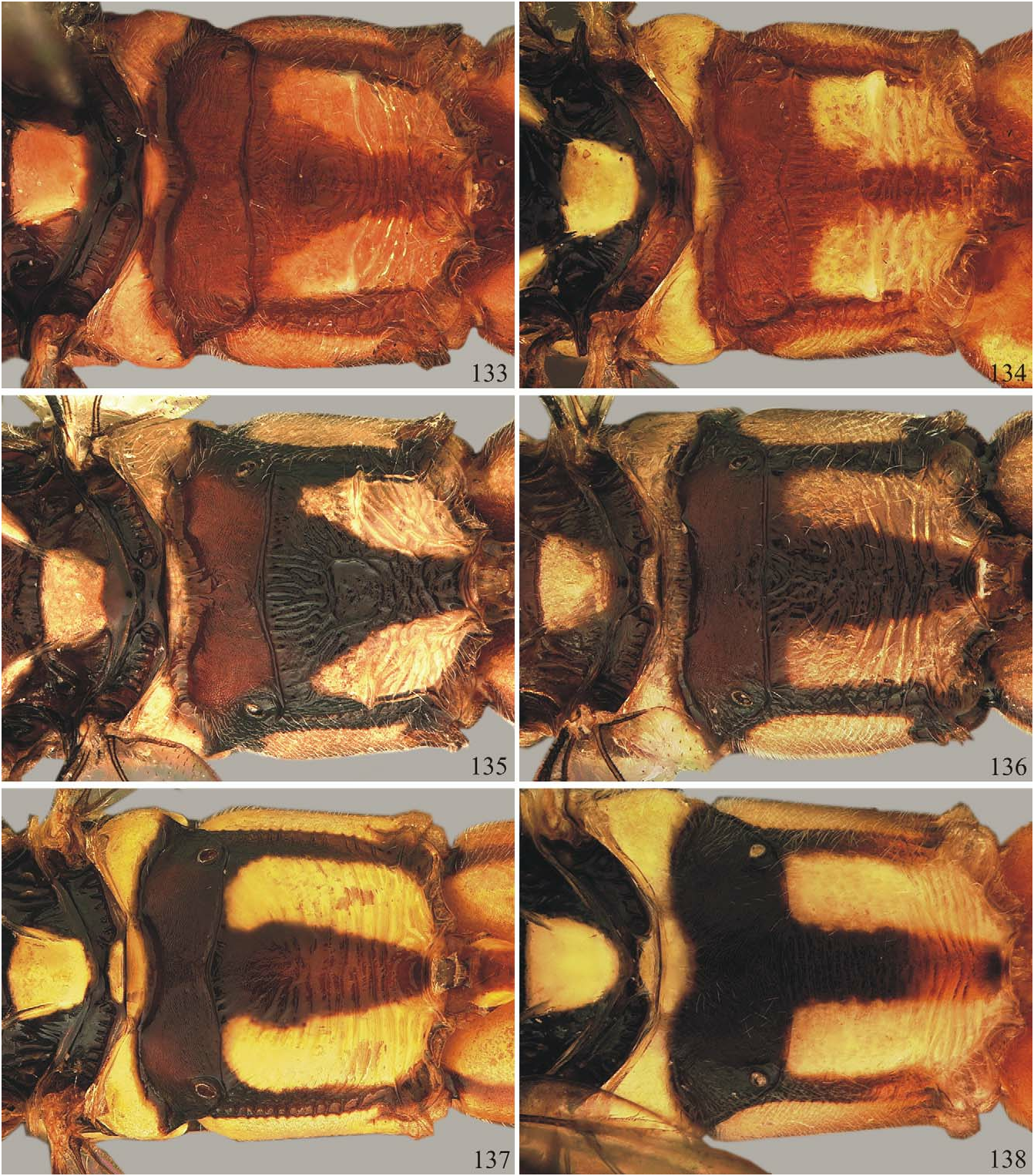
Comments. Very similar to T. vilhenus sp. nov., from which it can be separated by having supraclypeal area with two lateral longitudinal stripes ( Fig. 66 View FIGURES 55–69 ) (vs. entirely yellow in T. vilhenus sp. nov.); supra-antennal area with distinct median longitudinal carina (vs. without distinct median carina); supra-antennal area medially without elevation (vs. with small rounded elevation); occipital carina dorsally absent ( Fig. 50 View FIGURES 45–54. 45 ) (vs. conspicuous and uniformly arched, as in Fig. 52 View FIGURES 45–54. 45 ); mesopleuron ventrally and sternaulus, yellow (vs. with rounded black spot just behind epicnemial carina, and along posterior half of sternaulus; Fig. 99 View FIGURES 97–104. 97–98 ); hind coxa dorsally yellow (vs. entirely orange; Fig. 172 View FIGURES 163–174 ); T1 with basolateral tooth, as in Fig. 53 View FIGURES 45–54. 45 (vs. without, as in Fig. 54 View FIGURES 45–54. 45 ). Also similar to T. darienus sp. nov., from which it can be differentiated by having supraclypeal area with two lateral longitudinal black stripes (vs. ventrally with M-shaped mark in T. darienus sp. nov.; Fig. 78 View FIGURES 70–84 ); lateral black stripes at supraclypeal area not reaching antennal foramens (vs. reaching antennal foramens, even medially interrupted); malar space completely yellow (vs. ventrally black); occipital carina near mandible bright yellow (vs. black); juxtacoxal carina of mesopleuron faint and short (vs. stout and long); scrobe very shallow, forming a sulcus (vs. deeply impressed, forming a pit); lower division of metapleuron entirely yellow (vs. with ventral rounded black spot; Fig. 30 View FIGURES 28–31 ); mid and hind coxae mostly yellow to orange (vs. with conspicuous black marks).
Male. Unknown.
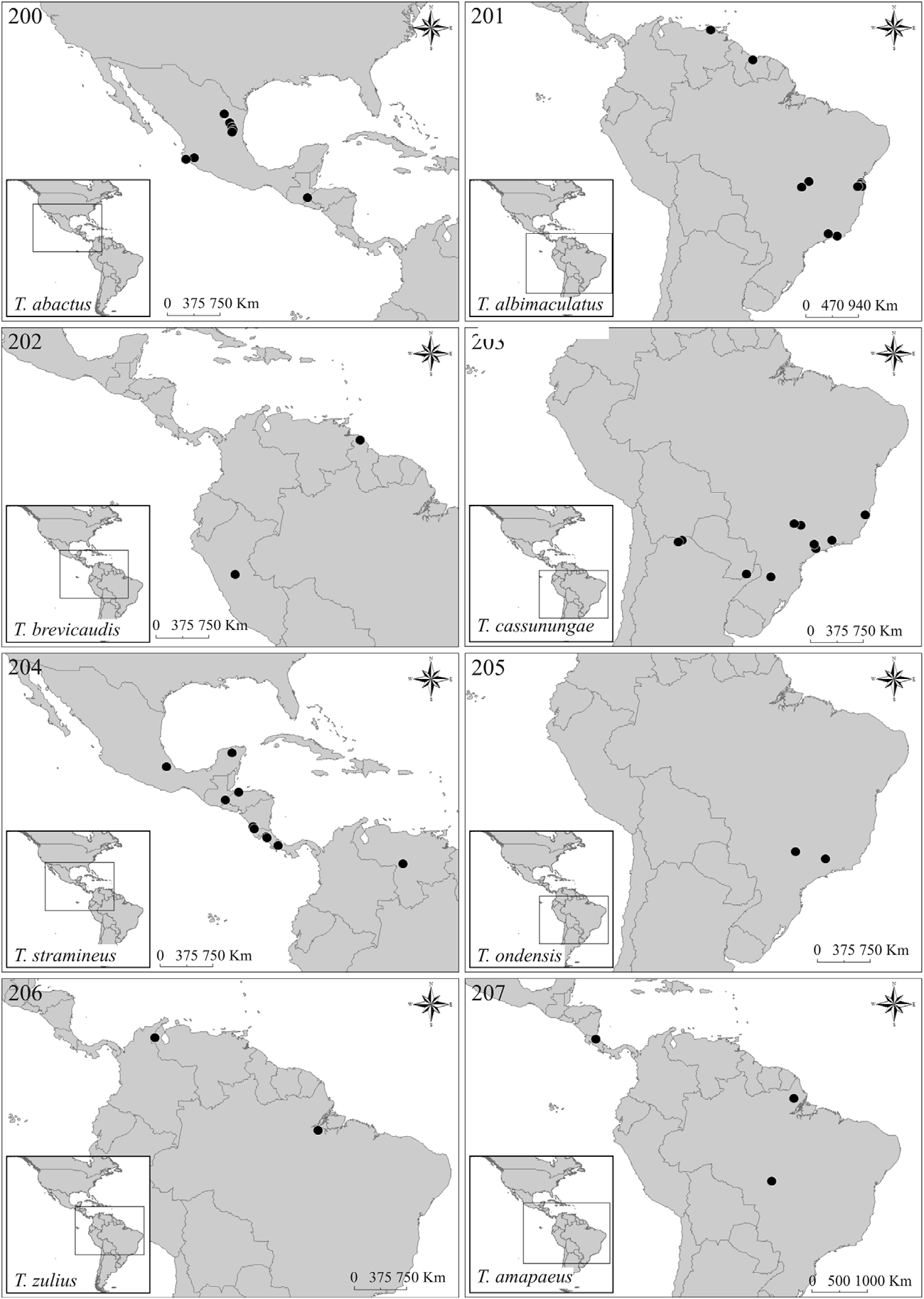
Distribution. Brazil. Recorded from Mato Grosso and Amapá ( Fig. 207 View FIGURES 200–207 ). The type locality is Sinop, Mato Grosso (12°31’S 55°37’W). These records comprise a range of 13°21’ in latitude.
Biology. Unknown.
Material examined. 2 females. Holotype ♀, BRAZIL: Amapá, Serra do Navio , X.1957, K.Lenko et al. leg. ( DZUP). Antennae apical half and left fore leg beyond tibia missing, mesoscutum somewhat damaged by pin; otherwise in good shape . Paratype: BRAZIL: 1 ♀ from Mato Grosso, Sinop , 12°31’S 55°37’W, October, 1976, M.Alvarenga, Toechorychus, S.Gupta, 1980 ( FSCA) GoogleMaps .
FIGURES 12–15. Lateral pictures of Toechorychus. 12, T. vilhenus sp. nov., holotype. 13, T. amapaeus sp. nov., holotype. 14, T. martinus sp. nov., holotype. 15, T. catarinus sp. nov., holotype.
FIGURES 45–54. 45, T. callangus sp. nov., holotype, ovipositor in dorsal view, showing dorsal valve with posterior V-shaped carina, a new synapomorphy discovered for the genus. 46, T. vinhaticus sp. nov., holotype, pronotum in lateral view, lateral portion of collar dorsally carinated. 47, T. morelus sp. nov., holotype, pronotum in lateral view, to show lateral portion of collar dorsally swollen. 48, T. fluminensis sp. nov., holotype, to show hind margin of metanotum without teeth or carinae. 49, T. jatainus sp. nov., holotype, to show hind margin of metanotum with two lateral carinae. 50, T. amapaeus sp. nov., holotype, head in posterior view, to show occipital carina dorsally absent. 51, T. paramaribus sp. nov., holotype, to show anterior margin of propodeum with two lateral teeth. 52, T. melgassus sp. nov., holotype, head in posterior view, to show occipital carina dorsally conspicuous. 53, T. zulius sp. nov., holotype, to show first tergite with two basolateral teeth. 54, T. nourageus sp. nov., holotype, to show first tergite without basolateral teeth.
FIGURES 55–69. Head, frontal view. 55, T. surinamus sp. nov., holotype. 56, T. callangus sp. nov., holotype. 57, T. coaracius sp. nov., holotype. 58, T. guarapuavus sp. nov., holotype. 59, T. itapuensis sp. nov., holotype. 60, T. benius sp. nov., holotype. 61, T. melgassus sp. nov., holotype. 62, T. stramineus Taschenberg. 63, T. tumazulus sp. nov., holotype. 64, T. ondensis sp. nov., holotype. 65, T. fluminensis sp. nov., holotype. 66, T. amapaeus sp. nov., holotype. 67, T. barticus sp. nov., holotype. 68, T. albimaculatus Taschenberg. 69, T. cassunungae Brauns.
FIGURES 97–104. 97–98: Mesoscutum, dorsal view. 97, T. guarapuavus sp. nov., holotype. 98, T. melgassus sp. nov., holotype; 99–104: Mesopleuron, lateral view. 99, T. vilhenus sp. nov., holotype. 100, T. taperinus sp. nov., holotype. 101, T. catarinus sp. nov., holotype. 102, T. coaracius sp. nov., holotype. 103, T. morelus sp. nov., holotype. 104, T. albimaculatus Taschenberg.
FIGURES 133–138. Propodeum, dorsal view. 133, T. cassunungae Brauns. 134, T. benius sp. nov., holotype. 135, T. guarapuavus sp. nov., holotype. 136, T. martinus sp. nov., holotype. 137, T. amapaeus sp. nov., holotype. 138, T. vilhenus sp. nov., holotype.
FIGURES 163–174. Hind coxa and metasoma color patterns, dorsal view. 163, T. napus sp. nov., holotype. 164, T. teutonius sp. nov., holotype. 165, T. kawus sp. nov., holotype. 166, T. taperinus sp. nov., holotype. 167, T. darienus sp. nov., holotype. 168, T. amapaeus sp. nov., holotype. 169, T. ondensis sp. nov., holotype. 170, T. jatainus sp. nov., holotype. 171, T. albimaculatus Taschenberg. 172, T. vilhenus sp. nov., holotype. 173, T. benius sp. nov., holotype. 174, T. cassunungae Brauns.
FIGURES 70–84. Head, frontal view. 70, T. martinus sp. nov., holotype. 71, T. morelus sp. nov., holotype. 72, T. zulius sp. nov., holotype. 73, T. amazonensis sp. nov., holotype. 74, T. paramaribus sp. nov., holotype. 75, T. heredius sp. nov., holotype. 76, T. linaresius sp. nov., holotype. 77, T. marowijnus sp. nov., holotype. 78, T. darienus sp. nov., holotype. 79, T. kawus sp. nov., holotype. 80, T. jatainus sp. nov., holotype. 81, T. taperinus sp. nov., holotype. 82, T. teutonius sp. nov., holotype. 83, T. calius sp. nov., holotype. 84, T. surinamus sp. nov., holotype.
FIGURES 28–31. Lateral pictures of Toechorychus. 28, T. ondensis sp. nov., holotype. 29, T. albimaculatus Taschenberg. 30, T. darienus sp. nov., holotype. 31, T. zulius sp. nov., holotype.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |