Serina egressa Sturany, 1900
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3620.1.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3870AC9F-A4EE-4E36-86C7-E1D6967A2A2E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6162550 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B8B70E-FF9E-FFD3-FF05-FC2AFED5B6BB |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Serina egressa Sturany, 1900 |
| status |
|
3. Serina egressa Sturany, 1900 View in CoL
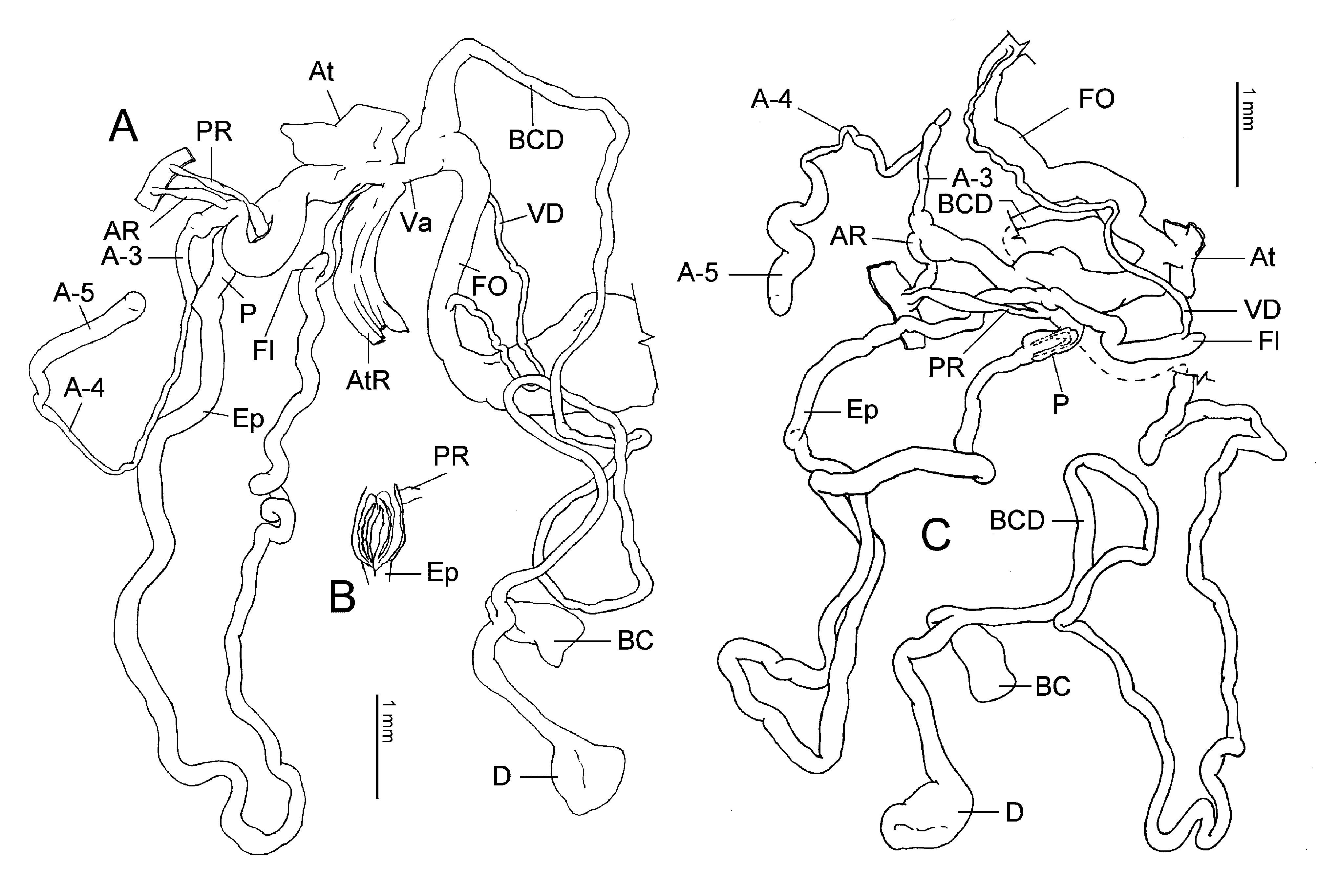
Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 , 2 View FIGURE 2. A E–J, 3, 9; Tables 1–3 View TABLE 1 View TABLE 2 View TABLE 3 , 6 View TABLE 6
Serina cathaica var. egressa Sturany, 1900: 35 , pl. 3, figs. 14–16.
Buliminus ( Serina) ser egressus— Möllendorff, 1901: 359. Kobelt, 1902: 859, pl. 124, figs. 28–30. Serina ser egressa— Yen, 1939: 86, pl. 8, fig. 17. Yen, 1942: 255. Chen, Zhou, Luo & Zhang, 2003: 442.
Type locality. Kutupa (between Yulingguan and Wenxian County, now belongs to Nanping, Sichuan).
Material examined. HBUMM-05426: 194 fma (24 for measurement and 2 for dissection), 41 juv.; 1070 m a.s.l., 32°57ʹ35.5ʹ N, 104°40ʹ41.6ʹ E, foot of Yuxushan hill, Wenxian County, Gansu, China, 2006–IX–27, colln. MW, JL, WZ & LG. HBUMM-05464: 26 fma (24 for measurement and 1 for dissection), 5 juv.; 943 m a.s.l., 32°56ʹ33.5ʹ N, 104°40ʹ33.2ʹ E, bank of Bailongjiang River, Wenxian , Gansu, 2006–IX–27, colln. MW, JL, WZ & LG. HBUMM-05538: 115 fma (20 measurement and 1 dissected), 4 juv.; from 829 m a.s.l., 32°51ʹ44.7ʹ N, 104°50ʹ48.2ʹ E to 779 m a.s.l., 32°51ʹ49.4ʹ N, 104°50ʹ37.7ʹ E, Hendan, Wenxian , Gansu, 2006–IX–29, colln. MW, JL, WZ & LG. HBUMM-05563: 132 fma (20 measured and 1 dissected), 2 juv.; 789 m a.s.l., 32°51ʹ41.6ʹ N, 104°50ʹ43.1ʹ E, Hendan, Wenxian , Gansu, 2006–IX–29, colln. MW, JL, WZ & LG. HBUMM-05648: 5 fma (all measured) and 2 juv.; rocks of limestone, from the site 1137 m a.s.l., 33°34ʹ21.7ʹ N, 104°39ʹ0 0.3ʹ E to the site 1151 m a.s.l., 33°34ʹ28.3ʹ N, 104°39ʹ10.7ʹ E, Jiaogong Town, Wudu County, S. Gansu, China, 2006–X–02, colln. JL & WZ. HBUMM-05673: numerous fma (20 measured and 2 dissected) and 11 juv.; eastern bank of Lianghekou, limestone, 1223 m a.s.l., 33°41ʹ47.3ʹ N, 104°29ʹ10.3ʹ E, Zhouqu County, S. Gansu, China, 2006–X–02, colln. JL & WZ. NHM-1902.5.13.21–22 Reg.: 2 fms. Gansu, China. SMF-42035: 6 fms. Labelled with " Serina ser Gredler".. SMF-42038: 1 fms, measured. SMF-104651: 2 fms. SMF-42039: 4 fms.. SMF-42040: 1 fms.
Distribution. Gansu ( Wenxian , Wudu, Zhouqu), Sichuan ( type locality).
Diagnosis. Shell with the most swollen part occurred at penultimate whorl and body whorl. Whorls with a narrow, defined zone below the suture,. Last whorl gradually ascending towards aperture, or ascending immediately near aperture; straight or concaved at periphery. Aperture duplicate; completely attached to body whorl. Columellar margin with one prominent tooth which is expanded inwards.
Shell. Ovate-turriform; with apex not abruptly pointed; dextral; with the most swollen part occurred at penultimate whorl to body whorl; height 10.1–11.5–14.1, diameter major 3.1–3.7–4.2, ratio of height /diameter major 2.62–3.09–3.66. Growth lines usually not very clear, or fine and clear. Whorls 8–9 1/8+– 10 1/2, convex; with a narrow, defined zone below the suture. Embryonic shell 1 1/2–1 3/4—2 1/8 whorls. Postnuclear whorls smooth. Last whorl gradually ascending towards aperture, or ascending immediately near aperture; straight or concaved at periphery; with smoothed spiral peripheral depression. Aperture in a plane and straight; rounded-ovate; slightly oblique; completely attached to body whorl; armed; height 2.9–3.3–3.7, width 2.3–2.9–3.4, ratio of shell height / apertural height 2.91–3.41–4.14. Duplicate aperture indistinctly present. Palatal tooth absent. Palatal margin rounded; toothless. Peristome and parietal callus almost completely fusing except for a channel at upper insertion of peristome. Reflexed part of peristome straight and not curved backward. Parietal tooth absent. Abapertural peripheral depression on body whorl spirally extending for ca. 0.750 whorl. Palatal wall without deep depression or tooth of irregular shape. Columellar margin reflexed; with one prominent tooth which is expanded inwards; not sinuous. Columella arched. Umbilicus widely open. Shell bandless; uniformly coloured or multicoloured; chestnut at apex. Subsequent whorls evenly reddish brown or reddish brown with numerous whitish streaks. Aperture white or brownish white. Measured specimens: HBUMM-5426, HBUMM-5464, HBUMM-5538, HBUMM-5563, HBUMM-5648, HBUMM-5673, SMF-42038: 114 shells.
Genitalia. Vas deferens short; proximally swollen; entering epiphallus laterally with distinct demarcation. Epiphallus long; narrowed towards distal end; forming numerous loops; without epiphallic caecum. Flagellum short; conic; proximally normal; with tip blunt. Penis shortly clavate and distally enlarged; terminally entering epiphallus; thin-walled. Longitudinal pilaster more than two; fused at epiphallic pore forming velum; forming 2 Vshaped structures. V-shaped pilaster with proximal free end approaching at penial retractor insertion; without papilla formed by fused distal pilasters. Penial process absent. Penial appendix short; branched off from penis at some distance from atrium; with A-1 fused with A-2, and with distinct A-3, A-4 and A-5. A-1 long; without verge toward penial chamber. A-2 internally with longitudinal pilasters; near A-3 internally with a ring of papilla. A-3 opening into A-2 by a long needle-like papilla. A-5 short; straight. Penial retractor biramous; with arms arising from diaphragm separately; with penial branch attaching to medial penis; with appendical branch attaching to A- 1+A-2. Atrium short; with strong atrial retractor. Free oviduct moderately long; longer than vagina. Vagina short; straight. Bursa copulatrix duct very long; proximally twisted. Bursa copulatrix in normal size; well defined; shortly with stalk; without apical ligament; with short neck. Diverticle longer than reservoir; expanded. Bursa copulatrix and diverticle almost indistinguishable; forked more distally from their base. Measurement of genitalia: See Table 2 View TABLE 2 (HBUMM-05673–specimen 22 and HBUMM-05563–specimen 21 were measured).
Taxonomic remarks. Conchologically, this species most resembles Serina ser, under which S. egressa was once treated as a subspecies. By principal component analysis (PCA analysis) it shows that aperture height contributes most in distinguishing S. egressa and S. ser: S. egressa has absolutely less aperture height than S. ser. Furthermore, the genitalian divergence, e.g. the presence or absence of ephiphallic caecum, suggests that they are two distinct species. Whether S. ser has the columellar tooth is not yet known through this study.
There are two types of shell ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2. A E–G, H–J), each of which is only found in a certain population of this species. One is evenly reddish brown and another one is brown with whitish streaks (respectively "brown pattern" and "striated pattern" in the text). However, both the PCA analysis upon brown pattern shells (88 shells from HBUMM-05426, HBUMM-05464, HBUMM-05538 and HBUMM-05563) and the striated pattern shells (26 shells from HBUMM-05648, HBUMM-05673 and SMF-42038), and the same genitalia anatomy ( Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 A–B of brown pattern shell and 3C of striated pattern shell) suggest that they are merely of the same species which shows divergence in shell coloration.
Ecological remarks. The brown pattern specimens were found in the slate area with lower altitude range of 780 to1070 metres and the striated pattern specimens lived in the limestone regions with a higher altitude range of 1140–1230 metres.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |