Calliopum splendidum
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.214261 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6170406 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03B69A7E-B04D-FF9B-DA81-73AEFBB886B6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Calliopum splendidum |
| status |
|
Egg ( Figs 41–43 View FIGURES 35 – 46 ). Length 0.65–0.74 mm Chorion slightly differentiated in dorsal and ventral side. Dorsal side with more developed longitudinal ridges and regular longitudinal channels.
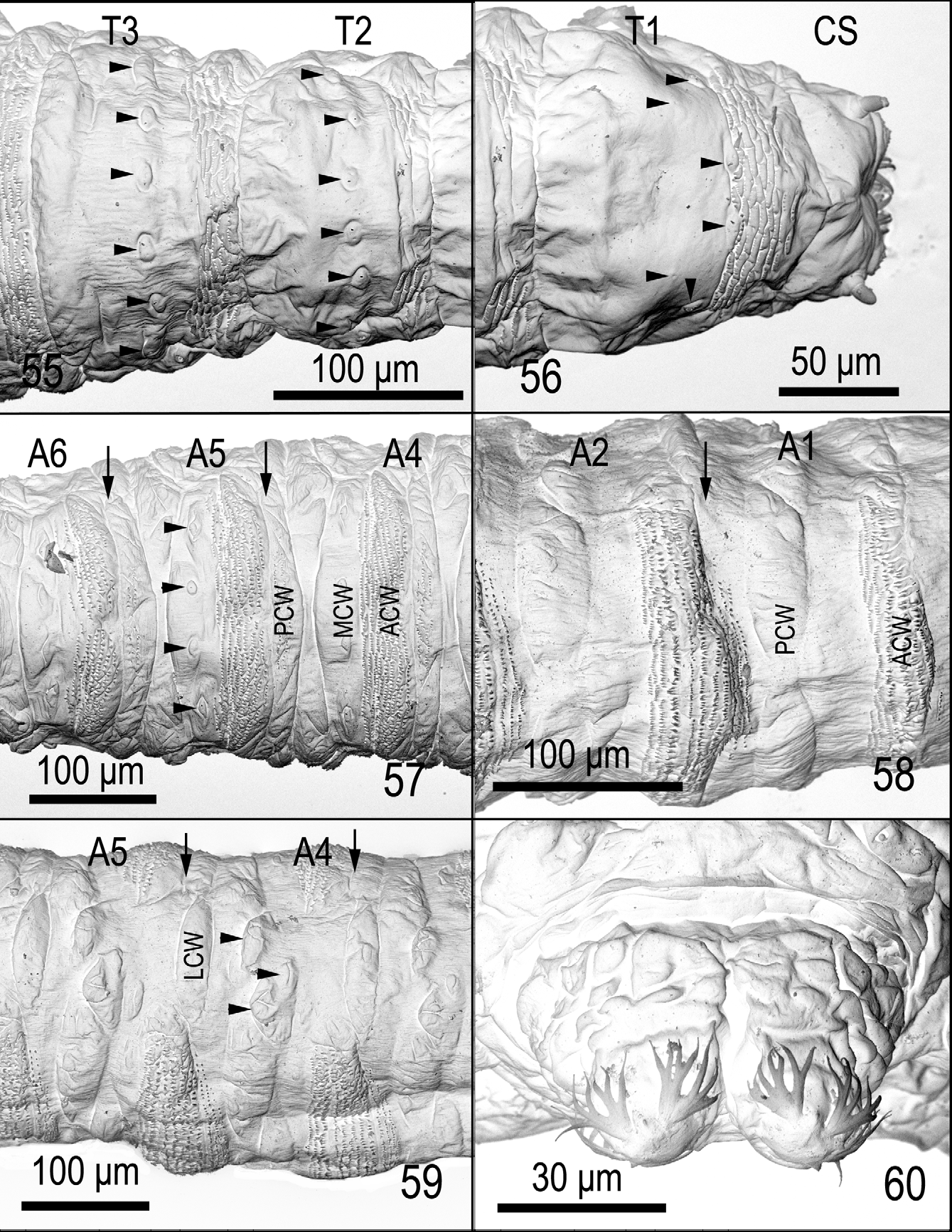
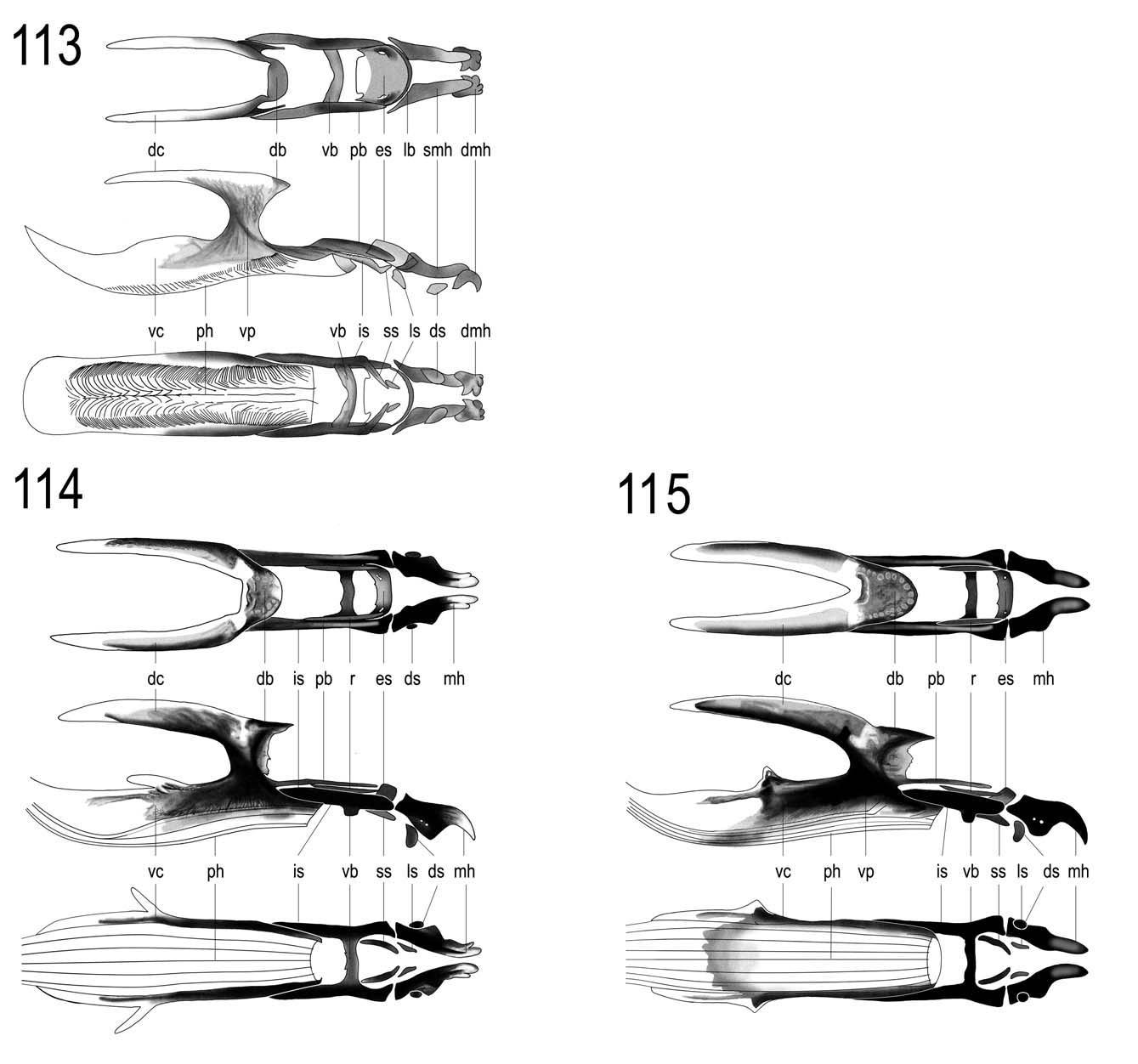
First larval instar ( Figs 51, 52 View FIGURES 47 – 54 , 55–60 View FIGURES 55 – 60 ). Length 1.12–2.16 mm. Length of cephaloskeleton ( Fig. 113 View FIGURES 113 – 115 ) 0.21–0.22 mm.
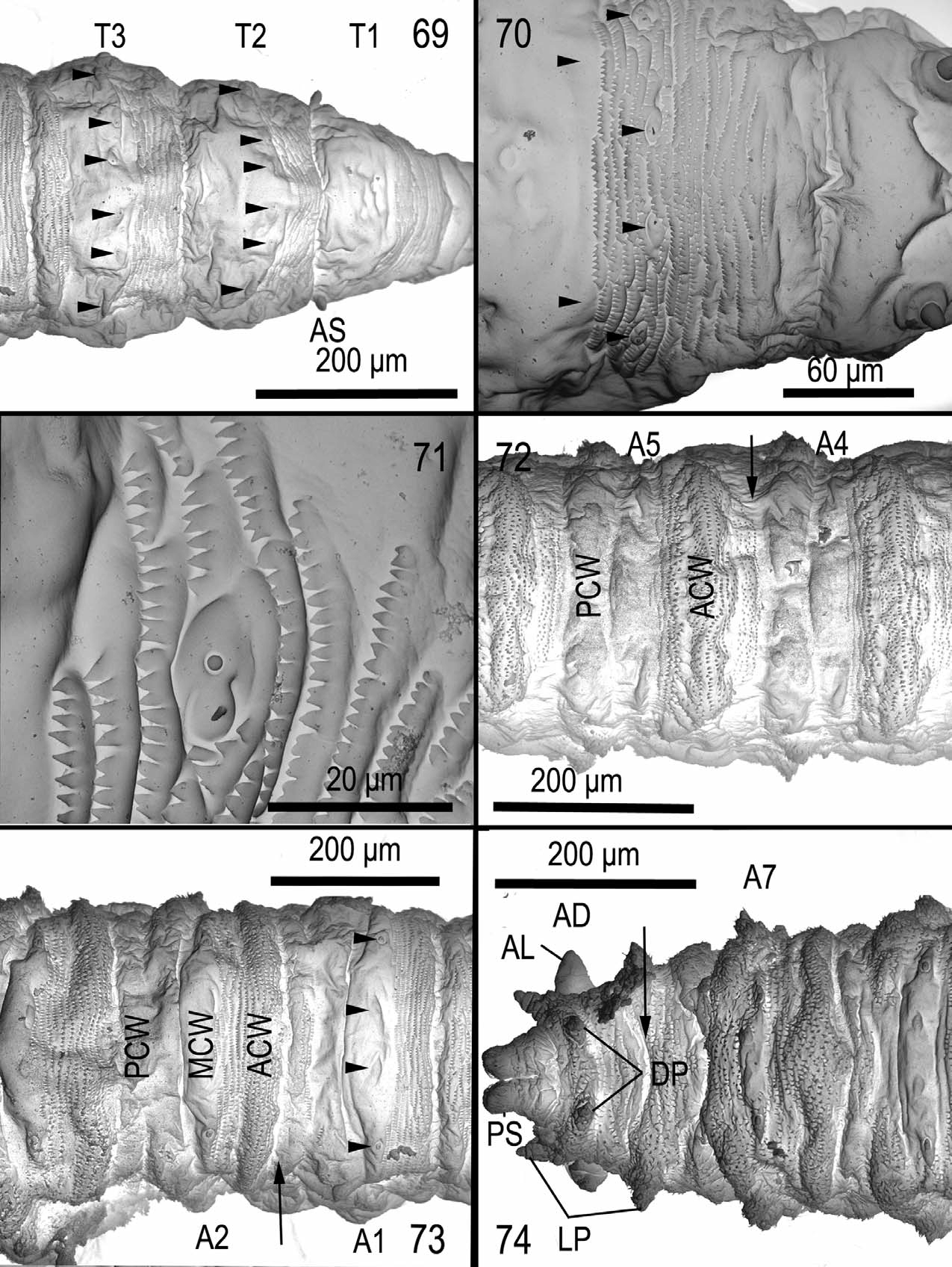
Second larval instar ( Figs 65, 66 View FIGURES 61 – 68 , 69–74 View FIGURES 69 – 74 ). Length 2.14–3.58 mm. Length of cephaloskeleton ( Fig. 114 View FIGURES 113 – 115 ) 0.37–0.39 mm.
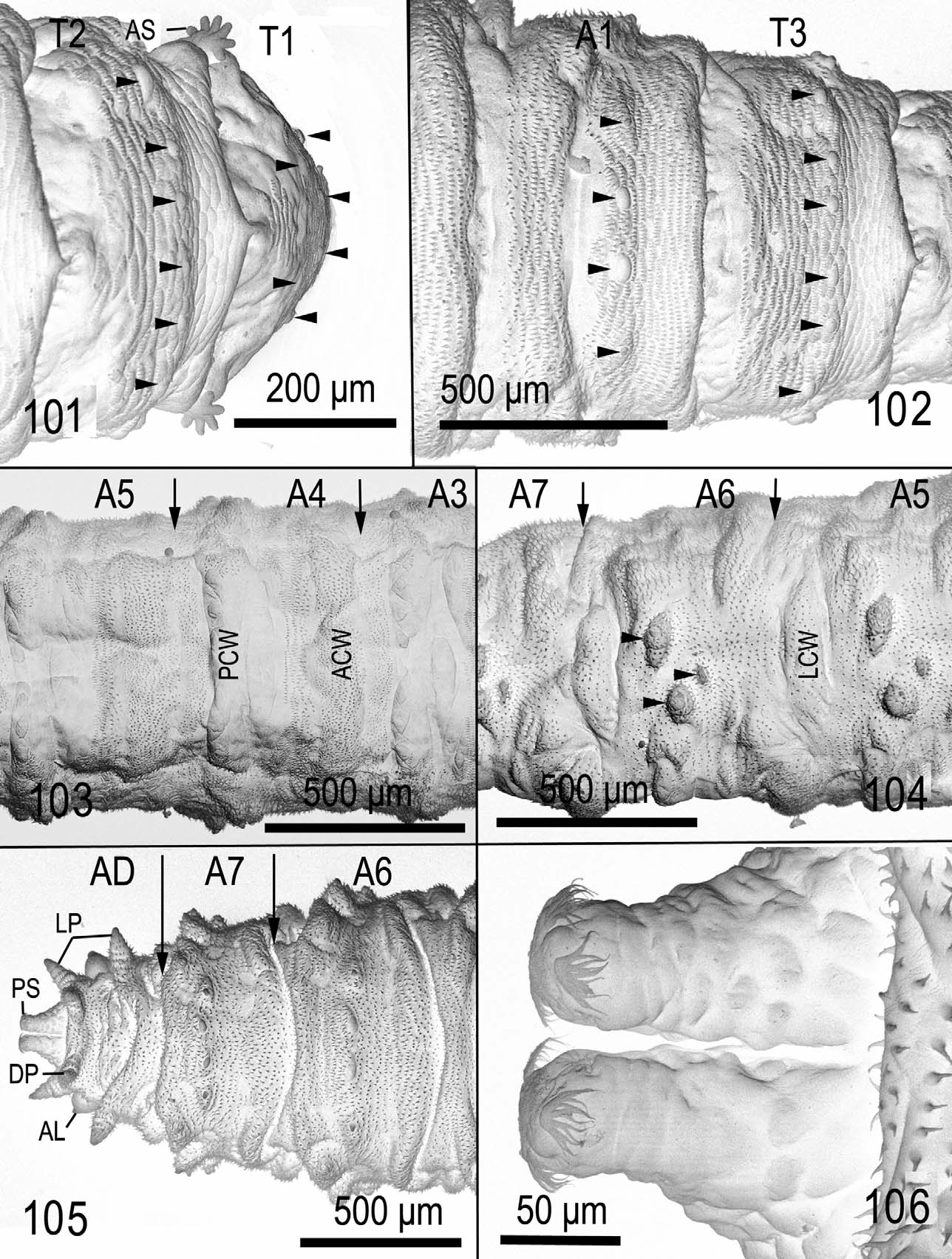
Third larval instar ( Figs 79 View FIGURES 75 – 82 , 101–106 View FIGURES 101 – 106 ). Length 3.53–4.30 mm. Anterior spiracles with 7 papillae, the two marginal papillae are curved back ( Fig 80 View FIGURES 75 – 82 ). Integument of abdominal segments and anal division villous, small smooth areas are retained behind dorsal tubercules in first four segments and partly between segment borders. Extensive smooth areas are on the ventral side behind anterior creeping welt. The only species of Calliopum with comb spines on the posterior half of the first thoracic segment. Length of cephaloskeleton ( Fig. 115 View FIGURES 113 – 115 ) 0.61–0.63 mm.
Puparium ( Fig. 121). Length 3.61–3.89 mm. Indistinguishable from C. simillimum . Smaller size can be result of unfavourable rearing conditions, as adult flies are comparably large to C. simillimum .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |