Pareuchiloglanis kamengensis
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.175973 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5613096 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AE87FA-FF92-2D16-7DDB-FE40FD4BFE21 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pareuchiloglanis kamengensis |
| status |
|
Pareuchiloglanis kamengensis View in CoL
( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 )
Euchiloglanis kamengensis: Chu, 1979: 77 View in CoL (Lancangjiang drainage); Wu et al., 1981: 77 (Lancangjiang drainage). Pareuchiloglanis kamengensis: Chu, 1986: 41 View in CoL (Lancangjiang drainage); Chu et al., 1990: 205 (Lancangjiang drainage); Wu & Wu, 1992: 552 -554 (Lancangjiang drainage); Chen, 1998: 305 -306 (Lancangjiang drainage); Chu & Mo 1999: 169 (Lancangjiang drainage).
Material examined. All examined specimens are from the upper Lancangjiang, Yunnan, China. SWFC 0411001-0411018 (18; 69.5-157.1 mm SL), Yingpan, Lanping County. SWFC 0409001-0409012 (12; 105.0- 155.6 mm SL), Yingpan, Lanping County. SWFC 0304001-0304002 (2; 154.5-177.4 mm SL), Tongdianhe, Lanping County.
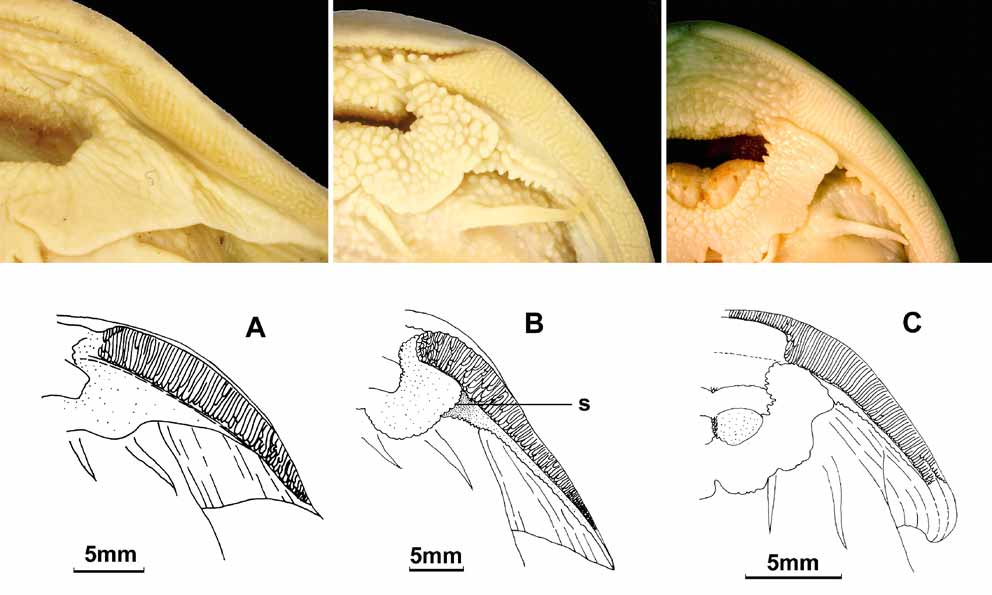
Diagnosis. Characters distinguishing Pareuchiloglanis kamengensis from P. abbreviatus , P. gracilicaudata P. myzostoma and P. prolixdorsalis are summarized in Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Morphometric and meristic data are in Table 2 View TABLE 2 . A species of Pareuchiloglanis with the following unique combination of characters: adipose-fin base not confluent with caudal fin (vs. confluent); premaxillary tooth patches appear separate (vs. joined with small median indention); lower lip not connected to base of maxillary barbel by skin flap, with sulcus between them (vs. connected, and without sulcus); 7 upper + 8 lower branched caudal-fin rays (vs. 6+7); dorsal fin i-5 (vs. i- 7); anal fin ii-3-4 (vs. ii-8); distance between pelvic-fin origin to anal-fin origin shorter than distance between pelvic-fin origin to mouth (vs. equal); pectoral fin extending beyond origin of pelvic fin (vs. not reaching); origin of pelvic fins opposite end of dorsal-fin base (vs. posterior to end of dorsal-fin base); anus nearer to anal-fin origin than to end of pelvic-fin base (vs. nearer to posterior end of pelvic-fin base); anal-fin origin nearer to caudal-fin base than to posterior end of pelvic-fin base (vs. nearer to end of pelvic-fin base).
Pareuchiloglanis kamengensis is distinguished from P. abbreviatus , P. anteanalis , P. gracilicaudata , P. myzostoma , P. nebulifer , P. robusta , P. m a c ro t re m a, P. prolixdorsalis , P. sinensis , P. sichuanensis , P. tianquanensis , P. rhabdurus , P. poilanei , P. longicauda and P. nebulifer by the following characters: two isolated premaxillary tooth patches (vs. premaxillary tooth patches appearing joined with a median indentation) ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 B); lower lip not connected to base of maxillary barbel by skin flap, with sulcus between them (vs. connected, without sulcus) ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 B). It differs from P. gracilicaudata , P. gongshanensis , P. longicauda , P. macrotrema , P. myzostoma , P. robusta and P. s i n e n s i s by having longer pectoral fin, extending beyond origin of pelvic fin (vs. not reaching). It differs from P. feae , P. poilanei , P. sichuanensis and P. tianquanensis by adipose-fin base not confluent with caudal fin (vs. confluent). It differs from P. abbreviatus and P. prolixdorsalis by having 7+8 branched caudal-fin rays (vs. 6+7). It differs from P. songmaensis by having fewer fin rays, dorsal fin i-5, anal fin ii-3-4 (vs. i-7, ii-8). It differs from P. longicauda and P. sinensis by having origin of pelvic fin opposite end of dorsal-fin base (vs. posterior to end of dorsal-fin base), and differs from P. songdaensis by having distance between pelvic-fin origin to anal-fin origin shorter than distance between pelvic-fin origin to mouth (vs. equal). It differs from P. abbreviatus , P. anteanalis , P. f e a e, P. longicauda , P. nebulifer , P. prolixdorsalis and P. rhabdurus by having anus nearer to anal-fin origin (vs. nearer to posterior end of pelvic-fin base) and differs from P. rhabdurus by its deeper caudal peduncle, 6.5-8.9% SL (vs. 4.2% SL).
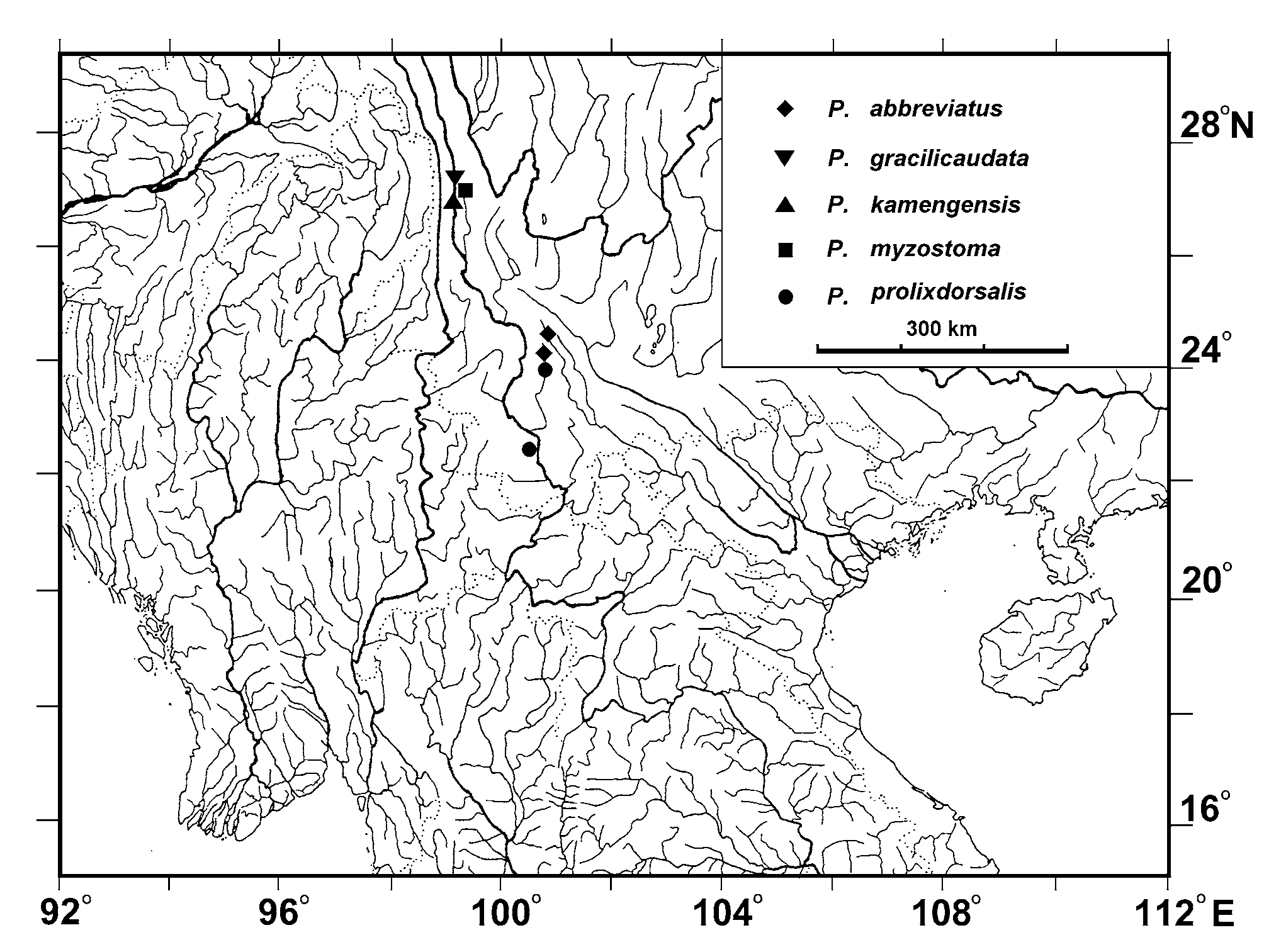
Distribution. Known from the upper Lancangjiang [Mekong] and Brahmaputra drainages ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ).
Remarks. Ng (2004) postulated that P. kamengensis recorded in the Lancangjiang by Chu & Mo (1999) could be P. m a c ro p t e r u s Ng, and that P. kamengensis is distributed only in Brahmaputra. However, the specimens of Pareuchiloglanis from the Lancangjiang are distinguished from P. macropterus by having a pectoral fin that reaches the origin of the pelvic fin (vs. not reaching), and no pale patches on the body (vs. presence). Based on the taxonomic study results of Chu & Mo (1999), specimens of Pareuchiloglanis from Lancangjiang are most similar to those of P. kamengensis . In the absence of sufficient evidence, the authors provisionally identify these specimens as P. kamengensis .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Pareuchiloglanis kamengensis
| Li, Xu, Zhou, Wei, Thomson, Alfred W., Zhang, Qing & Yang, Ying 2007 |
Euchiloglanis kamengensis:
| Chu 1999: 169 |
| Chen 1998: 305 |
| Wu 1992: 552 |
| Chu 1990: 205 |
| Chu 1986: 41 |
| Wu 1981: 77 |
| Chu 1979: 77 |