Cladopus fallax, C. Cusset
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.401.1.3 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5752603 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03AA87C3-FFA5-1016-FF4E-D9F9FADEF9A9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Cladopus fallax |
| status |
|
Cladopus fallax was distinguished from other congeners by combined characters. It differs from C. taiensis in the form (surface-viewed and in cross section), surface and number of the bract-segments, from C. nymanii H.Möller in the length of the stamens and the number of ovules, from C. queenslandicus (Domin) C.D.K.Cook & Rutish. in the length of the flowering shoots and the number and form of the bracts, and from C. javanicus M.Kato & Hambali in the length of the flowering shoots, the number of the bracts, and the length of the capsules and capsule stalks ( Table 2 View TABLE 2 ).
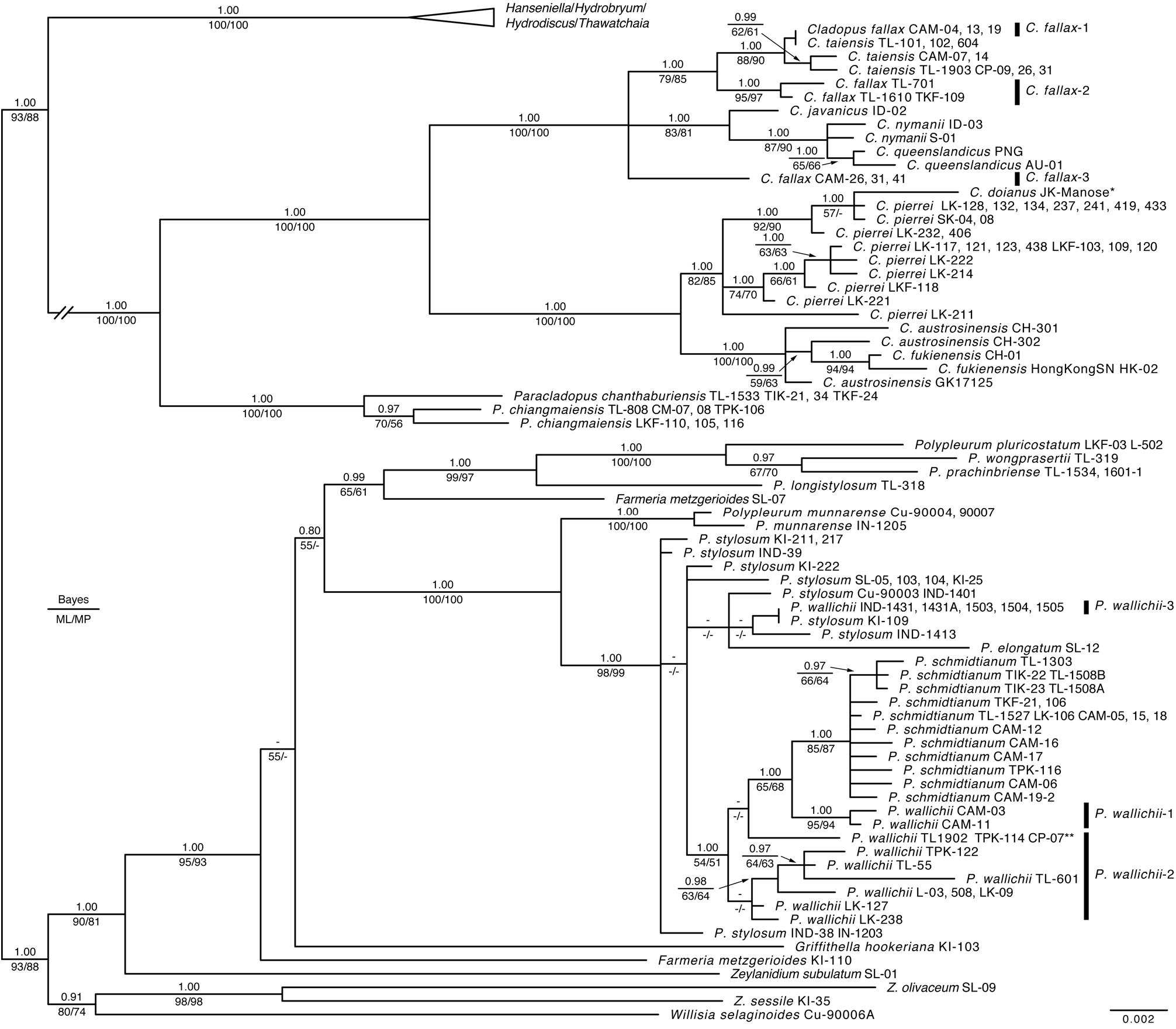
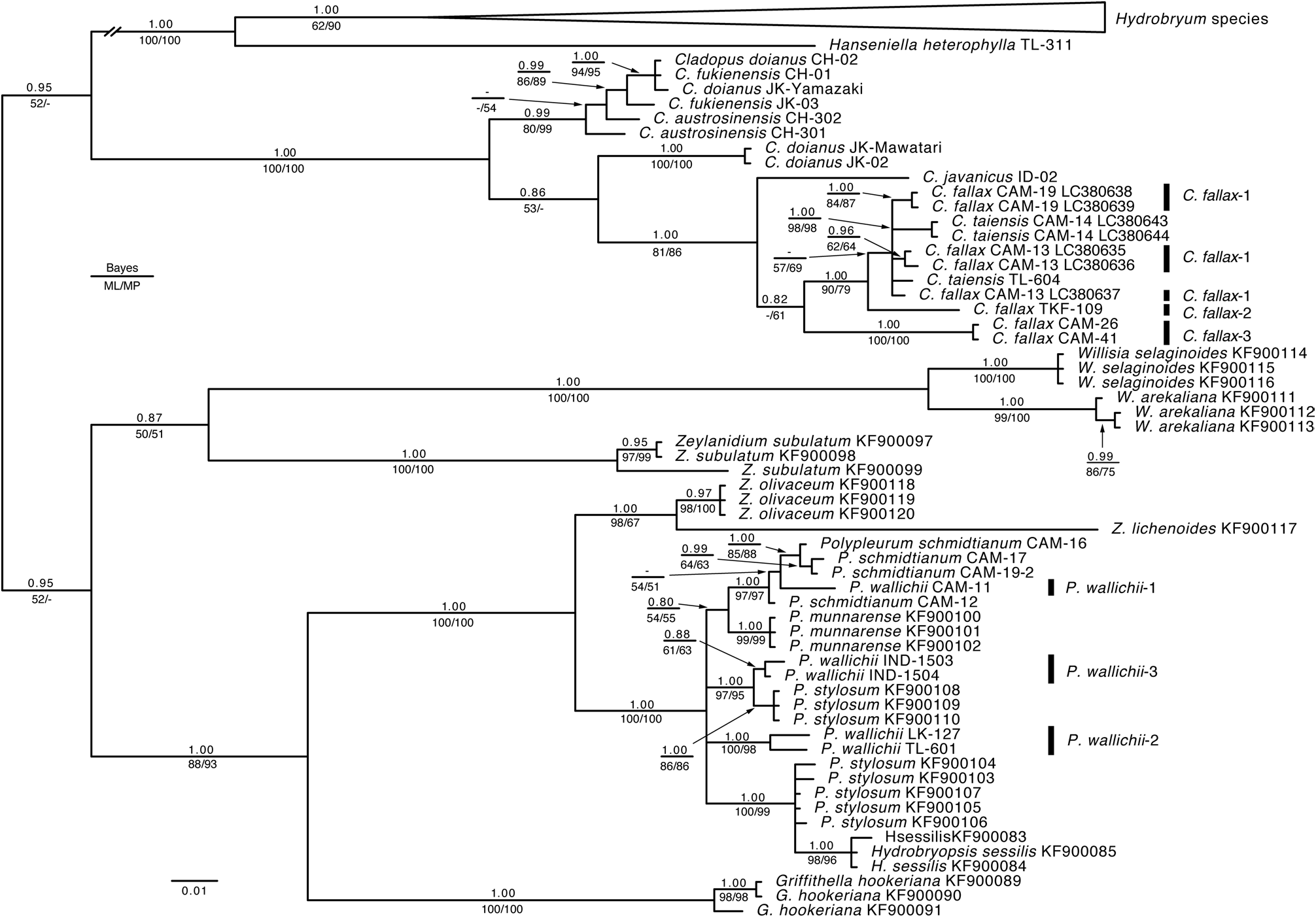
In the chloroplast matK tree ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ), Cladopus was divided into two clades with robust support. One clade (upper in Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ) was subdivided into three subclades, i.e. a subclade consisting of C. fallax -1 from Cambodia, C. fallax -2 from Thailand and C. taiensis ; a subclade of C. javanicus , C. nymanii and C. queenslandicus ; and C. fallax - 3 from Cambodia. Cladopus fallax -1 had the same sequence as the Thai specimens of C. taiensis (TL-101, TL-102, TL-604), the two were sister to the other C. taiensis from Cambodia and Thailand, and all were sister to C. fallax -2. Geographically, C. fallax -1 is adjacent to C. taiensis (CAM-07, CAM-14) of Cambodia (4.2 or 12.2 km apart) and far from the Thai populations.
The nuclear ITS tree ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ) showed that there are variations in the ITS regions of C. fallax CAM-13, C. fallax CAM-19 and C. taiensis CAM-14, while uniform in others (e.g. C. fallax CAM-26, C. fallax CAM-41, C. fallax TKF-109, C. taiensis TL-604). The variants of CAM-13 and CAM-19 of C. fallax -1, and CAM-14 of C. taiensis were grouped in each clade, although one C. fallax CAM-13 was isolated. These samples of C. fallax -1 and C. taiensis formed a monophyletic clade, with low support, which was sister to C. fallax -2 and together sister to C. fallax -3.
In the combined matK and ITS tree, C. fallax -1 and C. taiensis were monophyletic and sister to C. fallax -2 ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ). Then, C. fallax -1, C. fallax -2, C. fallax -3 and C. taiensis , together with C. javanicus , were monophyletic.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |