Thienemanniella absens, Fu, Yue, Saether, Ole & Wang, Xinhua, 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.194711 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5682155 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A087E6-FF83-3A01-FF24-F991FCB89CDB |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Thienemanniella absens |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Thienemanniella absens View in CoL sp. n.
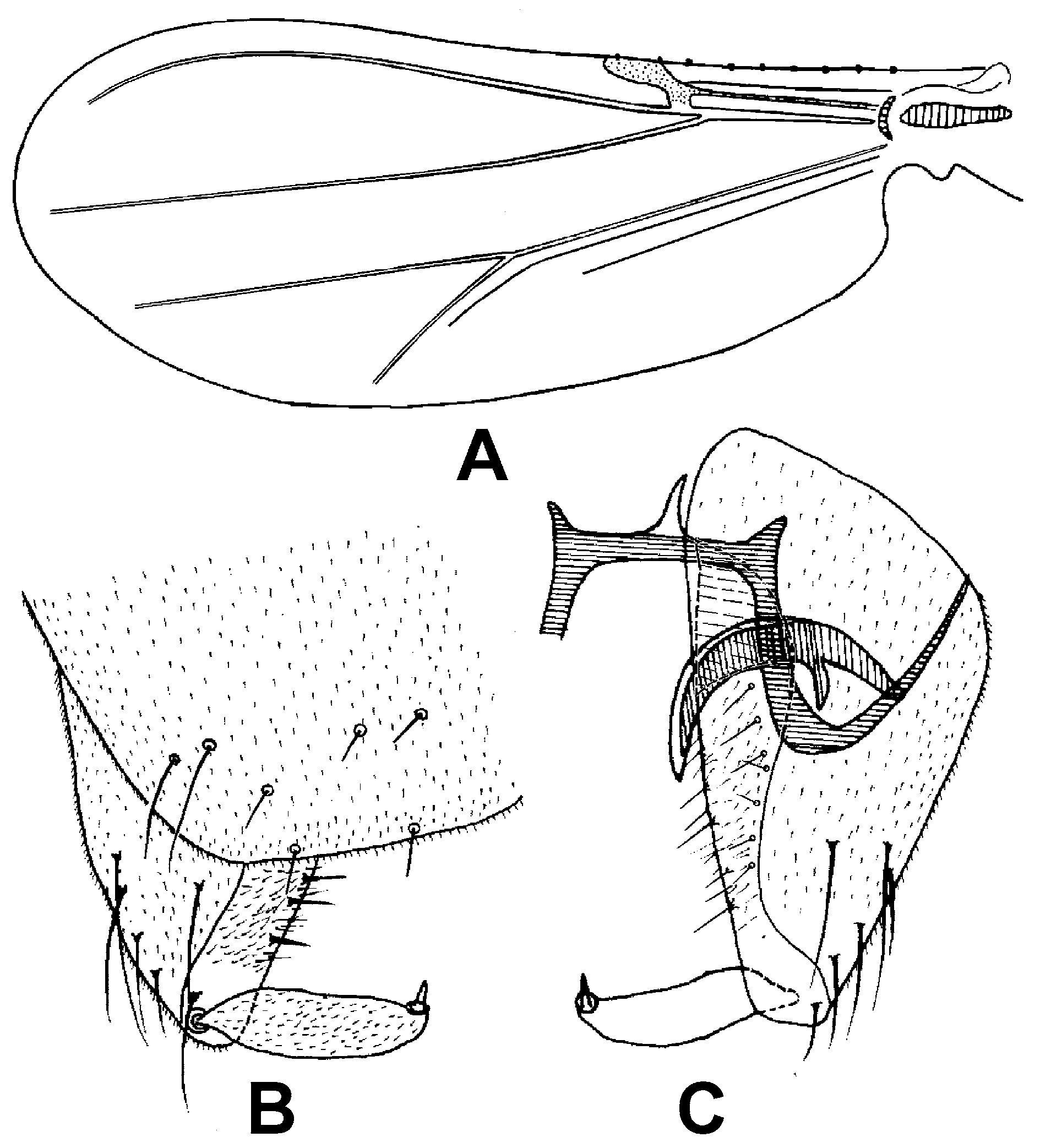
( Figs 4 View FIGURES 4 A–C)
Type material. Holotype male (BDN No. 26776), CHINA: Zhejiang Province, Taishun County, Wuyanling (27°30΄N, 119° 46΄E), 1611 m a.s.l., light trap, 1.viii.2005, Bingchun Ji. Paratypes: CHINA: Shannxi Province, Zhouzhi County (34°11΄N, 108° 13΄E), 2896 m a.s.l., light trap, 1 male (BDN No. 04450), 7.viii.1994, Xinhua Wang.
Diagnostic characters. The species resembles T. flaviscutella (Tokunaga) in having an antenna with 12 flagellomeres and AR 0.25–0.28, but may be separated by having hairy eyes, triangular superior volsella and absence of inferior volsella; the phallapodeme curved with a basal projection to join prelateral sternapodeme, lateral sternapodeme directed caudoventrad.
Etymology. From Latin, absens , absent, referring to the absence of inferior volsella.
Description. Male imago (n =2).
Total length 1.45–2.20 mm. Wing length 0.66–0.97 mm. Total length / wing length 2.2–2.3. Wing length / length of profemur: 2.6–2.7.
Coloration. Head brown. Thorax dark brown. Abdominal segments brown. Legs yellowish brown. Wings hyaline with yellow clava.
Head. Eyes hairy, reniform. Antenna with 12 flagellomeres; ultimate flagellomere 80–110, 95 µm long; antenna distally with apical sensilla chaetica, subapically expanded, thickening 75 µm long with maximum width 30 µm; AR 0.25–0.28. Temporals: 2 inner verticals. Clypeus with 13–15 setae. Tentorium 113–140 µm long. Stipes 68–98 µm long. Palpomeres length (in µm): 15, 25; 30–40; 35; 50–60; 125–135; palpomeres 2 and 3 ellipsoid, palpomere 4 rectangular, palpomere 5 long and slender; palpomere 5/3: 3.4–4.2.
Thorax. Dorsocentrals 8–13, 11 in single row; prealars 2. Scutellum with 2 setae.
Wing ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4 A). VR 1.8–1.9. C length 240–350 µm, C/ wing length 0.36. Cu length 340–450 µm. Cu/ wing length 0.46–0.51. Wing width/ wing length : 0.41–0.45. C with 11–19 setae.
Legs. Fore trochanter with small keel. Spurs of fore tibia 28–33 µm and 13 µm long, spurs of mid tibia 15–23 µm and 13 µm long, of hind tibia 20–33 µm and 18–25 µm long. Width at apex of fore tibia 20–30 µm, of mid tibia 20–28 µm, of hind tibia 28–35 µm. Hind tibial comb composed of 11–13 setae. Lengths and proportions of legs as in Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
Hypopygium ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4 B–C). Tergite IX with straight posterior margin, with many short setae, laterosternite IX without long setae. Superior volsella triangular, inferior volsella absent. Transverse sternapodeme 30–33 µm long, with developed oral projection; coxapodeme 40 µm long; phallapodeme curved, with basal projection, 50–55 µm long. Gonocoxite 83–110 µm long with 6 setae apically, and many strong setae on the inner side. Gonostylus straight, simple, 38–58 µm long; megaseta 5 µm long. HR 1.9–2.2, HV 3.9. Female and immature stages. Unknown.
Distribution. China (Zhejiang and Shannxi Provinces)
TABLE 1. Lengths (in µm) and proportion of leg segments of T. absens sp. n.
| fe | ti | ta1 | ta2 | ta3 ta4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1 250–360 | 275–365 | 190–250 | 75–105 | 30–60 13–23 |
| p2 320–490 | 280–415 | 200–295 | 115–135 | 50–75 15–20 |
| p3 275–395 | 285–415 | 195–270 | 115–160, | 48–73 13–20 |
| ta5 | LR | BV | SV | BR |
| p1 20–35 | 0.64–0.68 | 4.4–5.2 | 2.8–2.9 | 1.7–2.3 |
| p2 28–38 | 0.7–0.71 | 4.1–4.5 | 3.0–3.1 | 2.3–2.7 |
| p3 30–38 | 0.65–0.68 | 3.7 | 2.9–3.0 | 2.8–3.0 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Orthocladiinae |
|
Genus |