Cathorops (Cathorops) aguadulce ( Meek, 1904 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1590/S1679-62252008000100004 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03910B7A-B15F-0F32-6059-FE8EFEB3FDD4 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Cathorops (Cathorops) aguadulce ( Meek, 1904 ) |
| status |
|
Cathorops (Cathorops) aguadulce ( Meek, 1904) View in CoL Figs. 1 View Fig and 2 View Fig
Galeichthys aguadulce Meek, 1904: 9 View in CoL , pl. 4. Type locality: río TesechoacánatPérez , Veracruz,ríoPapaloapanbasin, Mexico. Holotype: FMNH4678 About FMNH .
Cathorops aguadulce View in CoL ; Taylor & Menezes, 1978 [only name]; Castro-Aguirre et al., 1999 (in part): 148–149 [remarks and distribution, Mexico, río Papaloapan basin]; Marceniuk & Ferraris, 2003: 449 [distribution, Mexico, río Papaloapan basin];Acero P., 2003:837 [only name]; Kailola, 2004: 132 [only name]; Miller et al., 2005 (in part): 170 [description and distribution, Mexico, from río Panuco to río Coatzacoalcos]; Marceniuk & Menezes, 2007 (in part): 42 [distribution, Mexico, río Papaloapan basin]; Betancur-R. et al., 2007:349 [only name]; Betancur-R. & Willink, 2007 (in part) [key features and distribution, Mexico, río Panuco to río Papaloapan].
Material examined. FMNH 4678 About FMNH , 1 About FMNH , 227.0 mm SL, Mexico , río Tesechoacán at Pérez, Veracruz, río Papaloapan basin, holotype of Galeichthys aguadulce Meek 1904 ; UMMZ 210777 View Materials , 1 View Materials , 152.0 mm SL, Mexico , Oaxaca, río Papaloapan ,ca 100 m below bridge to Papaloapan ; UMMZ 97483 View Materials , 5 View Materials , 134.0-187.0 mm SL, Mexico , Veracruz, río Papaloapan , 2 miles W of San Cristobal . UMMZ 186482 View Materials , 1, 190 mm SL, Mexico , Veracruz, Estero tributary to Bahia Tecolutla, on Tecolutla- Nautla hwy 2.8 mi SSE Tecolutla (ferry landing, S side) at Rancho, río Tecolutla basin .
Diagnosis. Cathorops aguadulce is distinguished from all congeners by the fleshy papillae intercalated with gill rakers on first two gill arches (vs. papillae absent in the remaining species, except in C. kailolae ) ( Fig. 3 View Fig ), posterior margin of pectoral-fin spine with long and conspicuous serrations (vs. short and inconspicuous serrations in all other species, except in C. kailolae , C. melanopus , C. multiradiatus , and C. tuyra ) ( Fig. 2 View Fig ), 14-16 gill rakers on first arch (vs. 19-23 in C. agassizii , 17-22 in C. arenatus , 19-20 in C. belizensis , 18-21 in C. higuchii , 37-40 in C. hypophthalmus , 20-24 in C. mapale , 19-22 in C. tuyra , and 17-21 in C. spixii ) ( Table 1), and snout length 9.3-11.6% SL (vs. 5.0-9.0% SL in the remaining species, except in C. hypophthalmus ) ( Fig. 4 View Fig ).
Cathorops aguadulce is further distinguished from C. belizensis by possessing a longer supraoccipital process (11.5- 16.3 vs. 8.8-10.5% SL), largerorbitaldiameter(4.6-6.9 vs. 3.6-4.4% SL), and shorter interorbital distance (9.9-12.3 vs. 12.9-15.1% SL). Cathorops aguadulce is additionally distinguished from C. higuchii by having 13-16 gill rakers on second arch (vs. 17-21), and a larger orbital diameter (4.6-6.9 vs. 3.3-4.4% SL). Cathorops aguadulce also differs from C. kailolae by having a longer distance from tip of snout to dorsal-fin origin (39.0-40.7 vs. 33.1- 38.0% SL) ( Fig. 5 View Fig ). Cathorops aguadulce is additionally distinguished from C. mapale species group in possessing 13-16 gill rakers on second arch (vs. 17-21). Cathorops aguadulce is further distinguished from C. melanopus by having a longer distance from tip of snout to dorsal-fin origin (39.0-40.7 vs. 30.0- 32.6% SL), and longer distance from tip of snout to posterior margin of dorsomedian groove of neurocranium (22.9-26.4 vs. 17.9-19.1%SL).
A. P. Marceniuk & R. Betancur-R. 27
Description. ( Tables 1 and 2). Head long and depressed, profile slightly convex at level of frontals and supraoccipital. Body broader rather than deeper on pectoral girdle area. Cephalic shield rugose, relatively short and narrow on lateral ethmoid, frontal, supracleithrum, and epioccipital areas. Osseous bridge formed by lateral ethmoid and frontal long and slender, evident under skin. Dorsomedian groove of neurocranium formed by frontals and supraoccipital, relatively deep and long, its margins well marked and progressively narrower posteriorly. Supraoccipital process relatively long and narrow on posterior portion, profile straight. Nuchal plate crescent-shaped, short and relatively wide. Snout long, rounded on transverse section. Anterior and posterior nostrils close to one another. Eye lateral and large. Interorbital distance short, distance between nostrils and orbit long. Maxillary barbel surpassing base of pectoral-fin spine, external mental barbel surpassing margin of gill membrane, internal mental barbel reaching margin of gill membrane.
Mouth narrows, lower jaw arched. Lips thick, lower lip thicker than upper lip. Vomerine tooth plates absent. One pair of elongated and narrow accessory tooth plates, small and distant from each other. Accessory tooth plates with small and few molariform teeth. Premaxilla quite narrow and moderately long.
Soft pectoral-fin rays 10. Pectoral-fin spine thick and short; anterior margin without granules or serrations; posterior margin with long and conspicuous serrations along almost its entire length. Soft dorsal-fin rays 7. Dorsal-fin spine relatively short, longer than pectoral-fin spine; anterior margin smooth; posterior margin serrated along almost its entire length.Pelvic fin high, with 6 rays. Anal fin high and short at base, with 21 rays. Upper and lower lobes of caudal fin long, upper lobe longer than lower lobe. Caudal peduncle high.
Acicular gill rakers on first arch 14-16 (14), 4 or 5 (5) on upper limb, 10 or 11 (10) on lower limb. Spike-shaped gill rakers on second arch 13-16 (13), 3 to 5 (3) on upper limb, 10 or 11 (10) on lower limb. Mesial surfaces of all gill arches with developed gill rakers. Lateral and mesial surfaces of first and second gill arches with fleshy papillae intercalated with gill rakers, papillae more developed on second arch.
Coloration inAlcohol. Dorsal and lateral portions of head brown, ventrally light beige. Body with same brown color, progressively lighter towards lateral line and rather light beige under lateral line. Maxillary barbel dark, mental barbels light; adipose fin dark, and other fins brown.
Sexual dimorphism. Sex of specimens was not examined (see Material and Methods).
28 Revision of the ariid species of the genus Cathorops
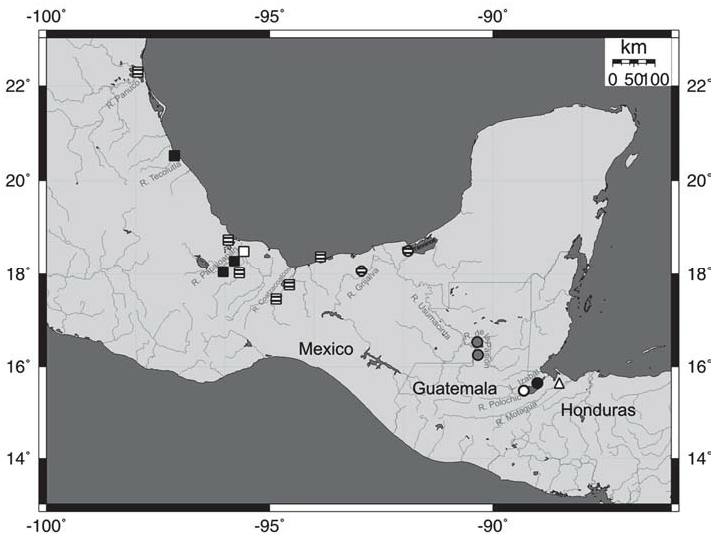
Distribution. Cathorops aguadulce was described based on material from río Tesechoacán, río Papaloapan basin in Veracruz, Mexico. Without considering the populations from the río Usumacinta/río Grijalva and río Polochic/Lago Izabal watersheds (see remarks), Miller et al. (2005, Map 6.144) suggested that C. aguadulce occurs from río Coatzacoalcos northwestwards to río Panuco as well as in the Gulf of Mexico ( Fig. 6 View Fig ). The species inhabits large to medium-sized rivers, lagoons and small drainages; typically freshwaters, but also occurring in marine waters ( Miller et al., 2005).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Cathorops (Cathorops) aguadulce ( Meek, 1904 )
| Marceniuk, Alexandre P. & Betancur-R, Ricardo 2008 |
Galeichthys aguadulce
| Meek, S 1904: 9 |