Sarika diadema ( Dall, 1897 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.5341400 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038F9713-FFBC-5367-09A3-F4B3B545FD15 |
|
treatment provided by |
Diego |
|
scientific name |
Sarika diadema ( Dall, 1897 ) |
| status |
|
Sarika diadema ( Dall, 1897) View in CoL
( Figs. 2A, B View Fig ; 3A–E View Fig ; 4A–C View Fig )
Nanina (Macrochlamys) diadema Dall, 1897: 37–38 View in CoL . (Type locality: Prang, Malay Peninsula); Dall, 1902: 499, Pl. 27 Figs. 1–3 View Fig View Fig View Fig (USNM 150277); Boss, Rosewater & Ruhoff, 1968: 104.
Macrochlamys diadema View in CoL – Gude, 1903: 50
Syama diadema – Abbott, 1989: 23, 133 (text figure); Panha, 1996: 102–104, Fig. 2b2 View Fig (Holotype, USNM 150277).
Type material. – Prang, Malay Peninsula: Holotype USNM 150277 About USNM ,
Other material examined. – Khao Wang Meng, Patthalung: USNM 420342; Kao Poo-Khao Ya National Park, Patthalung: CUMZ 2582, 3642; Khao Auk-Taru, Pattalung: CUMZ 2579; Botanic Garden, Trang: CUMZ 2580, 2583, 2585, 2587, 3616, 3619, 3620; Khao Chong, Trang: CUMZ 2581, 2588; Tam Sumano, Trang: CUMZ 3538, 3638; Tam Puttha Kodome, Trang: CUMZ 3639; Wat Khao Huy Haeng, Trang: CUMZ 3537; Tam Hong, Khao Nan National Park, Nakhonsrithammarat: CUMZ 3631; Tam Luang, Khao Nan National Park, Nakhonsrithammarat: CUMZ 3632; Tam Lord, Khao Nan National Park, Nakhonsrithammarat: CUMZ 3633; Tam Khun- Klang, Nakhonsrithammarat: CUMZ 3634; Tam Pannara, Nakhonsrithammarat: CUMZ 3536, 3539, 3643; Wat Nasarn, Suratthani: CUMZ 2592.
Shell. – Shell depressed conic, thin, translucent, polished, brownish, dextral and perforate ( Fig. 2A View Fig ). Whorls 6–7, increasing regularly, slightly convex, with wide and deep channel at suture. Spire convex; apex acute; embryonic shell smooth; following whorls structured with deep sinuously curved radial channels, which disappear below the periphery; descending whorls slightly elevated from suture, last whorl shouldered; aperture crescentic; lip simple. Columella slightly dilated; parietal callus thin and translucent.
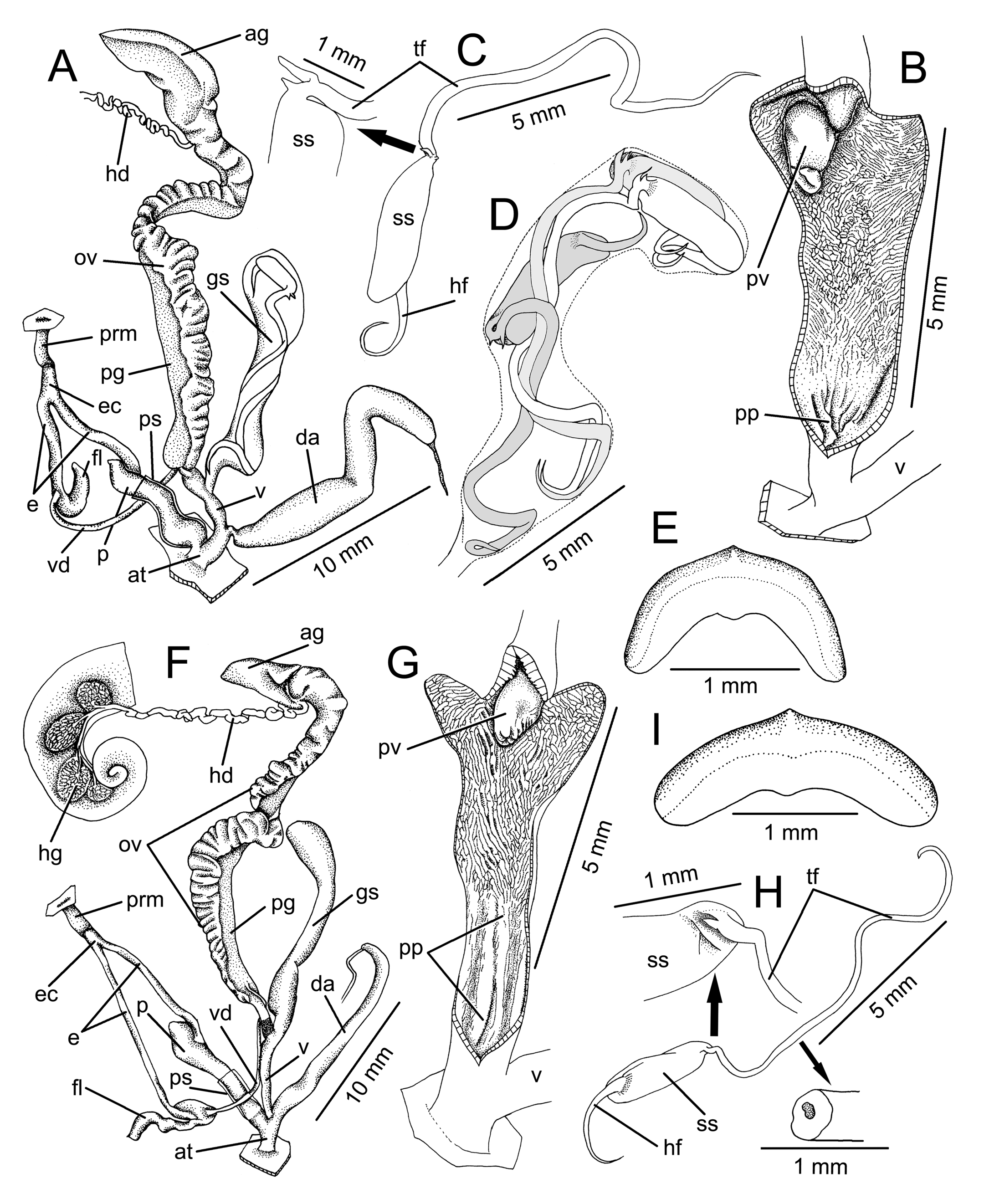
Genitalia. – Atrium (at) very short to nearly absent ( Fig. 3A View Fig ).
THE RAFFLES BULLETIN OF ZOOLOGY 2008
Penis (p): proximally enlarged, cylindrical, with thin penial sheath (ps). Ephiphallic caecum (ec) short, straight and located about half way along the length of the ephiphallic complex. Penial retractor muscle (prm) short, thick and attached at the tip of ephiphallic caecum. Epiphallus (e) long and slender tube, about twice length of penis; flagellum (fl) short. Vas deference (vd) small, relatively short, connected between free oviduct (fo) and distal end of epiphallus. Internal wall of penis nearly smooth; proximally around one-third of chamber with thin longitudinal pilasters (pp); distally with very thin and oblique wrinkled sculpture. Penial verge (pv) small, short conic and smooth ( Fig. 3B View Fig ).
Vagina (v) short and cylindrical. Dart apparatus (da) large, long, cylindrical and located at middle length of vagina. Gametolytic sac (gs) long, cylindrical and slightly swollen distally. Oviduct (ov) with large lobules; prostate gland (pg) runs alongside oviduct. Albumen gland (ag) short and enlarged. Hermaphroditic duct (hd) small and convoluted ( Fig. 3A View Fig ).
Allospermatophores (n = 14) long-needle shaped with three recognizable sections. (1) head filament (hf) rather short, thinning to terminal point ( Fig. 3C View Fig ). (2) cylindrical sperm sac (ss) containing sperm mass (3) tail filament (tf) long thickwalled tube with small hole in cross section (see also Fig. 3H View Fig ). Tail filament proximal to sperm sac with long and short spines. The gametolytic sacs of several individual specimens contained one or more spermatophores; four with one, four with two and one with three spermatophores ( Fig. 3D View Fig ).
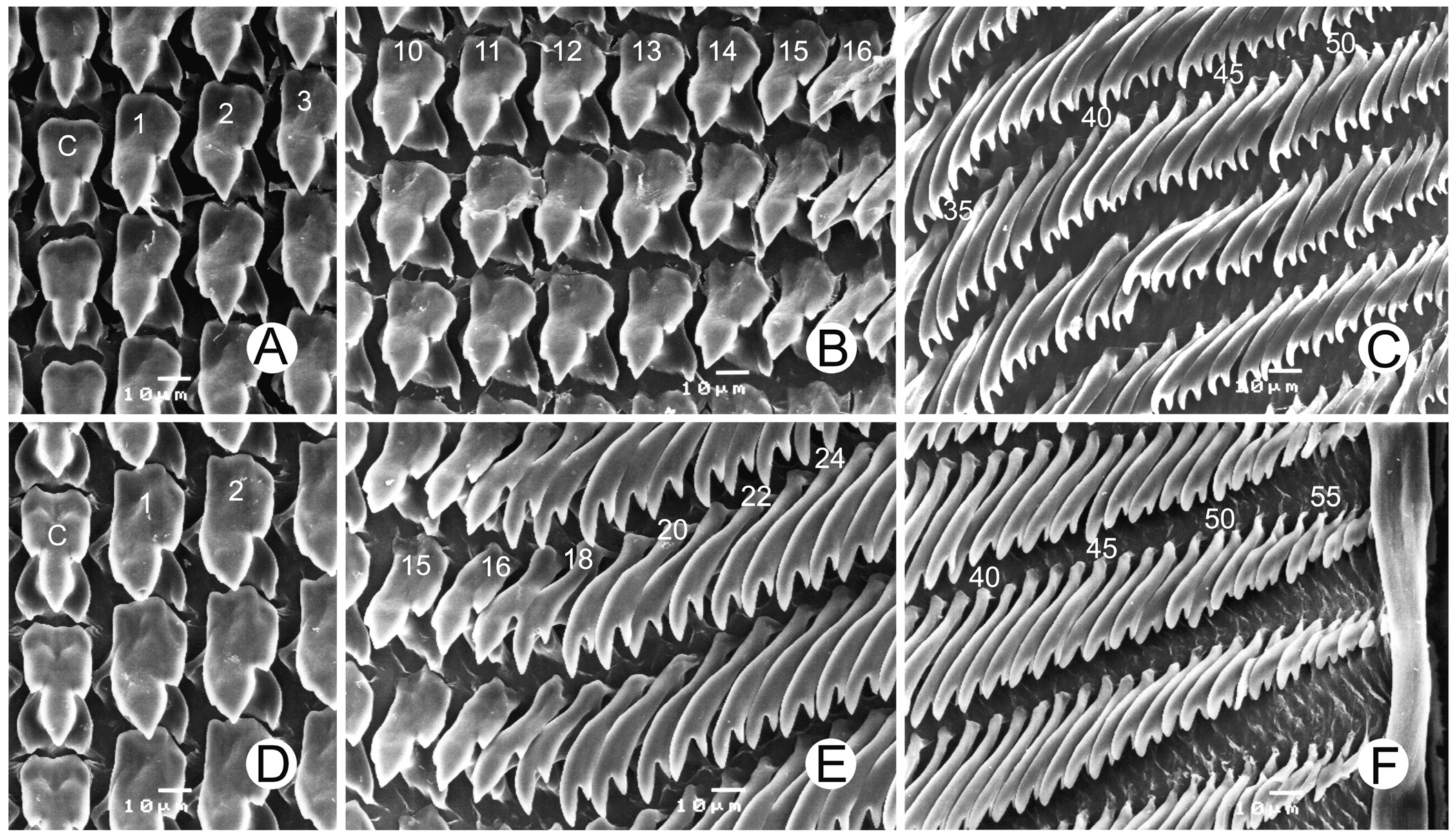
Radula and jaw. – Teeth arranged in V-shaped rows with approximately 141 (69-(16-17)-1-(15-17)-70) teeth. Central tooth symmetric tricuspid, mesocone large with pointed cusp, ectocones small and located in middle of tooth ( Fig. 4A View Fig ). Lateral teeth asymmetric tricuspid, mesocone large, approximately half of tooth height with pointed cusp, endocone small and placed near tip of tooth ( Fig. 4B View Fig ). Marginal teeth start from 15–17, elongated and obliquely bicuspid; outermost marginals progressively shorter ( Fig. 4C View Fig ).
Jaw smooth (without vertical ribs), crescentic, anteriorly convex with cutting margin ( Fig. 3E View Fig ).
External features. – Animal with long and narrow foot. Lung cavity visible through translucent shell. Tentacles long and blackish. Skin reticulated with yellowish stripe in middle of the body running from head to caudal foss. Foot lateral margin
THE RAFFLES BULLETIN OF ZOOLOGY 2008
blackish, sole of foot creamy to brownish; foot sole tripartite; caudal foss and caudal horn moderately long and blackish. Mantle collar yellowish or blackish (with yellowish edge); mantle flaps yellowish ( Fig. 2B View Fig ). Only blackish pigmentation retained in ethanol preserved specimens.
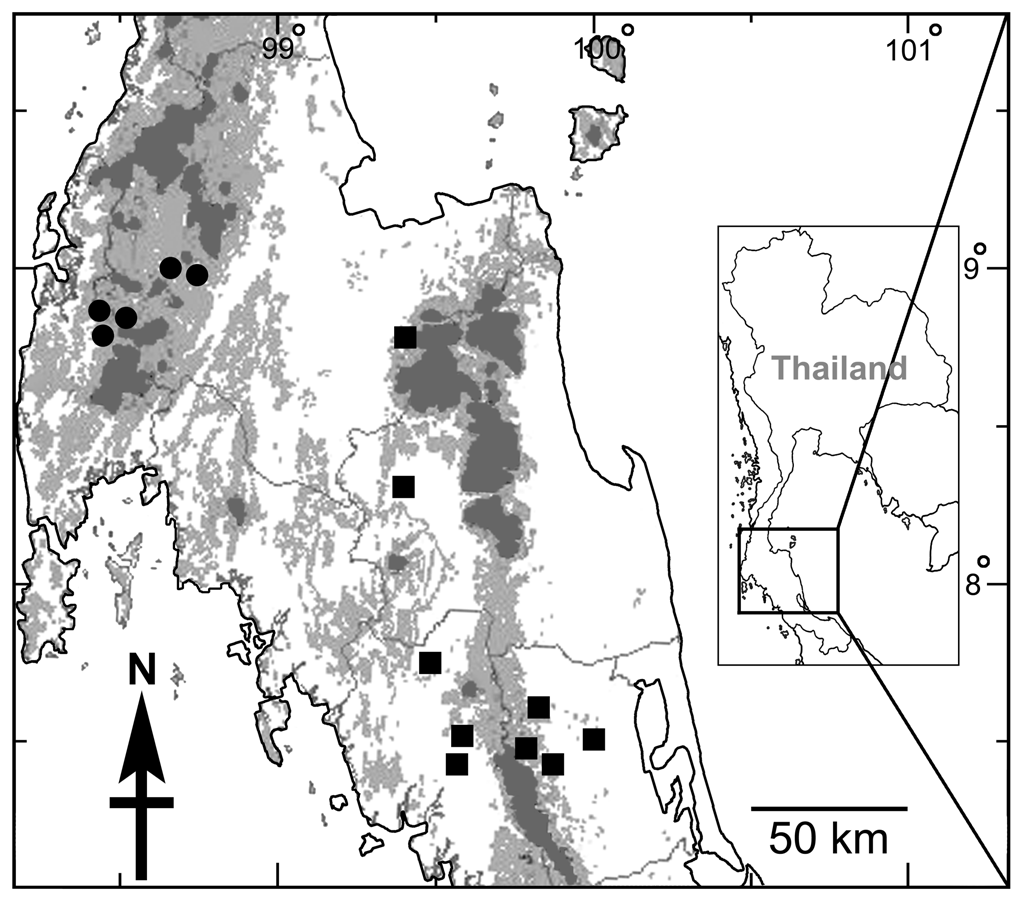
Distribution. – The original locality was given as in the vicinity of Prang, Malay Peninsula ( Dall, 1897). However, multiple field surveys in northern Peninsular Malaysia (Perlis, Perak, Ipoh and Kelantan) from 1999 to 2002 found no S. diadema (J. B. Burch, pers. comm.). One explanation might be that ‘Prang’ in the original description was confused with “Trang” in southern peninsular Thailand and that S. diadema is restricted to southern Thailand ranging from Nakhonsrithammarat, Trang, Pattalung to the Songkhla Provinces ( Fig. 1 View Fig ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Sarika diadema ( Dall, 1897 )
| Sutcharit, Chirasak & Panha, Somsak 2008 |
Syama diadema
| Panha, S 1996: 102 |
| Abbott, R 1989: 23 |
Macrochlamys diadema
| Gude, G 1903: 50 |
Nanina (Macrochlamys) diadema
| Dall, W 1902: 499 |
| Dall, W 1897: 38 |