Ctenolepisma (Ctenolepisma) venkataramani, Hazra & Jana & Mandal & Molero-Baltanás, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5222.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D686CDC4-7577-43BD-80A3-084226BA47E6 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7463578 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038C191E-1542-FFBE-08F7-FB0CFD96F850 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ctenolepisma (Ctenolepisma) venkataramani |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Ctenolepisma (Ctenolepisma) venkataramani sp. n.
( Figures 1−17 View FIGURES 1–7 View FIGURES 8–13 View FIGURES 14–17 , Table 1 View TABLE 1 )
Type material. Holotype: Under leaf litter near the East Thiopathak Waterfalls, Sri Venkateshwara National Park, Andhra Pradesh, India [ 13°45’4” N, 79°20’16” E], 17.vii.2000, 1 female, coll. A.K. Hazra, Registration number 3051/H14, Zoological Survey of India, Kolkata GoogleMaps . Paratypes: Same locality as holotype, 17.vii.2000, 9 examples. ( 6 males and 3 females), coll. A.K. Hazra, Registration number 3052/H14, Zoological Survey of India, Kolkata GoogleMaps .
Etymology. The species is named after Dr. K. Venkataraman, former Director of Zoological Survey of India, Kolkata for inspiration to explore the Indian Zygentoma .
Diagnosis. Apical article of labial palps with an unusually high number of sensory papillae (nine). Trichobothria of nota arranged as in C. ciliatum . All thoracic sternites with 1+1 subapical bristle-combs of macrosetae. Urotergite I with 1+1, II-VII with 3+3 and VIII with 2+2 bristle combs. Urosternites I and II without setae, III–VIII with 1+1 lateral bristle combs. Urotergal combs with 4−8 macrosetae and urosternal combs with 8−9 macrosetae each. Urotergite X trapezoidal, similar to that of C. boettgerianum Paclt, 1961 . Two pairs of abdominal styli. Ovipositor with 54−56 divisions.
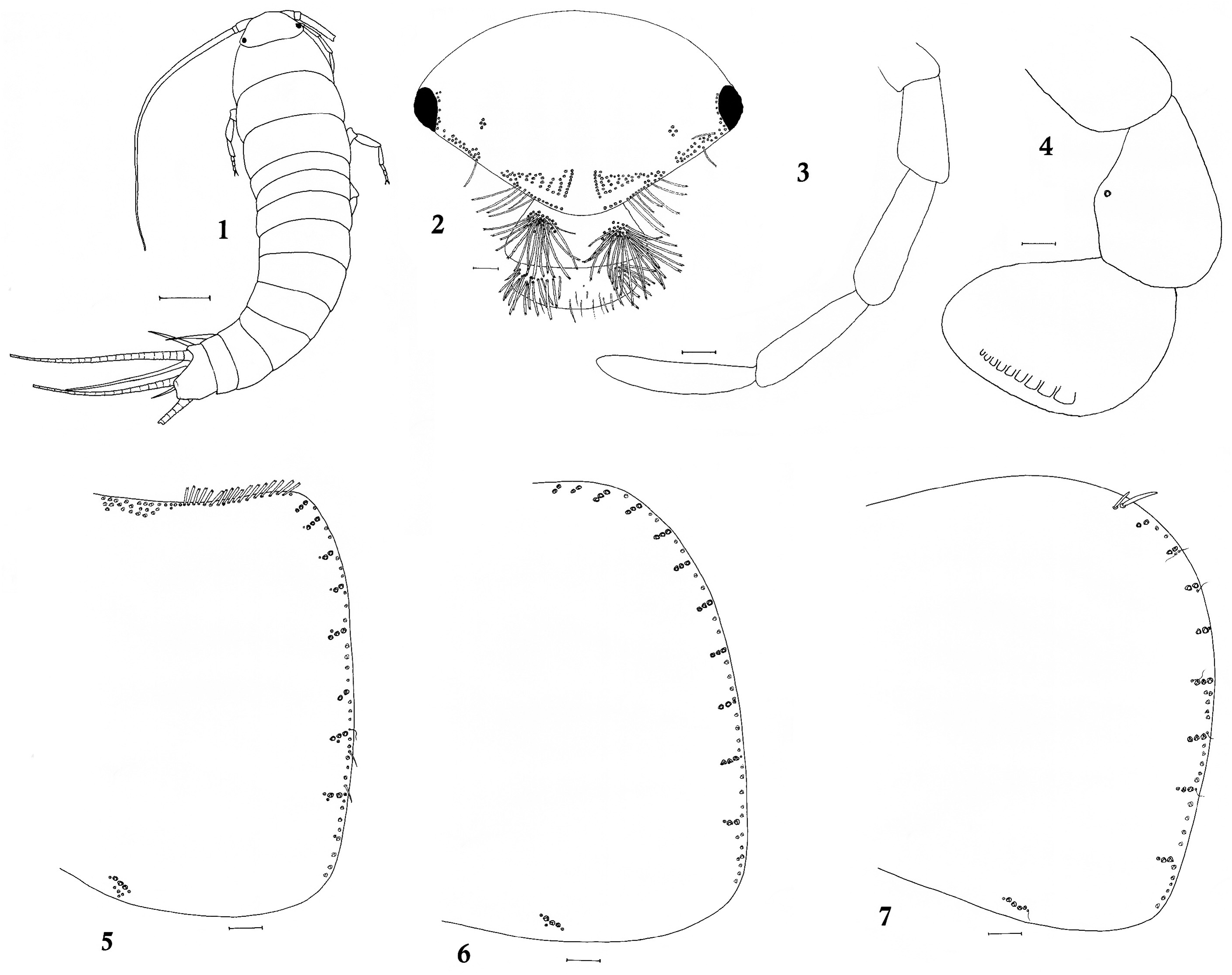
Description. Body length of female up to 8.8 mm; of male up to 7.8 mm. Base colour (in spirit) dorsally whitish yellow with a covering of light brown scales, ventrally whitish yellow. Shape of the body elongate, more or less parallel sided, dorso-ventrally compressed anteriorly, sub-cylindrical posteriorly; thorax slightly wider than abdomen ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1–7 ). Faintly brownish pigments distinct on sides and apical border of scapus and antennae, on second and third segment of maxillary palp; lateral margins of labial palp; upper part of coxa, lower part of trochanter, entire lateral margin of femur and outer margin of tibia; styli IX all along their length. Caudal appendages with uniform brown pigmentation, not arranged in alternating dark and light bands.
Head semi-circular in outline anteriorly; frons bearing two very conspicuous tufts of stout cephalic setae, pectinate and radially arranged. Numerous bifid and pectinate macrosetae present in both clypeus and labrum; those of the clypeus are grouped in two tufts composed of 28−32 each ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–7 ). Eyes relatively small, located well behind antennae. Head wider ( 1.17 mm) than long ( 0.58 mm). Antenna length up to 5.4 mm, shorter than body and reaching the sixth abdominal segment when directed backwards.
Maxillary palp ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1–7 ) slender, five-segmented, last article slightly longer ( 0.39 mm) than penultimate ( 0.37 mm). Apical article of labial palp ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–7 ) sub-globular in shape and bearing nine sensory papillae arranged in a single row; it is about 2.7 times wider at the apex than at the base and 1.1 times wider than long.
Anterolateral row of the pronotum ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1–7 ) composed of a single row of bifid and smooth macrosetae. Pronotal collar with oblique sub-parallel rows of 3−5 macrosetae. Lateral margins with 8+8 combs composed of 2‒3 macrosetae each. Two trichobothrial areas on each side, associated to the inner side of the last comb (N) and to inner side of the N-3 comb; trichoid sensilla inserted on the outer side of the combs N and N−1 and on inner side of N-2, N-4, N-5 and N-6. Mesonotum ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1–7 ) lateral margins with 11 combs each consisting of 2−3 macrosetae, including two trichobothrial areas, one in the inner side of the last comb (N) and one in the outer side of the N-2 comb; trichoid sensilla present in the outer side of N-1 and in the inner side of N-3, N-4 and N-5. Metanotum ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 1–7 ) lateral margins with 9+9 combs composed of 2‒3 macrosetae. Trichobothrial areas situated in the inner sides of the combs N and N-1; trichoid sensilla inserted on the outer side of combs N-1, N-2, N-5 and N-6 and on the inner side of combs N-2, N-3 and N-4. Hind borders of pro-, meso- and metanota with 1+1 bristle combs composed of 3−4 macrosetae each.
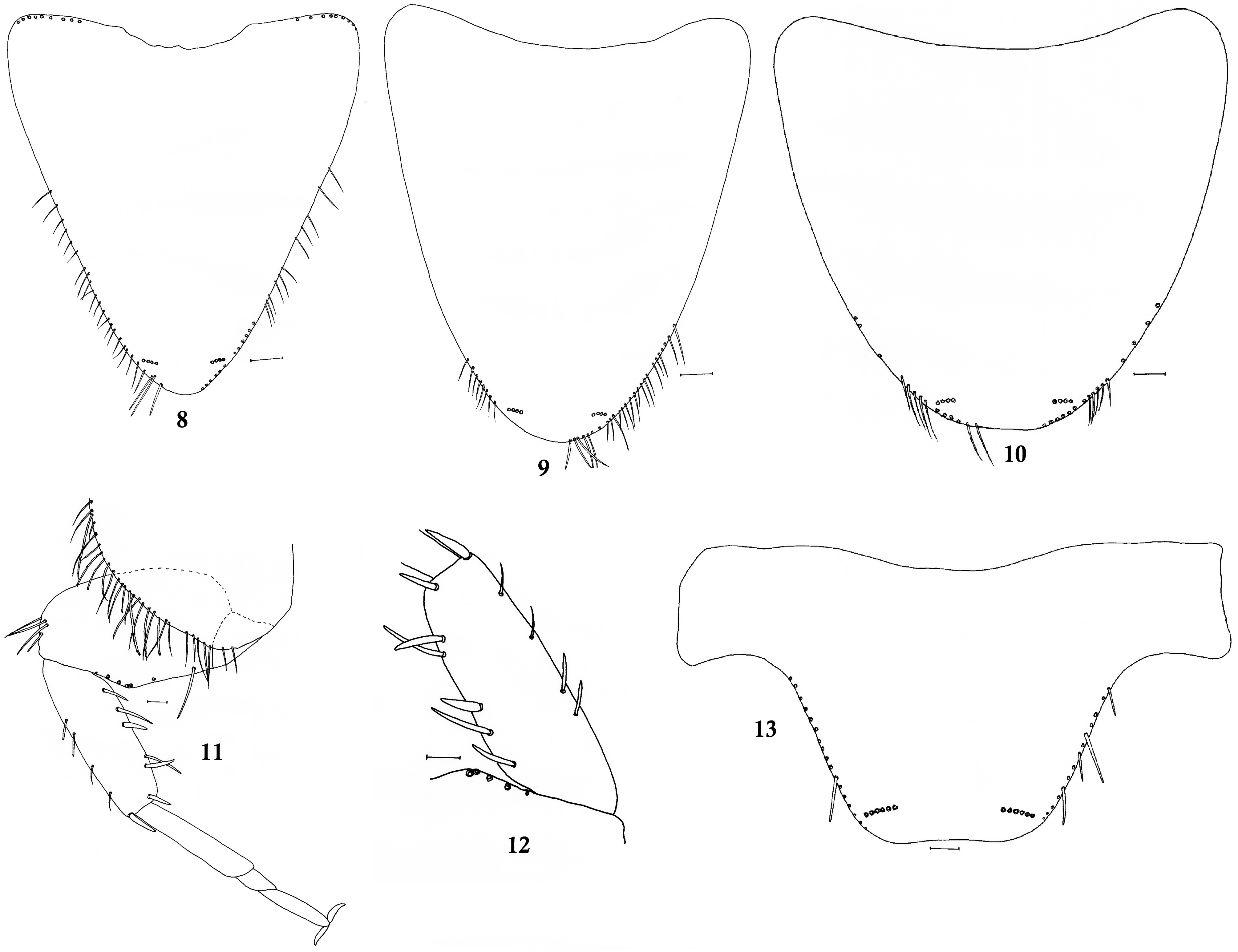
Prosternum ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 8–13 ) 1.2 mm long, its length/width ratio about 1, subtriangular, posteriorly elliptical in shape; apical part with 1+1 bristle combs each composed of 4 macrosetae. Mesosternum ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 8–13 ) 1.4 mm long, its length/ width ratio about 1.1, semi-elliptical in shape, with rounded apex and 1+1 subapical bristle combs each composed of 4 macrosetae. Metasternum 1.3 mm long, length/width ratio about 0.9; posterior margin broadly rounded, with 1+1 bristle combs each composed of 4 macrosetae ( Fig 10 View FIGURES 8–13 ); the distance between these combs about 5 times the width of a comb.
Legs stout; femora short, one strong seta on outer margin distally near the junction of tibiae; tibiae and tarsi moderately elongated; pretarsi with slightly curved claws ( Figs. 11 and 12 View FIGURES 8–13 ). Coxae and femora with scales. Protibia about 2.4 times longer than wide, with two macrosetae inserted in the dorsal margin and four macrosetae in the ventral margin. Protarsal tarsomere I length about 0.32 mm; tarsomere II, about 0.09 mm; tarsomere III, about 0.17 mm; tarsomere IV, about 0.12 mm. Mesotibia 2.7 times longer than wide, with two dorsal and three ventral macrosetae. Lengths of tarsomeres I, II, III and IV (in mm) on mesotarsus as follows: 0.41, 0.12, 0.15, 0.16. Metatibiae ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 8–13 ) about 3 times longer than wide, with four dorsal and six ventral macrosetae. In the metatarsus, the length of tarsomere I is about 0.63 mm; of tarsomere II is about 0.13 mm; of tarsomere III is about 0.18 mm and of tarsomere IV is about 0.21 mm.
Urotergite I with 1+1 bristle-combs, each composed of 4−5 macrosetae. Urotergites II−VII with 3+3 bristlecombs, each composed of 4−8 macrosetae, and urotergite VIII with 2+2 bristle-combs, each composed of 6−7 macrosetae. Urotergite IX without bristle combs. Urotergite X ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 8–13 ) shorter than the width at its base, subtrapezoidal, short, with rounded posterolateral corners and faintly emarginated hind border with 1+1 prominent bristle-combs, each composed of 7 macrosetae.
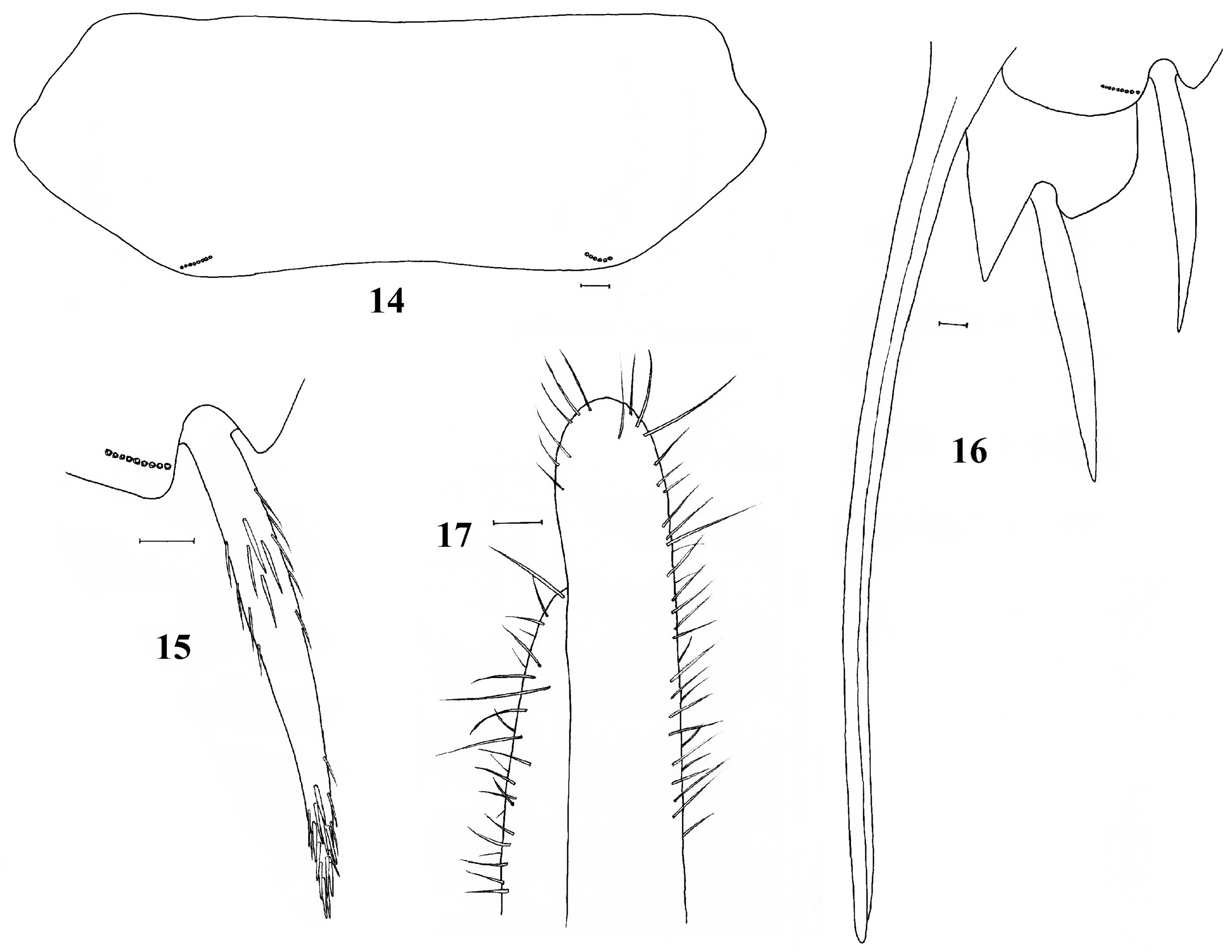
Urosternites I and II without setae, III−VIII with 1+1 lateral bristle-combs, each composed of (6)8-9 macrosetae. The width of the bristle combs and the gap distances between them varies in each urosternite, so that the ratio between the distance between the combs and the width of a comb varies from 8 on urosternite VII to 15 on urosternite III ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 14–17 ).
Both sexes with two pairs of styli, inserted on segments VIII ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 14–17 ) and IX. In female, the ratio length of styli IX/ length of styli VIII about 1.2. Posterior margin of the coxite VIII round. Inner process of coxite IX triangular and pointed at tip, in the female about 1.5 times longer than wide at its base and 4 times longer than the outer process. Ovipositor very long, with 54−56 divisions, surpassing the apex of the inner process of the coxite IX by 4.3 times the length of this process ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 14–17 ). Apical parts of gonapophyses not sclerotized, both the anterior and posterior regions with fine bristles; anterior region with two long setae ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 14–17 ).
Caudal filaments long but broken and incomplete on type material.
Distribution and habitat. Specimens of Ctenolepisma venkataramani sp. n. were found in large numbers generally in shady, semi-decomposed leaf litter and under stones beside East Thiopathak Waterfalls at Sri Venkateshwara National Park. The species is supposed to be abundant in this tropical forest of Indian Deccan plateau. The conservation of this habitat will protect this Zygentoma species.
Differential diagnosis. This new species is close to Ctenolepisma (Ctenolepisma) boettgerianum , as they have similar abdominal chaetotaxy (urotergite I with 1+1, II‒VII with 3+3 and VIII with 2+2 bristle combs; urosternites I and II without setae, III–VIII with 1+1 bristle combs), similar trapezoidal shape of the tenth urotergite and similar size. They differ in the characters presented in Table 1 View TABLE 1 . The most remarkable character of the new species is the presence of an unusually high number of sensory papillae (nine) on the apical article of the labial palp, a condition that can be occasionally found in C. longicaudatum Escherich, 1905 . In this latter species the number of papillae is variable, and most specimens bear the typical number (five), arranged as usual in a single row. However, C. longicaudatum is different because of its urotergal setation (3+3 combs in urotergite II‒VI), larger size (up to 15 mm or more), greater length of appendages and lighter epidermal pigment. Compared with other Indian species of the genus, there are 2 species of the subgenus Ctenolepisma s. str. bearing 3+3 combs on urotergites II‒VII and a trapezoidal tenth urotergite that are also present in some parts of Asia: C. mauritanicum (Lucas, 1846) and C. przewalskyi Kaplin, 1982 . These species are easily distinguishable from C. venkataramani sp. n. as they have 2 or more pairs of bristle-combs in their prosternum (only one pair in the new species), and their ovipositor has a lower number of divisions (about 40 or less).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |