Foranotum perforatum, Nabozhenko & Sadeghi, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4338.1.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8C7874C5-BFF6-4970-AEF1-FD46866B9A0F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6031828 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0388EA03-520F-FFC6-FF19-1345FE5EF44B |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Foranotum perforatum |
| status |
sp. nov. |
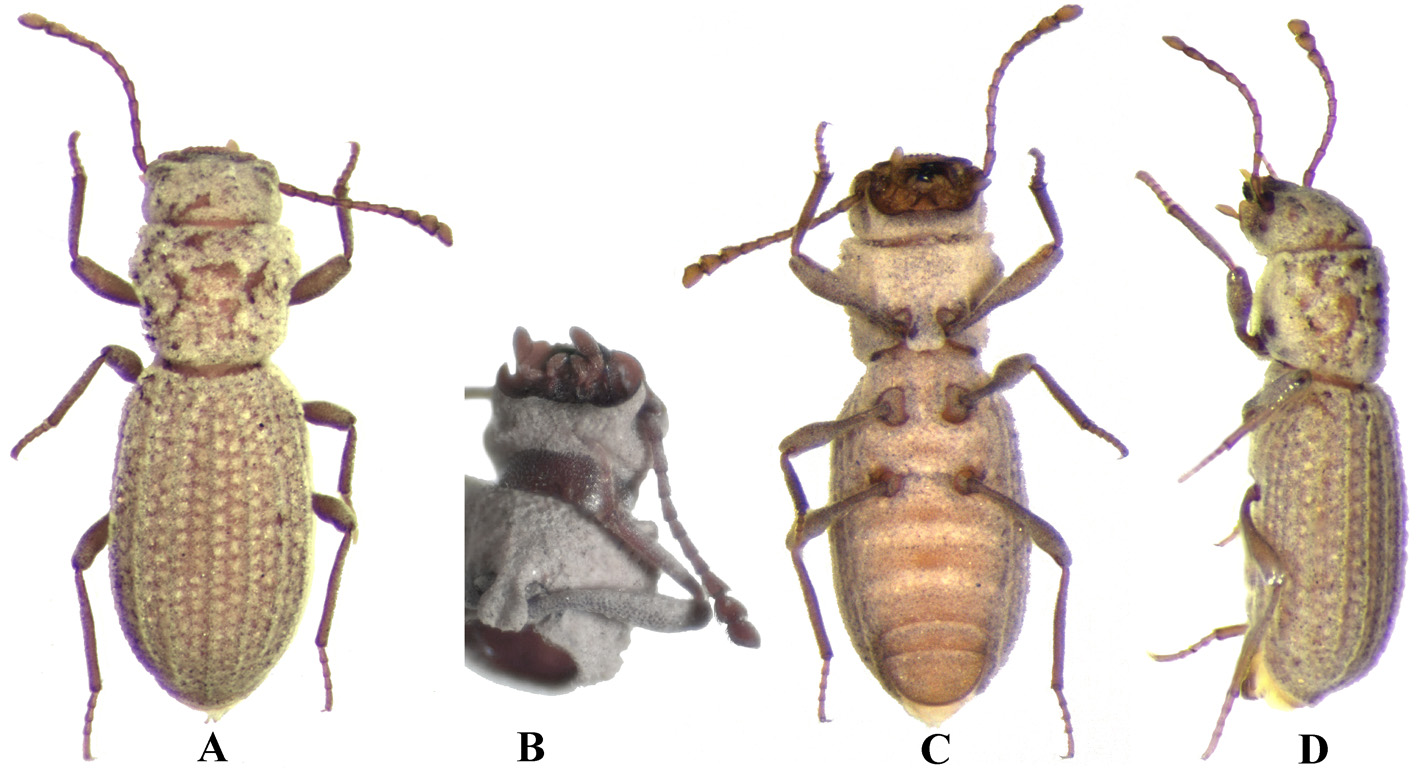
Foranotum perforatum sp. n.
( figs. 1–5 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 )
Holotype (male) and 4 paratypes (2 males and 2 females): Iran, Fars, Khan Cave, N 27°44ʹ41ʺ, E 53°20ʹ15ʺ, 19.v.2017, leg. S. Sadeghi. Holotype and 4 paratypes are deposited in ZM-CBSU ( Zoology Museum in Collection of the Biology Department of Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran) ; 2 paratypes from the same locality but from 12.vi.2016 (partly destroyed after cleaning and SEM) will be transferred to Zoological Institute RAS, St Petersburg, Russia .
Etymology. from Latin “ perforatum ” (perforated).
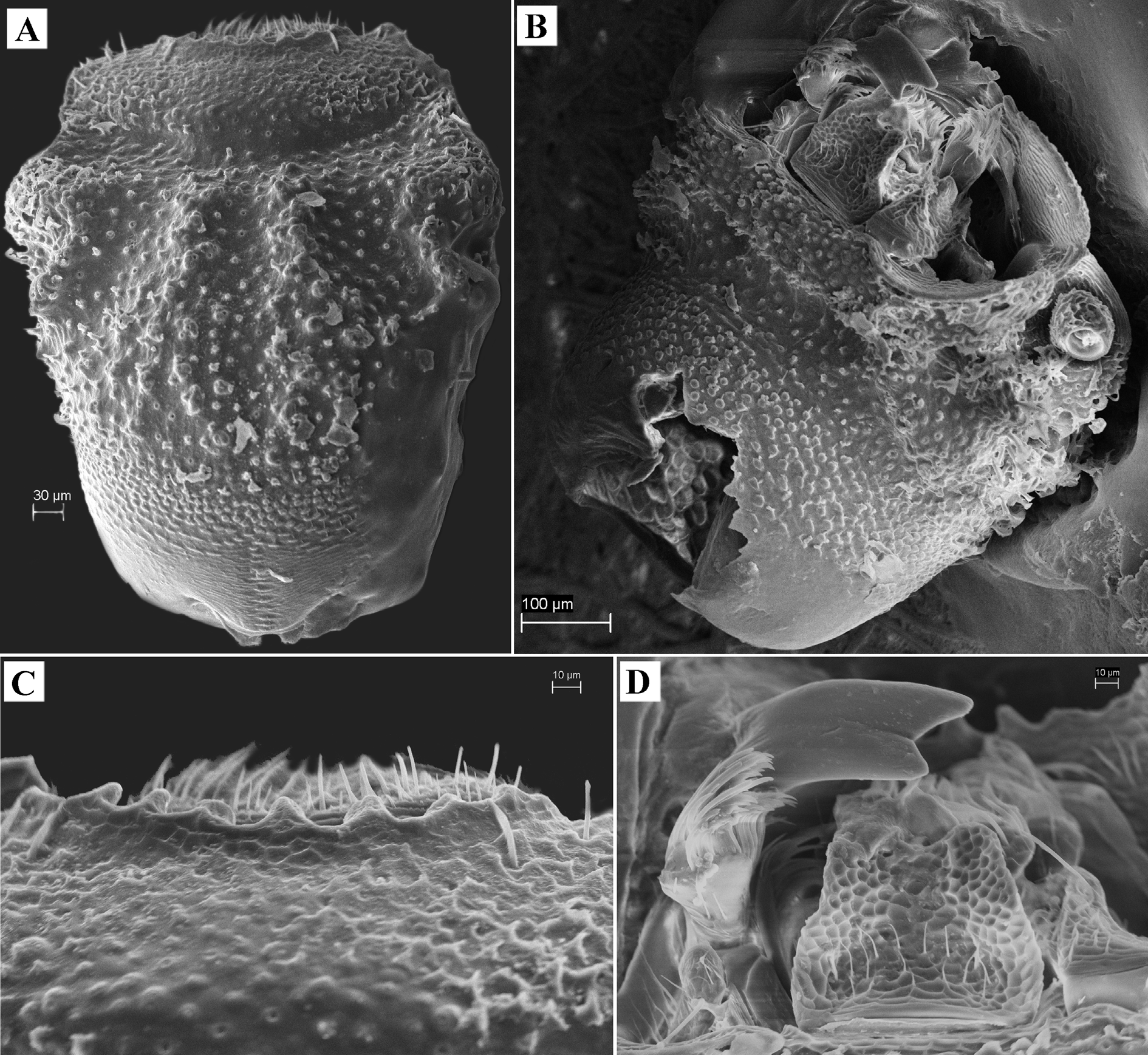
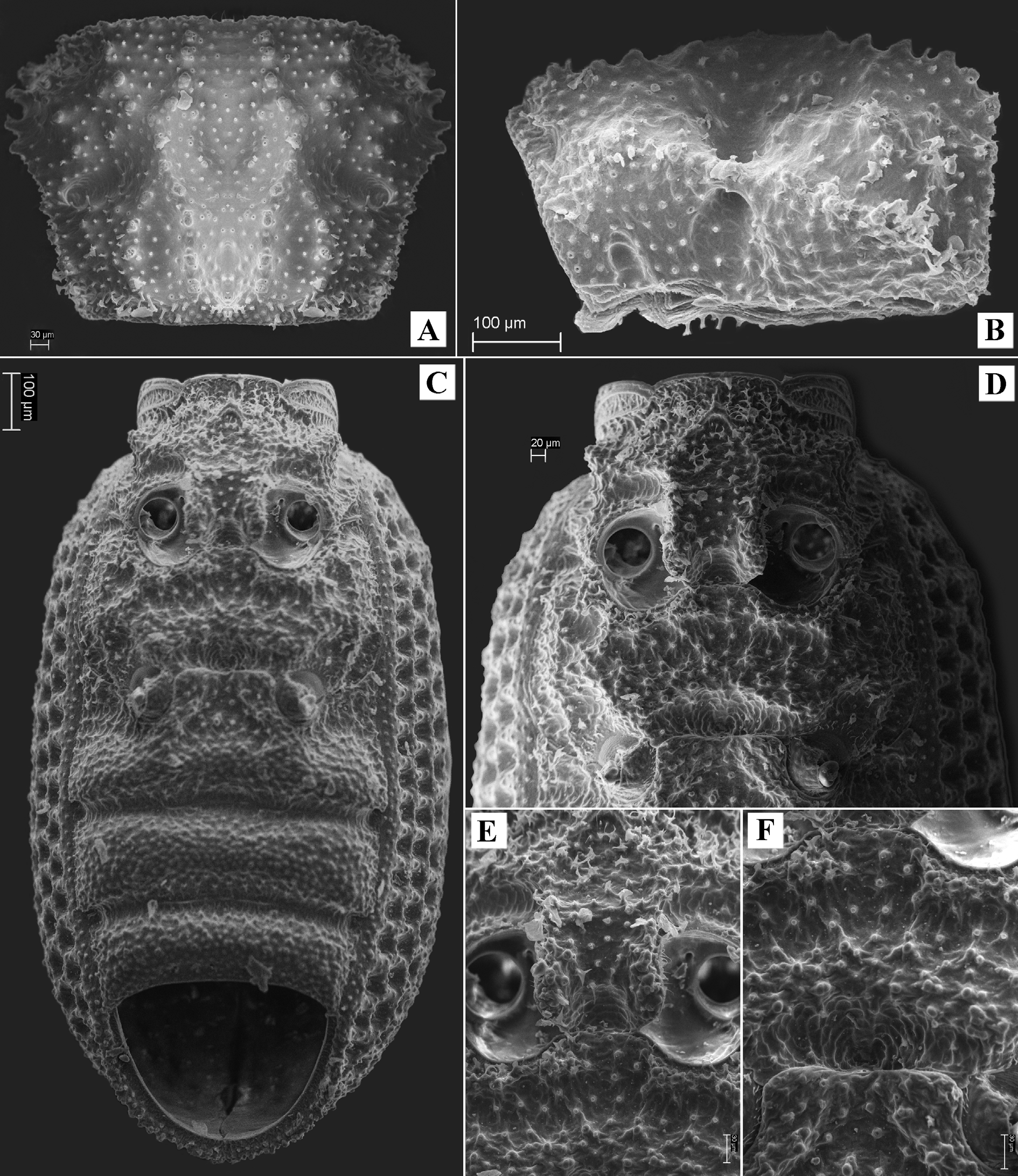
Description. Body small, moderately slender, brown, shiny, completely covered by granules bearing short erected setae, covered with very dense crust of soil. Body length 2.7 mm. Head widened from base to apex. Eyes absent. Head widest at level of genae. Anterior margin of head widely and weakly emarginate, with 7–8 large teeth. Labrum small, weakly transverse, with deep foveae and strong, anteriorly directed setae; clypeolabral membrane not exposed. Frontoclypeus convex, separated from frons by deep arcuate impression. Frons with three longitudinal impressions and two ridges between them: one oval depression in middle and two oblique impressions on side, separating frons from genae. Genae convex, with C-shaped ridge in basal half. Occiput with smaller, denser granules, transversely oriented in basal part. Sides of head with mushroom-shaped setae. Vertex with fine dense tubercles and deep transverse depression with sparse granules in middle. Sides of vertex with antennal grooves.
Mouthparts of open type: mentum exposing large part of maxillae. Mandibles bifurcated. Mentum with wide subtriangular depression in middle; surface of mentum with very coarse and dense deep foveae and long sparse recumbent setae near apex. Maxillary apical palpomeres fusiform, with small oval sensillar field on apex. Labial apical palpomeres narrowly rounded on apex. Galea triangular, with double line of dense long setae. Lacinia narrow, elongate, without apical tooth, with dense line of long curved setae. Prementum with very dense pubescence of long setae at apex.
Antennae 11-segmented, 1.65 times as long as pronotum, apical antennomere extending beyond base of pronotum. Antennomere 1 completely covered from above, thickened, short; antennomeres 2 and 3 longer than 4– 8; antennomeres 9 and widest 10 triangular, strongly widened and flattened; apical antennomere nearly rectangular, with weakly rounded sides. Length to width ratio of antennomeres 1–11 as 1:0.9, 1.5:05, 1.5:05, 1.3:0.5, 1.2:0.6, 1.1:0.6, 1.1:0.6, 1.1:0.7, 1.5:1, 1.6:1.5, 2:1.4.
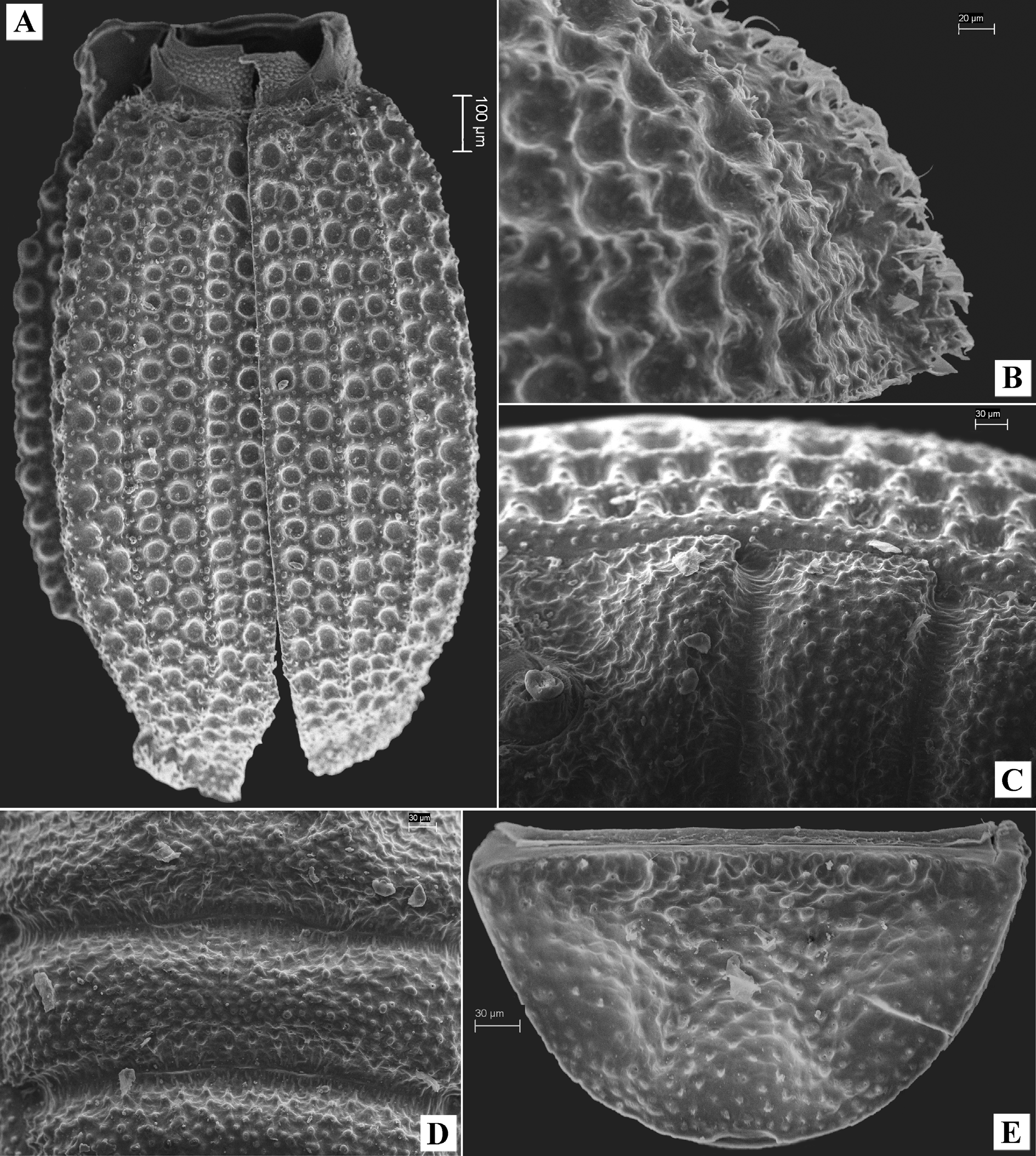
Pronotum transverse (1.22–1.50 times as wide as long), slightly cordiform, widest before middle. Lateral margins strongly rounded in widest part and with 4 large rounded teeth, weakly emarginate and finely serrate in basal third. Anterior margin weakly emarginate, finely serrate; base straight, without teeth. Anterior angles widely rounded, almost not exposed; posterior angles obtuse, rounded at apex. Margins of pronotum not beaded. Pronotal disc strongly convex in middle. Pronotum with hole on each side, going through prothorax and opening on side of prothoracic hypomeron. Middle of disc with strongly elevated X-shaped ridge on each side; ridges with large tubercles; centre of pronotum between ridges forming elevated platform with wide oval impression in anterior part and small narrow oval impression in basal part. Sides of disc with oblique ridge on each side directed from hole to anterior margin. Pronotal base shortly vertical and with transverse depression on end flap. Prothoracic hypomeron with short transverse oval impression in basal part. Prosternum with several large mushroom-shaped setae between anterior parts of procoxae. Prosternal process regularly expanded apically, depressed in middle. Procoxal cavities externally and internally open. Inner margins of procoxae concealed by prosternal process.
Hindwings absent. Mesoventrite transverse (1.56 times as wide as long). Anterior margin of mesoventrite bisinuate, beaded. Lateral sides of mesoventrite with two smooth transverse keels connected near middle. Surface of mesoventrite between keels with fine longitudinal wrinkles. Lateral margins behind transverse keels with two oblique transverse ridges and deep depression between ridges and mesocoxae; this depression with flat dense foveae. Centre of mesoventrite widely depressed; depression separated from other surface by Ʌ-shaped bead in anterior part. Mesocoxal process of mesoventrite with elevated margins, partly covering inner sides of mesocoxae, and very deep hollow on border with metaventrite; the hollow with dense flat foveae, without granules. Mesocoxal cavities slightly transversely oval, with round hole inside, externally closed by bridges of meso- and metaventrite. Suture between meso- and metaventrite on sides with elevated smooth bead. Sutures between mesepisterna and mesoventrite invisible.
Metaventrite transverse (2.56 as wide as long together with mesepimera). Sutures between metaventrite and metepimera invisible. Mesocoxal process of metaventrite weakly projecting, wide, with almost straight apex. Centre of metaventrite widely longitudinally depressed in anterior part and convex in middle; sides with two round impressions in anterior and posterior halves. Metanepisterna with wide longitudinal depression in base. Base of metaventrite with very deep hollow at middle near border with abdominal intercoxal process; hollow with dense flat foveae, without granules. Metacoxal cavities small (1.65 times as short as mesocoxal cavities in transverse diameter), widely closed externally by bridges of metaventrite and first abdominal ventrite.
Elytra elongate oval, strongly convex, their sides encompassing meso-metaventrite and abdomen. Humeral angles absent. Each elytron with 10 longitudinal rows of deep large foveae, forming twin pairs, scutellary striole absent. Inner pairs separated by weak ribs. Space between foveae covered with setigerous granules. Epipleura granulate, partly concealed by abdominal ventrites 1–4. Elytral edge thickened and flat, weakly wrinkled, partly concealed by abdominal ventrites.
Abdominal ventrites 4 and 5 movable, abdomen without membranes between ventrites 3, 4 and 5. Intercoxal process of first abdominal ventrite strongly projecting, wide, with straight anterior margin and broad triangular impression in middle, 1.9 times as wide as mesocoxal process of metaventrite. Abdominal ventrites convex, 1–3 with deep transverse depression in middle of base. Sutures between abdominal ventrites deeply depressed, with deep round holes for spiracles on sides. Abdominal ventrite 5 with deep transverse impression in base, two longitudinal elevations in middle and transverse fovea on apex.
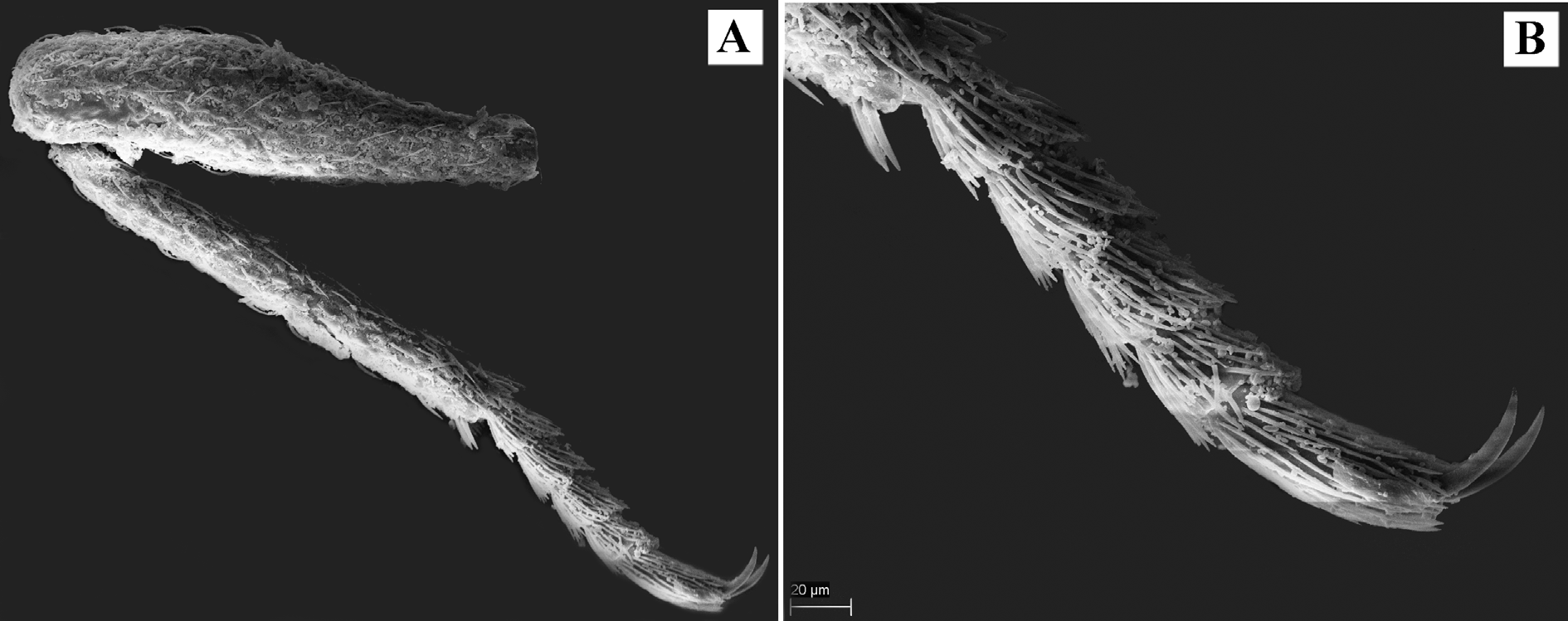
Coxae round, mesocoxae larger than pro- and metacoxae. Trochanters heteromeroid, small. Legs thin, slender, long. Femora pedunculate, thin at base and thickened to anterior part, covered with subdecumbent fine short setae, uniform in size. Tarsomeres cylindrical, regularly covered by dense long decumbent setae; tarsomeres 1–4 of all legs of approximately the same length; apical tarsomere of all legs twice longer than any other.
Male genitalia. Aedeagus of tentyrioid type: apical piece long, acute on apex, basal piece short, alae absent; penis with two separate baculi.
| RAS |
Union of Burma Applied Research Institute |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |