Falsopedilus aristophanousi, Gompel & Telnov, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5318.3.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:59DEAC2D-EE83-4857-8475-E2464760BA9E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8167035 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/AE26826C-A31F-4227-916A-75EB5D5FF85C |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:AE26826C-A31F-4227-916A-75EB5D5FF85C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Falsopedilus aristophanousi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
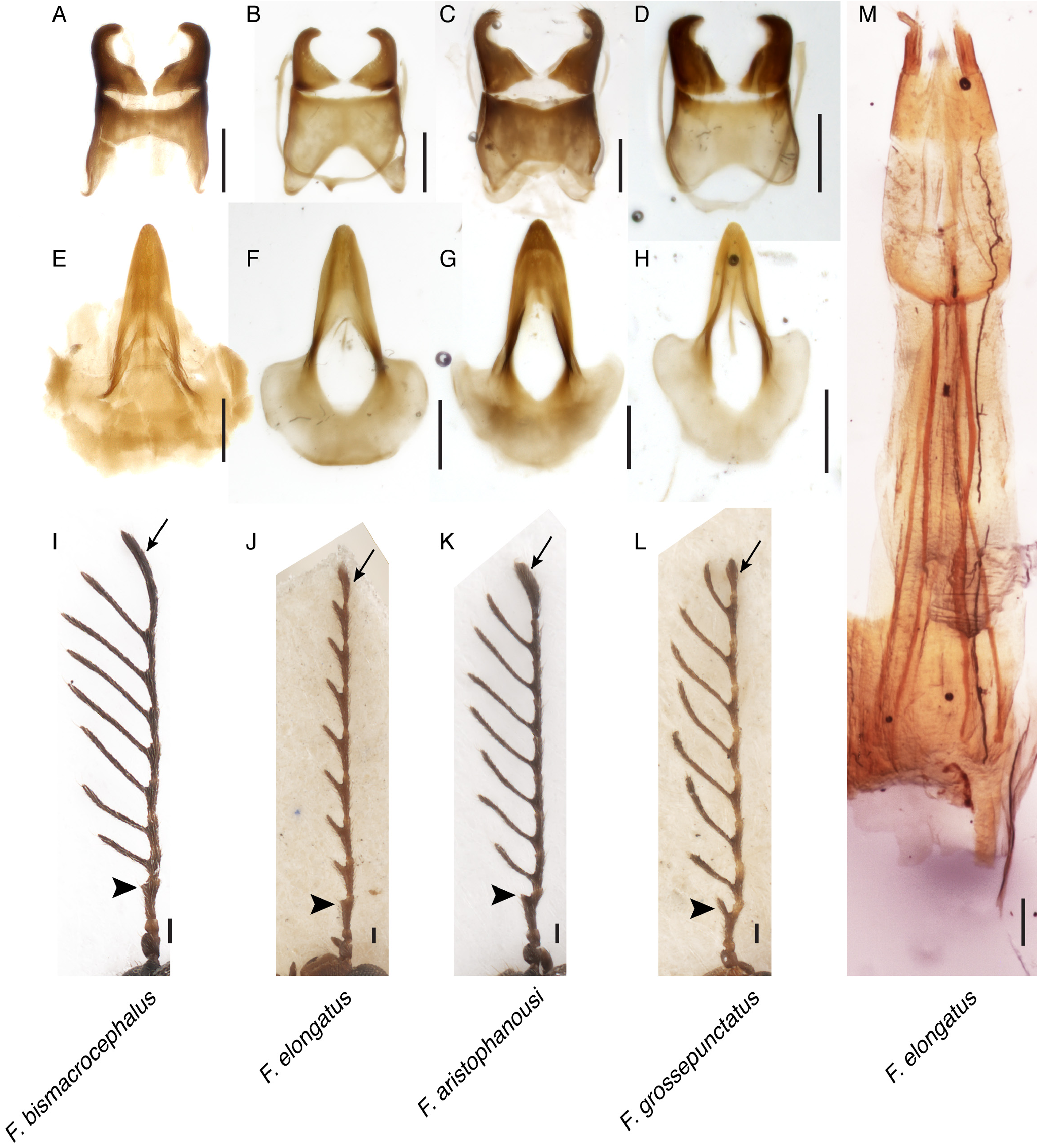
Falsopedilus aristophanousi , sp. nov. ( Figures 1E View FIGURE 1 and 2C, G, K View FIGURE 2 )
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:
Type material designated. Holotype ♁ BMNH: ZAMBIA 1205m Zambezi Rapids , Miombo / riverine forest mosaic 11°07’30’’S, 24°11’6’’E 4–9.xi.2018. [printed] // LepiLed light trap Aristophanous, M., Derozier, V., Laszlo, G., Oram, D. leg. ANHRT: 2018.40, BMNH (E) 2019-90 [printed] // NHMUK014390347 About NHMUK [printed, provided with QR code]. GoogleMaps
Paratypes 2 specimens. 1 ♁ BMNH: ZAMBIA 1179m Choma, Bruce-Miller Farm, Campsite ( Southern Miombo Woodland ) 16°38’12’’S, 27°01’30’’E // 28.ii–8.iii.2019 Lepiled Light Trap. Derozier, V., Imakando, M. Miles, W., Mulvaney, L. Leg. ANHRT: 2019.5, BMNH (E) 2020-19 [printed] // NHMUK014384932 About NHMUK [printed, supplemented with QR code]; 1 GoogleMaps ♁ BMNH: MOZAMBIQUE 22m Maputo Special Reserve, West Gate ( Sand Forest ) 26°30’14.2’’S, 32°42’59.6’’E 13–15.ii.2018 Actinic Light Trap Laszlo, G., Mulvaney, J., Smith, L. leg. ANHRT:2018.2, BMNH (E) 2018-154 [printed] // NHMUK014401738 About NHMUK [printed, provided with QR code] GoogleMaps .
Derivatio nominis. Patronymic. Named for Marios Aristophanous (The African Natural History Research Trust, Leominster, United Kingdom), one of the collectors of the type series.
Measurements. Holotype, total body length about 4.1 mm; head about 0.6 mm long, across compound eyes about 0.8 mm broad, pronotum 0.6 mm long, maximum width about 0.65 mm, elytra 2.9 mm long, combined maximum width 1.15 mm. Paratype ♁ from Zambia 3.7 mm long.
Description. ♁ holotype. Dorsal and ventral forebody black, elytra and abdominal ventrites black-brown. Antenna black-brown, antennomere two somewhat paler. Legs black-brown. Apicoventral binding patch of elytra pale brown in the holotype, black in the paratypes. Body elongate, flattened dorso-ventrally. Head subopaque, anterior part slightly inclined. Frons narrow, strongly narrows anteriad, about 0.6× as wide as dorsal eye length. Compound eye very large, hemispherical, occupying whole head side, very strongly protruding from lateral and dorsal outline of head, shortly notched at anterior margin, touching insertion of antenna. Tempus not present. Head dorsal punctures coarse and dense. Intervening spaces as wide as to twice as wide as punctures except on vertex (much narrower than punctures, in part corrugate).Antenna long, extending beyond mesocoxal cavity when directed posteriad (significantly shorter in the paratype from Mozambique), strongly pectinate. Antennomeres 4–10 strongly pectinate, each with subequally long median lobe, of which lobe of antennomere four is the shortest; all lobes of antennomeres longer than corresponding antennomere. Terminal antennomere elongate, asymmetrically clavate, about 1.2× as long as penultimate antennomere, apically rounded. Pronotum slightly glossy, slightly transverse, much narrower than head across compound eyes, subquadrate, flattened in dorsal aspect. Anterior and posterior margin broadly rounded. Lateral pronotal margins subparallel. Pronotal dorsal punctures dense and coarse. Intervening spaces smooth, narrower than to nearly twice as wide as punctures. Pronotal dorsal setation yellowish, appressed to subdecumbent, directed transversely. Scutellar shield transversely elliptical, posterior margin rounded. Elytron elongate, moderately glossy, dorsally flattened, moderately widened in apical third. Apicoventral binding patch present, elongate elliptical, slightly convex, provided with somewhat sparser setation. Elytral dorsal punctures generally larger than those on forebody, larger, denser and coarser along suture, sparser on lateral margins.Intervening spaces smooth, narrower than (at suture), generally as wide as punctures, on humeral area about twice as wide as punctures. Elytral setation brown, rather short, moderately dense, appressed to subdecumbent, directed posteriad to (along suture) obliquely laterally. Legs long, slender. Tibia densely setose on inner margin. ♁ basal metatarsomere shorter than combined length of remaining metatarsomeres. Genital organs as in Figure 2C, G View FIGURE 2 , median lobe comparatively broad, parameral apex rather slender, strongly curved inwardly. ♁ tergite VII and morphological sternite VII broadly rounded at posterior margin. ♁ tergite VIII and morphological sternite VIII bipartite, deeply cleft and interconnected basally, respectively, posterior margin of both terminalia with several long setae.
Sexual dimorphism. ♀ is unknown.
Differential diagnosis. The new species appears very similar to F. bismacrocephalus ( Báguena Corella, 1948) (consider new combination below), but differs in the comparatively larger distal tooth of the ♁ antennomere three, the coarser and denser punctured elytra (in particular, the area along the suture), the dark elytral setae (the setae are yellowish in F. bismacrocephalus ), the comparatively stronger convex ♁ apicoventral binding patch, and the comparatively less slender median lobe.
Ecology. Some of the examined specimens attracted to artificial light source.
Distribution. Mozambique & Zambia.
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |